
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
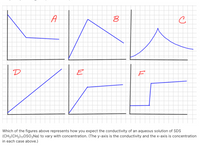
Transcribed Image Text:A
D
E
Which of the figures above represents how you expect the conductivity of an aqueous solution of SDS
(CH3(CH2)110SO3Na) to vary with concentration. (The y-axis is the conductivity and the x-axis is concentration
in each case above.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Phoose which of the following has the least4s . Omolten brass (alloy of Cu and Zn) Omethane Laqueous solution of KBr Umetallic Ptarrow_forwardCALCULATE the molarity of NaI in a solution obtained by adding 5 mL of 0.2M NaI to a mixture of 5 mL of 0.2M of K2SO4, 5 mL of K2S2O8, 4mL of H2O and 1 mL of starch.arrow_forwardNa3PO4 dissolves in water to produce an electrolytic solution. What is the osmolarity of a 2.0 × 10-3 MNa3PO4 solution?arrow_forward
- In which of the following aqueous solutions would you expect silver sulfide (Ag₂S, Ksp = 2 x 10-51) to have the greatest solubility? O 0.10 M NaOH O 0.10 M Bas O 0.10 M HNO3 O H₂0 (1) O 0.10 M AgNO3 1.0 L of a solution containing 2.0 x 10-7 M AgNO3 solution is mixed with 1.0 L of a 4.0 x 107 M NaBr solution. Ksp for AgBr is 5.0 x 10 -13 O a precipitate forms because Ksp < Q O no precipitate forms because K₁p < Q O a precipitate just begins to form because Q=Ksp Which of the following statements is true? The molar solubility of silver sulfate alone is approximately 1.6 x 102 M. Calculate the molar solubility of Ag2SO4 in a 0.20 M solution of AgNO3(aq). (Ksp (Ag2SO4) = 1.5 x 105) O 7.2 x 107 M O 6.2 x 10⁹ M O 3.2 x 10 M 99.94 M 3.8X18Marrow_forwardWhat is the concentration in parts per million of a 0.00175% w/v solution of mercuric nitrate?arrow_forwardHow does Cr3P2(s) break up in solution? Write subscripts and superscripts as normal numbers and do not include spaces in your answer. Do not include states like (aq) or "1" in front of single atoms or charges. For example, the answer for NiCl3(s) would be Ni3++3Cl- For example, the answer for Sb3(PO4)5(s) would be 3Sb5++5PO43- Possibly relevant polyatomic ions: CN-,OH-, NO3-, NO2-, ClO3-, ClO4-, CO32-, SO42-, CrO42-, Cr2O72-, PO43-, PO33- Screen Reader User: For example, the answer for NiCl3(s) would be Ni3++3Cl minus For example, the answer for Sb3(P O4)5(s) would be 3Sb5++5PO43 minus Possibly relevant polyatomic ions: CN minus,O H minus, N O3 1 minus, N O2 1 minus, Cl O3 1 minus, Cl O4 1 minus, C O3 2 minus, S O4 2 minus, Cr O4 2 minus, Cr2 O7 2 minus, P O4 3 minus, P O3 3 minus Question 10 options:arrow_forward
- Chemistryarrow_forwardThe Dead Sea on the Jordan-Israel border is the world's lowest lake (-430 m) with an atmospheric pressure of 106 kPa. If the Dead Sea were composed of freshwater at 0 oC, what would be the concentration of dissolved O2? The salinity of the Dead Sea is ~8 times higher than sea water. How would this affect the solubility of oxygen?arrow_forward28. Kindly please provide the answer only ASAParrow_forward
- Ll.120.arrow_forward8) What are the respective concentrations (M) of Fe3+ and I afforded by dissolving 0.200 mol Fel3 in water and diluting to 725 mL?arrow_forwardCalculate the molar solubility of MNCO3 in a solution in which [H30*] is held at 1.1 x 10-5 M. Show all essential steps. Kep = 5.0 x 10-10 (MNCO3) Ka1 = 4.45 x 10-7; Ka2 = 4.69 x 10-11 (H2CO3)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY