
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
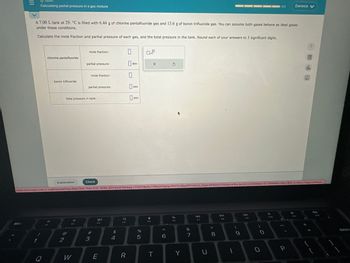
Transcribed Image Text:Calculating partial pressure in a gas mixture
esc
A 7.00 L tank at 29. °C is filled with 6.44 g of chlorine pentafluoride gas and 13.6 g of boron trifluoride gas. You can assume both gases behave as ideal gases
under these conditions.
Calculate the mole fraction and partial pressure of each gas, and the total pressure in the tank. Round each of your answers to 3 significant digits.
chlorine pentafluoride
boron trifluoride
R
Explanation
2
mole fraction:
W
partial pressure:
Total pressure in tank:
2
mole fraction:
partial pressure:
Check
#3
8.0
E
54
https://azinsight.adsrvr.org/track/clk?imp=fbec12b0-713d-4127-929d-a59782e61fbb&ag=r735012&sfe=1788cd47&sig=PCK7icABpePPZol9wVL E9gKn0Pi6FOTr7R3rMUmfWw.&crid=2zvfx50b&cf=5773664&fq=0&t=2&tds-www.chegg.com&rca
$
a
F4
0
R
atm
0
atm
atm
%
5
X
FS
T
Ś
< 6
s
F6
Y
&
7
F7
U
00
8
DIL
FB
1
(
9
DD
)
O
0/5 Danasia V
O
F10
.
P
Fad
d
da
delet
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- O A 10.0 L tank at 2.36 °C is filled with 10.5 g of sulfur tetrafluoride gas and 17.4 g of chlorine pentafluoride gas. You can assume both gases behave as ideal gases under these conditions. Calculate the mole fraction and partial pressure of each gas, and the total pressure in the tank. Round each of your answers to 3 significant digits. mole fraction: sulfur tetrafluoride partial pressure: atm mole fraction: chlorine pentafluoride partial pressure: atm Total pressure in tank: atm Explanation Check 021McCraw.lEdeation Al Dinhte Resened Torms of Uce Pri MacBook A - F6arrow_forwardPlease see imagearrow_forwardA 8.00 L tank at 18. °C is filled with 6.96 g of dinitrogen difluoride gas and 11.8 g of chlorine pentafluoride gas. You can assume both gases behave as ideal gases under these conditions. Calculate the mole fraction and partial pressure of each gas, and the total pressure in the tank. Round each of your answers to 3 significant digits. mole fraction: Ox10 dinitrogen difluoride partial pressure: ? atm mole fraction: chlorine pentafluoride partial pressure: atm Total pressure in tank: atmarrow_forward
- Some N, gas is mixed with some 0, gas, and the sketch below shows a representative sample of the mixture. The total pressure of the mixture is measured, and found to be 0,120 kPa. key carbon hydrogen nitrogen sulfur охудеn chlorine Calculate the mole fraction and partial pressure of each gas in this mixture. Round your answers to 3 significant digits. You may assume each gas behaves as an ideal gas. gas mole fraction partial pressure N2 | kPa O2 kPaarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided resonance structures, draw the curved electron- pushing arrows to show the interconversion between resonance hybrid contributors. Be sure to account for all bond- breaking and bond-making steps. :S: •S: O Select to Add Arrows > KO KOarrow_forwardA 9.00 L tank at 4.62 °C is filled with 14.5 g of sulfur hexafluoride gas and 16.1 g of dinitrogen difluoride gas. You can assume both gases behave as ideal gases under these conditions. Calculate the mole fraction and partial pressure of each gas, and the total pressure in the tank. Be sure your answers have the correct number of significant digits. sulfur hexafluoride dinitrogen difluoride mole fraction: partial pressure: mole fraction: partial pressure: Total pressure in tank: 0 0 atm atm atm x10 olo 18 Ararrow_forward
- A 7.00 L tank at 27.5 °C is filled with 2.64 g of chlorine pentafluoride gas and 2.36 g of dinitrogen monoxide gas. You can assume both gases behave as ideal gases under these conditions. Calculate the mole fraction of each gas. Round each of your answers to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardA 9.00 L tank at 1.5 °C is filled with 3.22 g of carbon monoxide gas and 16.7 g of chlorine pentafluoride gas. You can assume both gases behave as ideal gases under these conditions. Calculate the mole fraction and partial pressure of each gas, and the total pressure in the tank. Be sure your answers have the correct number of significant digits. carbon monoxide chlorine pentafluoride mole fraction: partial pressure: mole fraction: partial pressure: Total pressure in tank: atm atm atm x10 × Ś 0:39 0 Earrow_forwardA 7.00 L tank at 25.5 °C is filled with 9.44 g of sulfur hexafluoride gas and 4.78 g of sulfur tetrafluoride gas. You can assume both gases behave as ideal gases under these conditions. Calculate the mole fraction and partial pressure of each gas, and the total pressure in the tank. Round each of your answers to 3 significant digits. mole fraction: ab sulfur hexafluoride partial pressure: 5 ? atm mole fraction: sulfur tetrafluoride partial pressure: | atm n 11- 5 A... Total pressure in tank: O atm Explanation Check 2021 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of UseI Privacy Center Accessibility etv 25 424 14. $44 F10 80 11 F6 23 F4 esc F2 F3 1 & @ %23 $ 7 8. 2 T Y U W Karrow_forward
- A 9.00 L tank at 1.27 °C is filled with 15.1 g of sulfur tetrafluoride gas and 3.08 g of carbon monoxide gas. You can assume both gases behave as ideal gases under these conditions. Calculate the mole fraction and partial pressure of each gas, and the total pressure in the tank. Round each of your answers to 3 significant digits. sulfur tetrafluoride carbon monoxide mole fraction: partial pressure: mole fraction: partial pressure: Total pressure in tank: 0 0 atm atm atm Ix10 Xarrow_forwardA 10.0 L tank at 1.29 °C is filled with 3.89 g of carbon monoxide gas and 4.35 g of dinitrogen monoxide gas. You can assume both gases behave as ideal gases under these conditions. Calculate the mole fraction and partial pressure of each gas, and the total pressure in the tank. Round each of your answers to 3 significant digits. carbon monoxide dinitrogen monoxide mole fraction: partial pressure: mole fraction: partial pressure: Total pressure in tank: atm a atm Da atm ☐ x10 Xarrow_forwardA 8.00 L tank at 24.8 °C is filled with 4.16 g of chlorine pentafluoride gas and 11.6 g of sulfur hexafluoride gas. You can assume both gases behave as ideal gases under these conditions. Calculate the mole fraction and partial pressure of each gas, and the total pressure in the tank. Round each of your answers to 3 significant digits. chlorine pentafluoride sulfur hexafluoride mole fraction: partial pressure: mole fraction: partial pressure: Total pressure in tank: 0 0- 0 atm 0- atm Xarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY