
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A 30.0 kg door is 1.00 m wide, as shown in the diagram. A force of 85.0 N is applied is applied 0.750 m from the hinges at a 60° angle from the door. What is the
a. 5.52 rad/s2
b.1.84 rad/s2
c.6.38 rad/s2
d.2.60 rad/s2
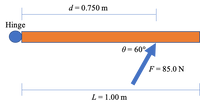
Transcribed Image Text:d = 0.750 m
Hinge
0 = 60%
F = 85.0 N
L = 1.00 m
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
from newtons second law of rotation we have
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An object starts from a rest and undergoes a circular motion for a period of 4.41s until it turns at the rate of 246/s. Calculate the angular acceleration of the object in rad/s.arrow_forwardThe spool has a weight of 30 lb and a radius of gyration ko 0.45 ft. A cord is wrapped around its inner hub and the end subjected to a horizontal force P = 5 lb. Determine the spool's angular velocity in 4 s starting from rest. Assume the spool rolls without slipping. 0.9 ft 0.3 ft 0 P = 5 lbarrow_forwardA hollow, spherical shell with mass9.7 kg rolls without slipping down a 61.7° slope. Find the acceleration (m/s?). *1=2/3MR2 9.8 = 9.8 m/s?arrow_forward
- A bar on a hinge starts from rest and rotates with an angular acceleration a = 15 + 7t, where a is in rad/s? and t is in seconds. Determine the angle in radians through which the bar turns in the first 3.93 s. radarrow_forwardAn optical disk drive in your computer is spinning at 10,000 rpm (1045 rad/s). It decelerates to a rest in 0.42 s. a. Find the rotational inertia of the disk given that its mass is 17 grams. b. Find the magnitude of the torque required to decelerate the disk.arrow_forward20. The 57.2cm diameter disk rotates counterclockwise on an axle through its center. F1=42.6N, F2=70.8N, F3=70.8N, F4=42.6N, and d=5.34cm. What is the net torque about the axle? Let the counterclockwise direction be positive. F31 +F₂ F d 45⁰arrow_forward
- A 0.24 m radius grinding wheel takes 5.8 s to speed up from 2.6 rad/s to 5.9 rad/s. What is the wheel’s average angular acceleration?arrow_forwardThe wheel and axle have forces applies tangentially as shown in the figure. There is also a frictional torque of 0.02 Nxm on the wheel, once the wheel starts moving. The radius of the axel is 20 cm and the radius of the wheelis 60 cm and F1 = 2.4 N, F2 = 3.0 N and F3 = 1.2 N. a. Calculate the net torque on the moving wheel due to the applied forces F1 F2 and F3. b. What direction of rotation would the applied forces cause? Explain. c. What is the direction of frictional torque? Explain. d. Calculate the net torque on the wheel and axle.arrow_forwardA wheel with thin spokes can be considered a hoop, where I=mr. A bicycle wheel has a mass of .35 kg with a radius of .30 m and is spinning at 25 rad/s in the positive direction. Brakes apply a force of friction of 15 N at the rim. We will consider the rim of the wheel to be on the very outside of the wheel. (Remember significant digits.) a.) What is the direction of the torque provided by the brakes (positive or negative) b.) What is the magnitude of the torque applied by the brakes? Nm c.) What is the moment of angular inertia of the wheel? kgm2 d.) What is the angular acceleration of the wheel? rad/s? e.) How far does the wheel travel (in radians) before coming to rest? rad f.) How long does this take? s g.) With faulty brakes, only 8 N can be applied. How long would it take to stop the wheel under these conditions? s MacBook Proarrow_forward
- A 0.37 m radius grinding wheel takes 6.1 s to speed up from 2.9 rad/s to 6.8 rad/s. What is the wheel's average angular acceleration?arrow_forwardThe figure below is for a 50 kg-m2 object. o(radis) 60.0 40.0 20.0 -20.0 2.0 4.0 t(s) Find the net torque. Find the angular displacement at t = 2.25 s.arrow_forwardA circular disk with a radius of 0.37 m is subject to 2 tangentially applied forces. The disc is fixed such that it will rotate about its center. Both forces produce a torque in the same direction. F1 = 4.7 N applied at the outer edge of the disc. F2 = 3.2 N applied at a distance of 0.3 from the center of the disc. What is the net torque on the disc?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON