
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
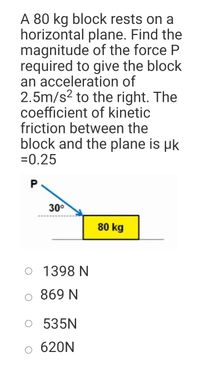
Transcribed Image Text:A 80 kg block rests on a
horizontal plane. Find the
magnitude of the force P
required to give the block
an acceleration of
2.5m/s? to the right. The
coefficient of kinetic
friction between the
block and the plane is µk
=0.25
30°
80 kg
O 1398 N
o 869 N
O 535N
o 620N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- pleae answer this questionarrow_forwardt=1.40 Please solve part Barrow_forwardWhen Crates A and B of mass ma = 31 kg and mB = 78 kg are released from rest, Crate A moves to the right on a rough surface (u = 0.4 ). The force P = 20 Newtons is always acting on Crate B. The linear spring has a stiffness of k = 490 N and is initially stretched 0.4 meters before the system is released from rest. Neglect the mass of the pulleys and cables and neglect friction in the pulley bearings. Determine the work done by the weight of Crate B (in Joules) when Crate A has moved a distance of 0.8 meters to the right. Consider g = 10 m. 82 Barrow_forward
- When the 3-kg box reaches point A it has a speed vA = 11 m/sm/s . Neglect friction and the size of the box. (Figure 1)arrow_forwardDetermine the vertical acceleration of the cylinder with a weight WA = 71 lb for each of the two cases. Neglect friction and the mass of the pulleys. The acceleration is positive if up, negative if down. Assume WB = 46 lb. W₂ W₂ B Answers: (a) a = (b) a = (a) 9.5162 i 5.2992 WA (b) ft/sec² ft/sec²arrow_forwardA 250 lb block A is released from rest. It pulls the 400 lb block B up the 30 ramp. The kinetic friction coefficient between block B and the ramp is 0.5. Determine the tension in the cable and the accelerations of block A and block B (or point C).arrow_forward
- The 250-lb pipe is being towed behind a truck, as shown in the figure. If θ = 25° and the coefficient of friction of the pipe with the ground is μk = 0.25, determine: a) the tension in the cable b) the acceleration of the truckarrow_forwardCart 1 Mass - M Cart 2 Mass = 3.5M Force Sensor The spring cart (cart 1) is released and collided inelastically with cart 2 and the two carts move off together. The spring does not add any mass to cart 1. Assume negligible friction in the cart wheels.arrow_forwardA slender bar with a length of 2 ft is pin-connected with a roller positioned on a smooth horizontal surface. The bar is at rest initially, and a horizontal force F is applied to the roller. If F = 13 lb and the weight of the bar is 10 lb, calculate the magnitude of the acceleration of the roller at that instant by neglecting the mass and the size d of the roller. Present your answer in ft/sec² using 3 significant figures. FOR COMARCA 2 ft Farrow_forward
- A 20-kg crate is subjected to force F = (2s2 + 3)N, where s is the displacement in meter. If the coefficient of friction between the surface is 0.20, what is the speed of the crate when it travels 10 m starting from rest? Farrow_forward- Determine the acceleration of the system. - Determine the magnitude of the force that each crate exerts on the other.arrow_forwarda box with a mass of 20kg pulls with constant force p=w if the box was initially at rest what is its speed after a time t=5 the coefficient of friction is mk=02arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY