
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
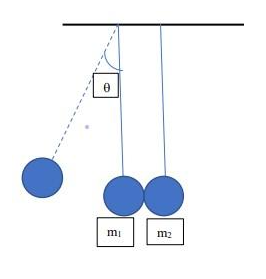
Two pendulums of equal length l = 1.15 m are suspended from the same ceiling and are hanging side by side just touching each other at rest as shown in the diagram. The pendulum bobs are steel spheres and weighs m1 = 0.35 kg and m2 = 0.77 kg. If bob m1 is drawn back to make an angle = 350 with the vertical and then let go
Part a. Draw the FBD for the problem
Part b. With what speed m1 strikes m2?
Part c. Consider m1 strikes m2 elastically, how high will m2 rise above its initial point after the strike?
Part d. What angle m2 makes with the vertical at this point?
Transcribed Image Text:0
mi
m₂
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A pulley has a negligible mass (that means, the radius is not relevant). It is supported with a pin at the center (and is free to rotate). A rope goes over the pulley. Block A, which has a mass of 5.723 kg is connected to one side of the rope. On the other side, Block B, with a mass of 12.602 kg is connected. The system is released from rest. What is the speed of block B, after B has traveled 0.716 m? Please enter a positive value in m/s (but without units) regardless of the direction of the motion of Barrow_forwardA baseball of mass m= 0.35 kg is spun vertically on a massless string of length L = 0.93 m. The string can only support a tension of Tmax= 10.6 N before it will break. Randomized Variables m = 0.35 kg L = 0.93 m Tmax= 10.6 N Part (a) What is the maximum possible speed of the ball at the top of the loop, in meters per second? Part (b) What is the maximum possible speed of the ball at the bottom of the loop, in meters per second?arrow_forwardA cord connected at one end to a block which can slide on an inclined plane has its other end wrapped around a cylinder resting in a depression at the top of the plane as shown in ( Figure 1). Determine the speed of the block after it has traveled 1.40 m along the plane, starting from rest. Assume there is no friction. Express your answer using two significant figures. Figure M = 33 kg R=0.20 m 58° 1 of 1 ΜΕ ΑΣΦ = 0.844 2+ Submit Previous Answers Request Answer ? m/s × Incorrect; Try Again; 2 attempts remaining Part B Determine the speed of the block after it has traveled 1.40 along the plane, starting from rest. Assume the coefficient of friction between all surfaces is -00310. Since the block is much lighter than the cylinder, ignore tension in the string when calculating the normal force on the cylinder. Do not ignore tension in the string when calculating the net torque (including friction) on the cylinder Express your answer using two significant figures. v= ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Submit Request…arrow_forward
- C?arrow_forwardTwo blocks, which can be modeled as point masses, are connected by a massless string which passes through a hole in a frictionless table. A tube extends out of the hole in the table so that the portion of the string between the hole and M1 remains parallel to the top of the table. The blocks have masses M1 = 1.2 kg and M2 = 2.7 kg. Block 1 is a distance r = 0.55 m from the center of the frictionless surface. Block 2 hangs vertically underneath. 1) If we Assume that block two, M2, does not move relative to the table and that block one, M1, is rotating around the table. What is the speed of block one, M1, in meters per second?arrow_forwardA narrow uniform rod has length 2a. The linear mass density of the rod is p. so the mass m of a length of the rod is pl. Part A A point mass is located a perpendicular distance from the center of the rod. Calculate the magnitude of the force that the rod exerts on the point mass. (Hint: Let the rod be along the y-axis with the center of the rod at the origin, and divide the rod into infinitesimal segments that have length dy and that are located at coordinate y. The mass of the segment is dm = pdy. Write expressions for the I- and y-components of the force on the point mass, and integrate from a toa to find the components of the total force). Express your answer in terms of the gravitational constant G and some or all of the variables m, p, a, and r. IVE ΑΣΦ ? a xa Xb √x xx x b IXI F= Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining The correct answer does not depend on: la Part B n(n+1)2 + n(n−1)(n−2) 1+nz+ T³ +... (|1| < 1).) What does your result…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON