
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:A 80-pF capacitor and a 320-pF capacitor are both charged to 1.70 kV. They are then disconnected from the voltage source and are connected together, positive plate to negative plate and negative plate to
positive plate.
(a) Find the resulting potential difference across each capacitor.
V
80 pF
= 1.02
kV
V
320 pF = 1.02
kV
(b) Find the energy lost when the connections are made.
3.7*10**6
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
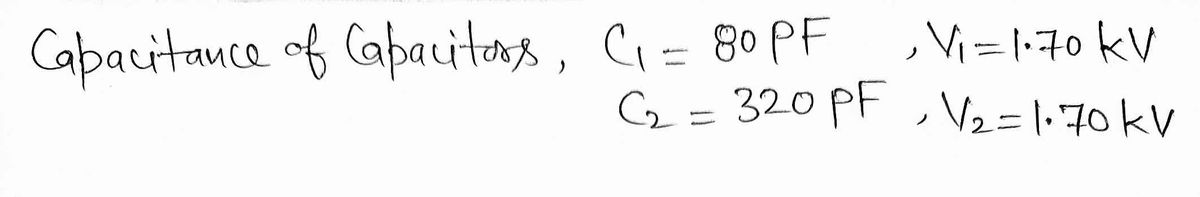
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 6: Suppose you have a 9.00 V battery, a 3.8 μF capacitor, and a 7.85 μF capacitor. Part (a) Find the total charge stored in the system if the capacitors are connected to the battery in series in C. Part (b) Find the energy stored in the system if the capacitors are connected to the battery in series in J. Part (c) Find the charge if the capacitors are connected to the battery in parallel in C. Part (d) Find the energy stored if the capacitors are connected to the battery in parallel in J.arrow_forwardA parallel-plate capacitor has square plates that have edge length equal to 1.20×10^2cm and are separated by 1.00 mm. It is connected to a battery and is charged to 12.0 V. 1)How much energy is stored in the capacitor? (Express your answer to three significant figures.)arrow_forwardA 50-pF capacitor and a 200-pF capacitor are both charged to 3.70 kV. They are then disconnected from the voltage source and are connected together, positive plate to negative plate and negative plate to positive plate. (a) Find the resulting potential difference across each capacitor. V50 kV pF kV V200 %D pF (b) Find the energy lost when the connections are made. еВookarrow_forward
- In the figure a potential difference of V = 106 V is applied across a capacitor arrangement with capacitances C₁ = 10.7 μF, C₂ = 6.06 µF, and C3 = 4.66 µF. If capacitor 3 undergoes electrical breakdown so that it becomes equivalent to conducting wire, what is the increase in (a) the charge on capacitor 1 and (b) the potential difference across capacitor 1? (a) Number Mi (b) Number i Units Units C V C₂arrow_forward(a )A researcher connects a 3.00 V battery to the plates of a capacitor. After waiting a while, the capacitor reaches a maximum amount of 16.0 µC of stored charge. What is the value of the capacitance (in µF)? µF (b) The capacitor is disconnected from the battery, discharged, and then connected to a 10.0 V battery. Again, a long enough time is waited for the capacitor to fully charge. How much charge (in µC) is stored now? (Assume the capacitor can handle this new voltage without failing.) µCarrow_forwardConstants A dielectric-filled parallel-plate capacitor has plate area A = 20.0 cm2 , plate separation d = 5.00 mm and dielectric constant k = 3.00. The capacitor is connected to a battery that creates a constant voltage V = 5,00 V Throughout the problem, use en = 8.85×10 12 C2 /N . m? The capacitor is now disconnected from the battery, and the dielectric plate is slowly removed the rest of the way out of the capacitor. Find the new energy of the capacitor, U3 Express your answer numerically in joules. • View Available Hint(s) VO AZO U3 = Submit Previous Answers X Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining Part D In the process of removing the remaining portion of the dielectric from the disconnected capacitor, how much work W is done by the external agent acting on the dielectric? Express your answer numerically in joules.arrow_forward
- A 0.40 µF and a 0.60 µF capacitor are connected in series to a 9.0 V battery. Calculate (a) the potential difference across each capacitor and (b) the charge on each. (c) Repeat parts a & b assuming the two capacitors are in parallel.arrow_forwardA 80-pF capacitor and a 320-pF capacitor are both charged to 1.70 kV. They are then disconnected from the voltage source and are connected together, positive plate to negative plate and negative plate to positive plate. (a) Find the resulting potential difference across each capacitor. kV V 80 pF kV V320 pF (b) Find the energy lost when the connections are made.arrow_forwardYou built a circuit consisting of three parallel plate capacitors with capacitances of 2.0 F, 3.0 F, and 5.0 F, respectively, which are connected in parallel. The whole circuit is connected to a 100 V line. What is the (a) total capacitance, (b) charge stored in each capacitor, and (c) potential difference across each capacitor?arrow_forward
- In the figure a potential difference of V = 104 V is applied across a capacitor arrangement with capacitances C₁ = 10.2 μF, C₂ = 6.76 μF, and C3 = 3.96 µF. If capacitor 3 undergoes electrical breakdown so that it becomes equivalent to conducting wire, what is the increase in (a) the charge on capacitor 1 and (b) the potential difference across capacitor 1? (a) Number i 856.8E-6 Units C (b) Number i 84 Units V C2arrow_forwardTwo capacitors, C₁ = 6.00 μF and C₂ = 13.0 μF, are connected in parallel, and the resulting combination is connected to a 9.00-V battery. (a) Find the equivalent capacitance of the combination. UF (b) Find the potential difference across each capacitor. V₁1 V₂ = = (c) Find the charge stored on each capacitor. Q₁ UC μC = Q₂ V V =arrow_forwardIf a voltage source of 24.0 V is connected from top to bottom, what is the charge accumulated on the 3.5 µF capacitor, in µC, when fully charged?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON