
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
From the following figure, determine: a) the flow rate through the pipe b) the velocity in the pipe c) the pressure at points A, B, C, D. d) outline the line of motor head for this situation . fluid is
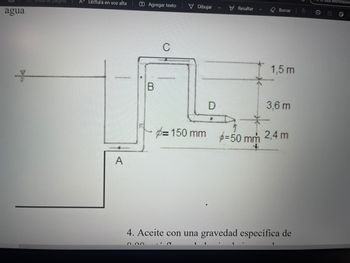
Transcribed Image Text:agua
f
vista de pagina
A" Lectura en voz alta
A
TAgregar texto
B
000
Dibujar
= 150 mm
M
D
.
V
Resaltar
Borrar
1,5 m
3,6 m
4. Aceite con una gravedad específica de
=50 mm 2,4 m
No se esta sincronizanc
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 6. The fill line for a tank swages up from 8" Schedule 40 pipe to 16" Schedule 40 pipe. The velocity entering the tank must be limited to 3 ft/s to avoid a static charge build up in the tank. A) What is the maximum velocity allowed in the 8" section of pipe? B) What is the maximum volumetric flow rate entering the tank?arrow_forwardpage: 2/8 8. For hydraulic pumps and motors, there are two types of losses, i.e. 9. The measure for oil trapping of gear pumps is 10. Three basic conditions for operation of pumps are and mechanism to separate suction from delivery stroke. 11. For the axial piston pump, the pulsation is minimized when the pump has 12. In neutral position, the port P and T of relief valves are (connected/disconnected). 13. The secondary air treatment unit of pneumatic systems include and air lubricator.arrow_forwardHydraulic motor calculations Theoretical flow = 1.5 GPMRPM output = 100 RPMMechanical power = 0.25 HP Total efficiency = 85%Volumetric efficiency = 92% a) Calculate the theoretical engine displacement (in3/r). b) Calculate the actual engine flow in GPM. c) Calculate the actual torque (lb.in).arrow_forward
- a) A suction pump. Consider a pipe that is inserted vertically into water. By suction, the pipe is evacuated of air. How high will the water rise? b) A water turbine is designed to extract kinetic energy from the hor- izontal flow of water and convert it into rotation of the turbine. You may assume that the height of the fluid does not change as it flows through the turbine, and that the fluid is incompressible. If the velocity is lowered from 100 m/s to 70 m/s as the fluid flows through the turbine, what is the change in pressure? c) Is the pressure higher upstream or downstream? d) The fluid in (b) is replaced by air to make a wind turbine. What is the change in pressure now for the identical change in velocity to (b)?arrow_forwardFor a 6.25-inch Model 4075 pump operated at 1160 rpm, if 450 GPM of water is to be delivered, what will be the estimated pump head in ft? HEAD IN FEET 30 25 0 0 0 10 O 6 ft 7.25" (184mm) 20 7.00" (178mm). 6.75" (171mm). 6.50" (165mm)] 15 6.25" (159mm). 5 O 16 ft O 20 ft O 12 ft aco® L/SEC 5 OT 10 Model 4075 FI & CI Series 15 -6-6 ⁰ dº 20 ANA 888 778 25 REQUIRED NPSH do 1160 RPM November 1, 2010 K ・dº- [M 90 do 30 8800 81 1HP(.75KW) DeJ kin do 60% 35 do 50 Curve no. 2175 Min. Imp. Dia. 6.25" Size 5 x 4 x 7.0 40 45 3HP(2.2KW), 2HP(1 5KW) 5HP(1 1KW)> CURVES BASED ON CLEAR WATER WITH SPECIFIC GRAVITY OF 1.0 L 75 150 225 300 375 450 525 600 675 FLOW IN GALLONS PER MINUTE NOWONG FEET 15 12 7 6 2 1 NPSH 758 50 5 HEAD IN METERS 45 586888 KPO 60 40 20 10 LO HEAD IN KILOPASCALSarrow_forwardThe general energy equation is . For the picture blow, select the simplified the form of the general equation for point 1 and 4____________arrow_forward
- Show in Figure 1 is the water flow system. The velocity head difference is . Volume flow rate is . The heights are and , respectively. The power output from the motor is , . The energy added by the pump is . The energy loss between point 1 and 2 is . Calculate 4) the pressure head difference in meter_________ marrow_forward1. If the pump rotated at 2000 rpm and instead and used a 9" impeller, what would the head be when moving 400 gallons per minute? 2. How much input power would be required to move 200 gpm of gasoline in the pump described in the chart with an impeller diameter of 8 3/4"?arrow_forwardDisplacement (c): 0.2 in3/revShank diameter (d) = 0.625 in.Piston diameter (D) = 1.5 in.Rotation speed (n): 1725 RPMPressure (P): 600 PSIStroke (L) = 18in. a) Calculate the theoretical flow rate of the pump in in3/min and US GPM.Theoretical flow (Q) = Theoretical displacement (C) x Speed of revolution (n)Theoretical flow (Q) = 0.2 in3/rev x 1725 rpmTheoretical flow (Q) = 345 in3/min = 1.49 US GPM b) Calculate the cylinder output speed in in/s.Cylinder output speed (VS) = Piston side flow (Q) / Piston area (Ap)Cylinder output speed (VS) = (Displacement x Speed of revolution) / Piston area (Ap)Cylinder output speed (VS) = (0.2 in3/rev x 1725 RPM) / 1.77 in2Cylinder output speed (VS) = (0.2 in3/rev x 1725 RPM) / 1.77 in2Cylinder output speed (VS) = 196.02in/s = 196.02 / 60s = 3.20 in/s Questions: c) Knowing the output velocity (ram speed), calculate the rod side flow in GPM when the ram is extending. d) Calculate the piston exit time in seconds. e) Calculate the piston entry time in…arrow_forward
- A hydraulic motor has 7.5-in³ volumetric displacement. If it has a pressure rating of 1200 psi and receives oil from a 25-gpm theoretical flow-rate pump, find the motor a. Speed b. Theoretical torque C. Theoretical horsepowerarrow_forwardAbsolute Open Flow (AOF) Is the maximum flow rate into the wellbore when the BHP is zero; It’s a theoretical flow rate, which sometimes reflects the ability of the reservoir to deliver fluid into the wellbore Select one: True Falsearrow_forwardThe answer is one of the options below please solve carefully and circle the correct option Please write clear .arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY