
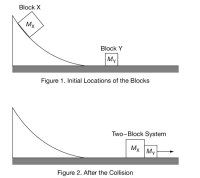
A solid block X of mass MX may be placed at different locations along a curved ramp. At the bottom of the ramp is a solid block Y of mass MY that is at rest on a horizontal surface. Figure 1 shows both blocks before block X is released. A group of students must graphically determine the relationship between the release height of block X and the speed at which the two-block system travels after the blocks collide and stick together. Figure 2 shows both blocks after the collision. Frictional forces between block X and the ramp and between both blocks and the horizontal surface are considered to be negligible.
i. State the basic physics principles, laws, or equations that students could use to graphically determine the relationship between the release height of block X and the speed at which the two-block system travels after the blocks collide and stick together.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

- A projectile has undergone an elastic one-dimensional collision with an initially stationary target, along an x axis. The figure below is a graph of position versus time for the projectile and target, before and after the collision. (Two line segments are parallel to the time axis.) Which is true about the masses of the projectile and target? 4 O the projectile's mass is greater O the target's mass is greater O the masses are equalarrow_forwardPlease help me understand the concept of this practice problem and how to work these types out. Thanksarrow_forwardA block is released from rest at the top of the frictionless ramp shown in the figure. Mass 1 is 1.27 kg and it is released from a height of 1.56 m. The block collides elastically with block 2, initially at rest. Mass 2 is 4.12 kg. How far back up the ramp does mass 1 move after the collision? (Take the initial direction of block one as positive.)arrow_forward
- Blocks A and B are moving toward each other on a horizontal, frictionless surface. Block A has a mass of 5 kg and a velocity of +40 m/s, while B has a mass of 10 kg and a velocity of -6 m/s. They suffer a head on, completely inelastic collision. What is the common speed of the blocks after the collision.arrow_forwardTwo cars each with a speed of 30 m/s are sliding on frictionless ice at an intersection and collide. Car #1 has mass 1400 kg and Car#2 has mass 1300 kg. The cars stick together after colliding. A) What is the angle the combined mass comes off the collision at ? B)What is the speed of the combined mass?arrow_forwardTwo hockey pucks slide along a flat sheet of ice with no friction, and then collide with each other. The diagram below shows a top-down view of the colliding hockey pucks. The masses of the hockey pucks are mA = 2.00 kilograms (kg) and mB = 1.50 kg. Before the collision, puck A moves to the right at a speed of 2.50 meters per second (m/s) and puck moves to the left at a speed of 1.25 m/s. After the collision, puck A moves at a speed of 1.00 m/s at 50.0 degrees relative to the x axis. (a) Find find the final speed (in m/s) of puck B after the collision. (b) Find find the direction of travel of puck B after the collision. Give your answer as an angle in degrees, measured relative to the x axis. (c) What is the total change in kinetic energy of the hockey pucks during the collision, in units of Joules (J)?arrow_forward
- Two blocks are released from the positions shown in the diagram. Block 1 has a mass of 3.69 kg and is released from a height A = 1.36 m. Block 2 has a mass of 4.21 kg and is released from B = 3.7 m. The blocks undergo an elastic head-on collision on the frictionless track. What are the velocities of the blocks just before they collide? (Take the initial direction of block 1 to be positive.)arrow_forwardAn air hockey puck is moving with a velocity of 2 in/sec towards a second puck that is at rest. After the two pucks collide, the first puck reverses direction and moves at 0.7 in/sec. If the pucks have the same mass, what is the velocity of the second puck after the collision in m/s? Assume the air hockey table has no friction and that all of the motion is in one dimension.arrow_forwardA 7-kg object moving with a velocity of 5 m/s in the positive x direction strikes and sticks to a 2-kg object moving with a speed of 3 m/s in the same direction. What is their speed after the collision?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





