
Concept explainers
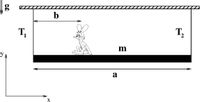
A 4.2‑kg brown hare walks on a horizontal beam (the beam's mass m = 2.8 kg and length a = 2.4 m). The beam is suspended with two ropes attached to the ends of the beam. What should be the distance between the hare and the left end of the beam so that the tension in the left rope is three times as big as the tension in the right rope?
1. The distance from the left end, b =
If the hare is at the distance found in the previous question, calculate the tension in each rope.
2. The tension in the left rope, T1 =
3. The tension in the right rope, T2 =
------------------------------------------------------------------
A bike wheel has a radius of R = 0.62 m and a mass of m = 2.6 kg spins at 270 rpm. What is the angular momentum of the wheel? Assume that the wheel has a shape of a ring.
The angular momentum of the wheel, L ?
A typical bowling ball might have a mass of 7 kg and a radius of 12 cm. How fast the ball should spin to have the same angular momentum as the wheel from the previous question?
The angular speed of the ball, ω ?
Which of the above objects is harder to stop?
How strong torque is needed to completely stop the wheel in 2.5 sec time?
The torque needed to stop the wheel, τ ?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- 1) A stepladder is constructed as shown in the figure. The total mass of the ladder is 10 kg (each side has a mass of 5 kg). There is no friction between the ladder and the floor. a. What is the tension in the chain? b. What is the magnitude of the force exerted by the hinge on one side of the ladder? Hinge- Chain CG 0.50m Uniform board (CG at center) 1.10 m 1.30marrow_forward3) Find the forces developed in beams FE, CE, and CD. State whether they're in tension or compression. A 20 № 20cm f B 4444 20cm 20cm 20cm 100 N 3 9 5 20cm с E 20cm 55Narrow_forwardA) Determine the force in the spring with unstretched length 3 inches and a spring constant of 240 lb/ft. B) Determine the forces at A, B, C, D, and F. A 6 in. B 6 in. D 6 in. E G 8 in. 8 in.arrow_forward
- 4.8 m 2. The frame shown below is loaded with an unknown horizontal force, P. At point E, the surface exerts a force of 130 lb. on the roller. a) Draw and label all the reactions and forces acting on the frame and on the individual components, using the diagrams provided on the back of this handout. b) Determine the magnitude of the force, P, required for the frame to be in equilibrium. c) Determine the x- and y- components of the force acting at point C on member CDE, and specify the directions (→, +, t. 1). Note: For each calculation, state which diagram number (1, 2, 3, 4) you are using. Ans: P = 80 lb, C = 100 lb , C, = 75 lb 1 (by the way, FBC = 125 lb (T)) 4 in. 8 in. C 3 in. В 6 in. 1 3arrow_forwardQuestion 1 The generator shown is being lifted by a (91 0001)9 G2(250 lb) crane, and the moving team needs to know the center of gravity so that the generator does not tip during transport. The weights of multiple components of the generator (91 007)'ɔ are shown. a) Find the distance from A to the center of gravity, x. x = 4. 28ft b) Determine the support reactions at YE point A and point B. A, = 830 Ib, B, = 620 Ibarrow_forwardAs indicated in the diagram below, a beam is loaded. kN is the equivalent of the reaction R2. 20 kN 40 kN 2 m W= 20 kN/m 2 m 4 m R1 R2arrow_forward
- 1. A tripod whose legs are gach 4 meters long supports a load of 1000 kg. The feet of the tripod are vertices of a horizontal equilateral triangle whose side is 3.5 meters. Determine the load of each leg. 1000 kg 1.75 cos 30' = AE R. AE = 2.02 AE sine= AD 2.02 e= sin 4 /1.75 8 = 30.33 RA = R =Rc =R 1.75 1.75 1.75arrow_forward3.] The uniform boom shown below weighs 3000 N. It is supported by the horizontal guy wire and by the hinged support at point A. What are the forces on the boom due to the wire and due to the support at A? Does the force at A act along the boom? Answers Wire Force = 2000 N Force of A = 2828.43 N 2000 N 45°arrow_forwardAs shown below, a sign weighing 121 N is hanging (via a wire) from a uniform 256 N beam of length L. Additionally, the beam is attached to a cable that makes an angle 0 (0 = 51°) with the beam. 0.9 L 0.7 L 501 OAK 8 X Determine the tension in the cable and the magnitude & direction of the force the hinge (the orange circle) exerts on the beam. Cable tension = Hinge force = Direction of hinge force = in quadrant - Choose quadrant - 21 CHER ° relative to the horizontal MacBook Pro kg ro from n. The o the ce tvarrow_forward
- A sandwich board advertising sign is constructed as shown in the figure below. Hinge- Chain G2001 Brooks/Cole Thomson Learning CG CG 0.50 m Uniform board (CG at center) 1.10 m 1.30m The sign's mass is 5.30 kg. (a) Calculate the tension in newtons in the chain assuming no friction between the legs and the sidewalk. XN (b) What force is exerted in newtons by each side on the hinge? X Narrow_forward1.2 m 1.4 m Im 30° 2 m A) Draw a Free Body Diagram of the 75 kg hatch. Make an assumption to keep the problem statically determinate. B) Compute the tension in the rope. C) Compute the reactions at A and B.arrow_forward
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





