
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
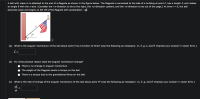
Transcribed Image Text:A ball with mass m is attached to the end of a flagpole as shown in the figure below. The flagpole is connected to the side of a building at point P, has a length e, and makes
an angle 0 with the x-axis. (Consider the +x-direction to be to the right, the +y-direction upward, and the +z-direction to be out of the page.) At time t = 0, the ball
becomes loose and begins to fall off of the flagpole with acceleration –gĵ.
(a) What is the angular momentum of the ball about point P as a function of time? (Use the following as necessary: m, l, g, t, and 0. Express your answer in vector form.)
(b) For what physical reason does the angular momentum change?
There is no change in angular momentum.
The weight of the flagpole exerts a torque on the ball.
There is a torque due to the gravitational force on the ball.
(c) What is the rate of change of the angular momentum of the ball about point P? (Use the following as necessary: m, l, g, and 0. Express your answer in vector form.)
dL
dt
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In this question the unit vectors i and j are in the directions east and north respectively. A particle R of mass 2kg is moving on a smooth horizontal surface under the action of a single horizontal force FN. At time t seconds, the velocity vms of R, relative to a fixed origin O, is given by v = (pr -31)i + (81 +q)j, where p and q are constants and p<0. (a) Given that when t= 0.5 the magnitude of F is 20, find the value of p. When t= 0, R is at the point with position vector (2i – 3j) m. (b) Find, in terms of q, an expression for the displacement vector of R at time t. When t = 1, R is at a point on the line L, where L passes through O and the point with position vector 2i - 8j. (c) Find the value of q.arrow_forwardA uniform chain of length L and mass M lies on a frictionless horizontal table with a very small part hanging from the edge of the table. The chain begins to fall under the weight of the hanging part. Obtain the expression for the velocity of the chain at the instant when the length of the hanging part becomes L/n where n > 1.arrow_forwarda student is skateboarding down a ramp that is 5.82 m long and inclined at 24.1% with respect to the horizontal. the initial speed of the skateboarder at the top of the ramp is 3.75 m/s. neglect friction and find the speed at the bottom of the ramp.arrow_forward
- There are two boxes with same mass couple together by a massless rope. One of the masses is on a ramp raised to an angle of 42 degrees, the other mass is hanging off to the right as shown in the figure. In between the two masses, the rope sun over a frictionless, massless pulley. If the mass on the ramp starts the problem at the top of the inclined plane, and the system is given a push, so that it is moving with an initial velocity pointing down the ramp. Ignore wind resistance for this problem. a) If the coefficient of friction is 0.30, what is the magnitude and direction of the acceleration of the system? Use the coordinate system given in the figure. (a=-2.71362 m/s^2 along the -x direction) What is the angle required for the the acceleration of the system to equal zero? Explain you reasoning with a few sentences.arrow_forwardTarzan grabs a vine, which is initially horizontal, and attempts to swing to the ground. Tarzan weighs 890 N and the breaking strength of the vine he knows is 1780 N. A Tarzan swings he is surprised to find that the vine breaks at a certain angle theta. Find theta.arrow_forwardPlease helparrow_forward
- The diagram shows the all of the forces acting on a body of mass 3.13 kg. The three forces have magnitudes F1 = 59.2 N, F2 = 27.7 N, and F3 = 74.4 N, with directions as indicted in the diagram, where θ = 55.8 degrees and φ = 21.4 degrees. The dashed lines are parallel to the x and y axes. At t = 0, the body is moving at a speed of 5.29 m/s in the positive x direction. 1.)What are the x and y components of the acceleration in m/s2?arrow_forwardThe high-speed winds around a tornado can drive projectiles into trees, building walls, and even metal traffic signs. In a laboratory simulation, a standard wood toothpick was shot by pneumatic gun into an oak branch. The toothpick mass was 0.14 g, its speed before entering the branch was 221 m/s, and its penetration depth was 17 mm. If its speed was decreased at a uniform rate, what was the magnitude of the force of the branch on the toothpick?arrow_forwardAs illustrated in the figure, consider a soccer player kicking a stationary ball of mass m = 0.5 kg. Assuming that the air resistance is negligible, the ball undergoes a projectile motion (shown in figure). It is recorded that the angle of release of the ball is 0 = 25.2° and the maximum height reached by the ball is h = 4.5 m. If the time during which the foot of the soccer player remained in contact with the ball is At = determine: (a) The speed of release, V, of the ball 0.12 s, (b) The horizontal distance, I, between the initial position of the ball and the landing point (c) The momentum, p, of the ball at the instant of takeoff (d) The magnitude of force, F, applied on the ball by the soccer player Уarrow_forward
- A ball with mass m is attached to the end of a flagpole. The flagpole is connected to the side of a building at point P, has a length ℓ, and makes an angle θ with the x-axis. (Consider the +x-direction to be to the right, the +y-direction upward, and the +z-direction to be out of the page.) At time t = 0, the ball becomes loose and begins to fall off of the flagpole with acceleration −gĵ. (a) What is the angular momentum of the ball about point P as a function of time? (Use the following as necessary: m, ℓ, g, t, and θ. Express your answer in vector form.) (b) For what physical reason does the angular momentum change? (c) What is the rate of change of the angular momentum of the ball about point P? (Use the following as necessary: m, ℓ, g, and θ. Express your answer in vector form.)arrow_forwardAt a pool, a 3.26 kg life ring is thrown by a lifeguard to a struggling swimmer. The lifeguard stand is 1.75 m above the water. If air resistance is negligible and the life ring is launch with a speed of 8.23 m/s at the angle indicated in the figure: a) Find the height of the life ring and the net force on the life ring at point P. b) Find how far the life ring lands from the base of the stand. c) With what velocity did the life ring strike the water at point Q? 30°arrow_forwardAt a local swimming pool, the diving board is elevated h = 8.5 m above the pool's surface and overhangs the pool edge by L = 2 m. A diver runs horizontally along the diving board with a speed of v0 = 4.2 m/s and then falls into the pool. Neglect air resistance. Use a coordinate system with the horizontal x-axis pointing in the direction of the diver’s initial motion, and the vertical y-axis pointing up. Determine the horizontal distance, dw in meters, from the edge of the pool to where the diver enters the water.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON