
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
A 6.75 g wire of length L 15.0 cm is suspended by a pair of flexible leads in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.440 T (Fig. 28-30). What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (left or right) of the current required to remove the tension in the supporting leads?
Please explain the solution step by step
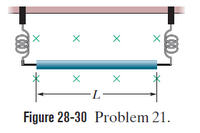
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 28-30 Problem 21.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Current I = 2 A is into the page. Point P is 0.2 cm away from the wire. I X At point P, the magnitude and the direction of the magnetic field is: A 0.2 mT; up. B) 4 mT; to the left. C) 4 mT; to the right. D 0.2 mT; down. E 2 mT; into the page. F 2 mT; out of the page. G 4 mT; down. H 4 mT; up.arrow_forward11 In Fig. 29-42, two long straight wires are perpendicular to the page and = 0.75 cm. separated by distance d₁ Wire 1 carries 6.5 A into the page. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (into or out of the page) of the current in wire 2 if the net magnetic field due to the two currents is zero at point P lo- cated at distance d₂ = 1.50 cm from Figure 29-42 Problem 11. wire 2? ata of bot Wire 10 Wire 20- P has mA ne me ma 90 25 ry tharrow_forwardTwo long straight wires are parallel and 12 cm apart. They are to carry equal currents such that the magnetic field at a point halfway between them has magnitude 430 μT. (a) Should the currents be in the same or opposite directions? (b) How much current is needed? (a) opposite (b) Number i 6.5 Units A ✰arrow_forward
- If the potential difference over a length of copper wire is 1.5 V, how long must the copper wire be so that when placed in the magnetic field of the Earth at the equator, the copper wire will levitate? In which direction (North, South, East, or West) must the current flow in the wire in order to pull off this trick? Can this be done at the North or South Pole?arrow_forwardA uniform magnetic field points vertically upward; its magnitude is 0.520 T. An electron with kinetic energy 6.50 × 10−18 J is moving horizontally eastward in this field. What is the magnetic force acting on it? Answer in units of "N north"arrow_forwardA long, straight wire carries a current. There is a uniform magnetic field directed downward (not due to the wire) and the force exerted on the wire is directed to the left. In what direction is the current?arrow_forward
- Chapter 28, Problem 001 A proton traveling at 23.8° with respect to the direction of a magnetic field of strength 1.98 mT experiences a magnetic force of 9.59 × 10-¹7 N. Calculate (a) the proton's speed and (b) its kinetic energy in electron- volts. Chapter 28, Problem 009 In the figure, an electron accelerated from rest through potential difference V₁=1.06 kV enters the gap between two parallel plates having separation d = 24.5 mm and potential difference V₂= 99.1 V. The lower plate is at the lower potential. Neglect fringing and assume that the electron's velocity vector is perpendicular to the electric field vector between the plates. In unit-vector notation, what uniform magnetic field allows the electron to travel in a straight line in the gap? [₁}v₂arrow_forwardA proton that has a speed equal to 9.00105 m/s enters a region with a uniform magnetic field that has a magnitude of 0.730T and points into the page, as shown in the figure below. The proton enters the region at an angle θ= 60°. Find the exit angle φ and the distanced d.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON