Question
A block A, placed on a horizontal surface with friction, is connected by a rope passing through a pulley to a suspended block B.
The mass of block B is sufficient to set the system in motion and both masses accelerate with acceleration a.
Test your model to obtain the kinetic friction coefficient uc and its uncertainty for this phase of the motion using the following values:
We use g=(9.81±0.01) m/s^2 as usual.
mA=(0.415 ± 0.005)kg;
mB=(0.22 ± 0.004)kg;
a=(1.48±0.04) m/s^2;
find an equation giving the modulus of kinetic friction (fc) under the horizontal slider when it is accelerated by the fall of the suspended mass and the value of uncertainty as well.
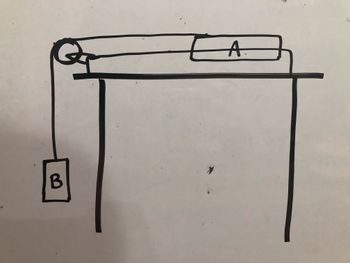
Transcribed Image Text:B
A.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Pls help and show all steps ASAP ASAP ASAP ASAParrow_forwardEach measurement we take has a level of uncertainty in it. The smaller the uncertainty, the larger the precision our measurement has. Let's revisit how one might go about estimating the uncertainty in a measurement. If we assume our instrument is properly calibrated and we are not introducing systematic error through improper techniques, then if we take enough measurements, the average of these measurements will be around the true value. The upper and lower bounds of these measurements would then give us one method for determining our measuring device's uncertainty. (This of course is only true for a large set of measurements, but the approximation is good enough for now to get us started). For example, say we perform last week's experiment of pulling a block at a constant velocity with a force sensor across another rough surface. We take the following five measurements: F, = {2.51 N, 2.53 N, 2.50 N, 2.54 N, 2.49 N} The average of this dataset is F, = 2.51 N Now we have the choice of…arrow_forwardhow do we find the mass in this case? if we know that mass of single nuts is 0.0069kg W=m.gravetyarrow_forward
- Assume that the board you used was covered with two materials, material 1 and material 2. If the height where the wooden block started to slide down is higher on material 2 than on material 1, what can we say about the μs and μk associated with material 2 as compared to material 1? a. μs and μk on material 2 is higher than on material 1b. μs and μk on material 1 is higher than on material 2c. μs on material 2 is higher than on material 1, but μk material 1 is higher than on material 2d. μs on material 1 is higher than on material 2, but μk material 2 is higher than on material 1e. Regarless of any height, μs and μk is same on material 1 and material 2arrow_forwardPart C Evaluate AVL at t = 1.0 ms, if L = 20 mH, Io = 50 mA, and T = 1.0 ms. Express your answer using two significant figures and include the appropriate units. ► View Available Hint(s) ▼ AVL = Value Submit HA Part D μÀ V Evaluate AVL at t = 3.0 ms, if L = 20 mH, Io = 50 mA, and T = 1.0 ms. Express your answer using two significant figures and include the appropriate units. ► View Available Hint(s) P Pearson ? www ?arrow_forwardn/course.html?courseld=17544544&OpenVellumHMAC=a830981ff68f36618e84254ba22c5db5#10001 Aktiv Chemistry DZL Homepage - Vande... ▼ Lobby | Top Hat Part A Pe - Pb Submit Part B A cardinal (Richmondena cardinalis) of mass 4.20x10-2 kg and a baseball of mass 0.150 kg have the same kinetic energy. What is the ratio of the cardinal's magnitude pe of momentum to the magnitude p of the baseball's momentum? ► View Available Hint(s) Km Kw = V—| ΑΣΦ Submit ? Provide Feedback M Gmail A man weighing 750 N and a woman weighing 440 N have the same momentum. What is the ratio of the man's kinetic energy Km to that of the woman Kw? ► View Available Hint(s) 195| ΑΣΦ ? Handshake 4 VYES - Vanderbilt - S... Course Home P Pearson Copyright © 2022 Pearson Education Inc. All rights reserved. | Terms of Use | Privacy Policy | Permissions | Contact Us | Other TACTION | VOISIUMIS Next > 545 DIarrow_forward
- Needs Complete typed solution with 100 % accuracy.arrow_forwardI1:00:00 PM Problem 3: Suppose the speed of light were only 3000.0 m's. A jet fighter moving toward a target on the ground at 810 m/s shoots bullets, each having a muzzle velocity of 1050 m's. Randomized Variables v-810 m/s v2 1050 m's ed What is the velocity of the bullets relative to the target in km's? Grade Sommary Deductions 0% Potential 100%arrow_forwarda)Find an expression for the bullet's initial speed v_B in terms of m, M, k, and d. Express your answer in terms of the variables m M k d b)What was the speed of a 1.8 g bullet if the block's mass is 1.1 kg and if the spring, with k = 37 N/m , was compressed by 16 cm? Express your answer in meters per second. c)What percentage of the bullet's energy is "lost"? Express your answer in percent to four significant figures.arrow_forward
- What is the difference between accuracy and precision? Explain 2. Calculate the volume and percent error/uncertainty in the volume of a rectangular sample block of length 13.51 ±0.05 cm, width 6.23 ±0.02 cm, and thickness of 1.76±0.02 cm. 3. Calculate the mass density and uncertainty in the mass density of the sample block. Mass of the block is 289± 1gr. 1.arrow_forwardApply error propagation to determine the associated uncertainty in the average volume… Plzarrow_forwardTwo metal bars are welded together to shape a more extended bar. The length of the primary bar is L₁ = = 0.97 ± 0.02 m And the length of the secondary bar is L2₂ 1.13 0.01 m. = Figure out the length of the bar (including uncertainty). Show your steps.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios