
Concept explainers
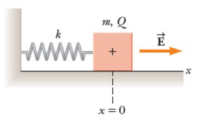
A 70.0-g block carrying a charge Q = 31.0 µC is connected to a spring for which k = 72.0 N / m. The block lies on a horizontal frictionless surface and is immersed in a uniform electric field of magnitude E = 4.64 ✕ 104 N / C directed as shown in the following figure. The block is released from rest when the spring is not stretched (x = 0).
(a) By what maximum distance (in cm) does the block move from its initial position?
(b) Determine (in cm) the rear equilibrium position of the block and the range of its motion. (Indicate the address with the sign of your answer.)
(c) Using conservation of energy, find a symbolic relationship that gives the potential difference between your initial position and the point of maximum extension in terms of the spring constant k, the amplitude A, and the charge Q.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

- A parallel plate capacitor has a surface charge density of magnitude o = 0.00433 C/m² on each plate. A small sphere, charged to Q = 9.40 × 10-6 C and located between the plates, undergoes a displacement of magnitude d = 0.143 m. Refer to the figure, which is not drawn to scale. y +++++++ Using the symbols in the palette, not their numeric equivalents, enter an expression, in Cartesian unit-vector notation, for the electric field within the capacitor. If the displacement is from left to right, then how much work, in joules, is performed on the sphere by the electric field? At what speed, in meters per second, is the sphere moving when it completes the displacement if it starts from rest and its mass is 0.115 kg? Xarrow_forwardA uniform electric field 3.41E3 N/C is applied in a cubic box with each side being 2.23 m long. What is the energy stored by the electric field in the box (in J)?arrow_forwardA constant electric field of 20.0 N/C points along the positive x-direction. An electron, initially at rest, moves a distance of 0.500 m in this space. How fast is the electron moving after its 0.500 m journey?arrow_forward
- A small plastic ball with a mass of 6.65 10-3 kg and with a charge of +0.149 µC is suspended from an insulating thread and hangs between the plates of a capacitor (see the drawing). The ball is in equilibrium, with the thread making an angle of 30.0° with respect to the vertical. The area of each plate is 0.0138 m2. What is the magnitude of the charge on each plate? Carrow_forwardA positively charged particle of mass 50 grams and charge 10 µC is released from rest at the origin in the uniform electric field of 100 N/C directed along the +X-axis. Determine its speed at x = 10 cm position.arrow_forwardA small drop of water is suspended motionless in air by a uniform electric field that is directed upward and has a magnitude of 7420 N/C. The mass of the water drop is 4.78 × 10-9 kg. How many excess electrons or protons reside on the droparrow_forward
- The drawing shows an electron entering the lower left side of a parallel plate capacitor and exiting at the upper right side. The initial speed of the electron is 3.13 × 106 m/s. The capacitor is 2.00 cm long, and its plates are separated by 0.150 cm. Assume that the electric field between the plates is uniform everywhere and find its magnitude. 15.30 + A + 2.00 cm Number i + + + 0.150 cm Unitsarrow_forwardA particle of charge +7.3 µC is released from rest at the point x = 79 cm on an x axis. The particle begins to move due to the presence of a charge Q that remains fixed at the origin. What is the kinetic energy of the particle at the instant it has moved 40 cm if (a)Q=+38 µC and (b)Q--38 µC? (a) Number: (b) Number Units Unitsarrow_forwardA spherical capacitor is composed of two concentric conducting spheres, one of radius a and the other of radius c (c > a). In addition, between the two conductors there is a spherical shell of dielectric material (relative permittivity/relative dielectric constant ) with inner radius b (c > b > a) and outer radius c. The charge on the inner conductor is +Q. The charge on the outer conductor is -Q. (a) Make a sketch of the situation, indicating the relevant dimensions. (b) Determine the magnitude of the electric field E at radius r for a < r < b. (c) Determine the magnitude of the electric field E at radius r for b < r < c. (d) What is the (induced) surface charge density on the inner surface of the dielectric. (e) Sketch the radial component of the electric field versus r . (f) Sketch the electrostatic potential versus r . (g)Calculate the potential difference between the conductor at r = a and that at r = c. (h) What is the capacitance of this capacitor?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





