
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
The following rigid structure ABCD is supported by a hinge at B and two bars at C and D. The applied load is 100 kN. The data is shown in the table. Determine:
- The stress in each bar. Answ: 27.01 MPa, 328.01 MPa
- The vertical displacement at the point where the load is applied. Answ: 0.9403 mm.
- The rotation at point B. Answ: 0.001069 rad.
- The horizontal displacement 400 mm below point B. Answ: 0.42741 mm.
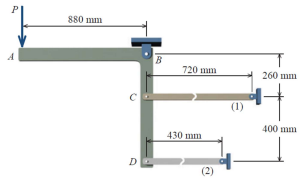
Transcribed Image Text:A
880 mm
C
B
720 mm
260 mm
400 mm
430 mm
D

Transcribed Image Text:Bar (1) Aluminum
Bar (2) Steel
Elastic modulus, E
70 GPa
200 GPa
2
Area, A
200 mm²
400 mm²
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 1 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Determine the principal stress and absolute maximum shear stress developed at point B on the cross section of the bracket at section a-a. Show the Mohr's circle for point B. -300 mm- 150 mm 2.5 kN 12 mm 6 mm BH 6 mm Figure 4 A 36 mm 36 mm Section a - a 6 mmarrow_forwardy 50 lb-ft T2 (1) 30 lb-ft A B C D Assume for the above sketch that the shaft is restrained from rotation at the left support, but free to rotate at the right support. If T1= 60lb-ft and T2 = 10 lb-ft, what is the max torsion across the shaft? Solve for the maximum shear stress, if the shaft is solid, having a diameter of 0.5in. Enter you final answer into D2L answer box, assuming units of psi.arrow_forwardFOR THE TRUSS SHOW BELOW, SOLVE FOR THE STRESSES (ORANGE) IF ALL MEMBERS 750 mm^2.. 3m 2m 2m 2m C 3m E 200 KN 2m G F 100 kN H 4m Barrow_forward
- A rod consisting of two cylindrical portions AB and BC is restrained at both ends. Portion AB is made of steel (ES = 200 GPa and as = 11.7 x 10-6/°C) and portion BC is made of brass (En= 105 GPa and an= 20.9 x 1o-6rC). Knowing that the rod is initially unstressed, determine the compressive force induced in ABC when there is a temperature rise of 50°C. 30-mm diameter 250 mm B 50-mm diameter 300 mm The compressive force induced in ABC is kN.arrow_forwardDraw a free body diagram too thank youarrow_forward1. For the W 21x 62 steel beam below determine the actual value of om in the beam and the maximum value of the principal stress omax at the junction of the flange and the web. 20 kips 20 kips A B 10 ft 2 kips/ft 30 ft- C 10 ft Darrow_forward
- Q.3) A simply supported wide-flange (see figure below) beam of span length L carries a vertical concentrated load P acting through the centroid C at the midpoint of the span. The beam is attached to supports inclined at an angle a to the horizontal. Determine the orientation of the neutral axis and calculate the maximum stresses at the outside corners of the cross section (points A, B, D, and E) due to applied load P. Data for the beam are as follows: W 10 x 30 section, L = 8.5 ft., P = 5 kips, and a = 26.57 degrees. 2. E αarrow_forwardA force P of magnitude 1,100 N is applied to the pedal shown satisfies a shearing stress in the pin is 42 MPa. a. Determine the reaction (in N) at the hinge at C. b. Determine the diameter of the pin at C in mm. c. Determine the corresponding bearing stress in the pedal at C in MPa. d. Determine the corresponding bearing stress in each support bracket at C in MPa. 9 mm H 11€ |||| 5 mm A 75 mm 125 mm B C 300 mm PI Darrow_forwardQ.2.arrow_forward
- Required information Consider the beam and loading shown. If a=8 in, b=9.0 in, c=1 in. For a section at n-n, determine the shear stress at b. A 25 kips 20 in.- 10 in. 25 kips - 20 in.- B a +6 i in.. in. b b a с in.arrow_forwardThe rigid bar ABCD of negligible weight is initially horizontal, and the steel rods attached at A and C are stress-free. If a 20-kip load is applied, determine the vertical displacement in the bar at A and C that will cause a stress in the rod at C to be 50 ksi. Indicate the direction of movement. Use E = 29x106 psi for steel. A = 0.5 in.2 3 ft A B D 20 kips 2 ft2 ft- 4 ft 4 ft A =0.75 in.2arrow_forwardDetermine the location of the shear center for the following section. Determine the shear stress at point A, if a 20 kN (downwards) shear load is applied at the shear center. Given: h1 = 25 mm h = 100 mm b = 50 mm Thickness = 4 mm. V ke- A |▬▬b▬|| h₁arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning