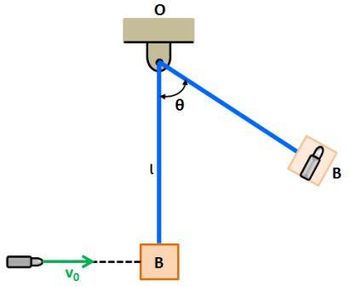
After reading the physics question below, choose the correct answer from the following options.
A ballistic pendulum can be used to measure the speed of a bullet from a gun. A ballistic pendulum consists of a block hanging from a string. You would shoot a bullet at the block, which would lodge itself inside the block, causing the block to swing forward. The faster/heavier the bullet, the larger the angle the block will swing.
Consider the 2D collision when the bullet (traveling horizontally) hits the block (at rest). During this brief collision (ignoring the pendulum aspect for now), which of the following would apply?
Options:
|
A)
|
Kinetic energy and momentum are both conserved. |
|
B)
|
Kinetic energy is conserved but momentum is not. |
|
C)
|
Kinetic energy is not conserved but momentum is. |
|
D)
|
Neither kinetic energy, nor momentum are conserved. |
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

- The figure below shows three points in the operation of the ballistic pendulum. The projectile approaches the pendulum in part (a) of the figure. Part (b) of the figure shows the situation just after the projectile is captured in the pendulum. In part (c) of the figure, the pendulum arm has swung upward and come to rest at a height h above its initial position. Three points in the operation of a ballistic pendulum are shown in parts a, b, and c. A block of mass m2 is attached to the bottom of a rigid rod, which is suspended freely. The projectile (a sphere) has a mass of m1 and is approaching the block directly from the left with velocity vi. The sphere is superimposed on the block to show that the projectile has been captured in the pendulum. An arrow extends from the block and points to the right, and is labeled vf. The pendulum is angled to the right, with the sphere still superimposed on the block. The block is a vertical distance h above its starting height. (a) Prove that…arrow_forwardAs shown in the figure (Figure 1), a superball with mass m equal to 50 grams is dropped from a height of h₁ = 1.5 m. It collides with a table, then bounces up to a height of hf = 1.0 m. The duration of the collision (the time during which the superball is in contact with the table) is tc = 15 ms. In this problem, take the positive y direction to be upward, and use g = 9.8 m/s² for the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity. Neglect air resistance. Figure Before During After he 1 of 1 Find the y component of the time-averaged force Favg,y, in newtons, that the table exerts on the ball. Express your answer numerically, to two significant figures. ► View Available Hint(s) 17 ΑΣΦ Favey = Submit Part E Kafter - Kbefore = Submit Find Kafter - Kbefore, the change in the kinetic energy of the ball during the collision, in joules. Express your answer numerically, to two significant figures. ► View Available Hint(s) Provide Feedback B Π| ΑΣΦΑ ? N Ċ **** pod ? Jarrow_forwardAn elastic collision occurs in one dimension, in which a 10 kg block traveling at 5 m/s collides with a 5 kg block traveling at 3 m/s in the same direction. What are the velocities of the two blocks immediately after the collision?arrow_forward
- A ballistic pendulum consists of a 3.5-kg wooden block originally at rest, 0 = 0°. When a 2-g bullet strikes and becomes embedded in it, it is observed that the block swings upward to a maximum angle of 0 = 6°. (Figure 1) Figure 1.25 m 0 1.25 m 1 of 1 Part A Estimate the speed of the bullet. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. UB= Submit Value Provide Feedback Request Answer Units ?arrow_forwardYou have been asked to design a "ballistic spring system" to measure the speed of bullets. A spring whose spring constant is k is suspended from the ceiling. A block of mass M hangs from the spring. A bullet of mass m is fired vertically upward into the bottom of the block and stops in the block. The spring's maximum compression d is measured. a. Find an expression for the bullet's speed v in terms of m, M, k, and d. b. What was the speed of a 10 g bullet if the block's mass is 2.0 kg and if the spring, with k = 50 N/m, was compressed by 45 cm?arrow_forwardPlease write the answer on paper. I do not understand when the answer is typed out. Thank you.arrow_forward
- 5. The figure shows three balls of clay moving on a frictionless horizontal surface just before a collision. The three collide simultaneously and stick together. Find the speed and direction of the blob of clay after the collision. Draw the blob after the collision and show its velocity vector. 40 g 45° 4.0 m/s 3.0 m/s 30 g 2.0 m/s 20 garrow_forwardOne block of mass m_1=2.0 kg is sliding down along a frictionless ramp from a height of h=2.5 m. It then collides with another block of mass m_2=1 kg and after the collision the stick together. Then, both of the blocks slide together into a region where the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.500 and comes to a stop after distance d m within that region. a. Find the velocity of the block of mass m1 at the bottom of the ramp. b. Find the velocity of the two-block at which they slide into the region with kinetic friction coefficient 0.500. c. Find the value of distance d at which they stoparrow_forwardI don't understand how my professor simplified this equation. Can you break it down for me in detail, showing each step and then explaining why you did what you did?arrow_forward
- The mass of a regulation tennis ball is 57.0 g (although it can vary slightly), and tests have shown that the ball is in contact with the tennis racket for 30 ms. (This number can also vary, depending on the racket and swing.) We assume a 59.0 g ball and a 26.0 ms contact time in this problem. In the 2011 Davis Cup competition, Ivo Karlovic made one of the fastest recorded serves in history, which was clocked at 156 mi//h (70 m/s). Part A: What impulse did Karlovic exert on the tennis ball in his record serve? Take the +x direction to be along the final direction of motion of the ball. Part B: What average force did Karlovic exert on the tennis ball in his record serve? Part C: If his opponent returned this serve with a speed of 55.0 m/s, what impulse did his opponent exert on the ball, assuming purely horizontal motion? Take the +x direction to be in the direction the ball is traveling before it is hit by the opponent. Part D: If his opponent returned this serve with a speed of 55.0…arrow_forwardA physics student hurls a 315-gram ball directly into a 3.54-kg box which is at rest on a table top. The baseball strikes the box with a pre-impact speed of 54.1 m/s. The box is filled with towels to help absorb the blow and effectively catch the ball. The coefficient of friction between the box and the table is 0.714. Determine the distance which the ball and box slide across the table after the collision.arrow_forwardWhy is the selected answer wrong? What is the correct answer?arrow_forward