
Organic Chemistry
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305580350
Author: William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
None
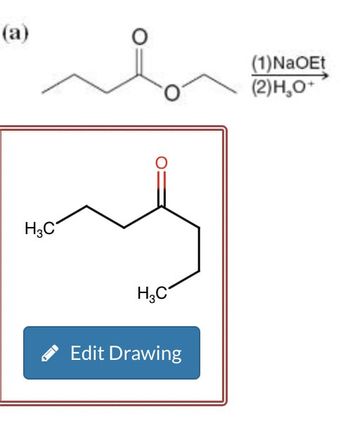
Transcribed Image Text:(a)
(1)NaOEt
(2)H₂O+
H3C
H3C
Edit Drawing
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Name the corresponding salts of organic acids: (HCOO)2Ca; CH3CH2COOK.arrow_forward(a) Predict the products of the following acid-base reactions using curved-arrow mechanisms to indicate electron flow. (b) Indicate the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base of each reaction. (c) Indicate whether the reactants or products are favored at equilibrium a) CH,COOH CH3O b) CH,CH,OH H2Narrow_forwardCH3NH2 is a (a)Arrhenius acid. (b)Arrhenius base. (c)Bronsted-Lowry acid. (c)Bronsted-Lowry base. (e)Louis base.arrow_forward
- The amount of tartaric acid is responsible for the tartness of wine and controls the acidity of the wine. Tartaric acid also plays a very significant role in the overall taste, feel and color of a wine. Tartaric acid is a diprotic organic acid The chemical formula for tartaric acid is C4H6O6 and its structural formula is HO2CCH(OH)CH(OH)CO2H. A 50.00 mL sample of a white dinner wine required 21.48 mL of 0.03776 M NaOH to achieve a faint pink color. Express the acidity of the wine in terms of grams of tartaric acid, H2C4H4O6 (M. M. = 150.10) per 100 mL of wine. Assume that the two acidic hydrogens are titrated at the end point. MM H2C4H4O6 = 150.10 MM NaOH = 40.00 Below is the balanced chemical equation for this titration.arrow_forwardEnter the balanced equation for the ionization of the following carboxylic acid in water. Express your answer as a chemical equation without phases using the formula CH3,CH(CH3),COOH for the carboxylic acid.arrow_forward2-11 2.19] A solution has an H+ concentration of 10-5 M. (a) What is the pH of this solution? (b) What is the pOH (Assume that the temperature of the solution is 25°C.) Answer: (a) 5 (b) 9 BMarrow_forward
- Equation 1 : HA + H2O -> A- + H3O+ weak acid conjugate base (a) Using Equation 1 as a guide, write an equation for the reaction of acetic acid (CH 3COOH) with water.(b) Identify the conjugate base of acetic acid in the reaction equation.arrow_forwardFor the following acid-base reaction, (1) predict the products, showing both reactants and products complete Lewis structures and arrows showing electron flow; (2) label each structure with the lowing: Bronsted acid, Bronsted base, conjugate acid, conjugate base; (3) give a brief definition of a ronsted acid and Bronsted base; (4) predict the direction of the equilibrium and justify your answer. HC0OH + CH3 Nta PRん106Y pkb = 3.36arrow_forward1) 9-BBN, THE 2) NaOH, H20arrow_forward
- OH HzCrOu 4 Chromic acidarrow_forwardPhenylamine is an aromatic amine that is used in the manufacture of dyes. When absorbed through the skin itcauses the Fe+2 in hemoglobin to become oxidized into Fe+3, resulting in the formation of methemoglobin whichcannot bind to or transport oxygen. Phenylamine is soluble in water and acts as a weak base.C6H5NH2 (aq) + H2O (ℓ) ⇋ C6H5NH3+ (aq) + OH- (aq)a. When you measure the concentrations of the ionized substances you find them to be:[C6H5NH2] = 0.234 mol/L [C6H5NH3+] = 2.8 x 10-5 mol/L [OH-]= 2.8 x 10-5 mol/LIf the Kb is 4.27 x 10-10, is the reaction at equilibrium? If not, which direction does it need to move (rightor left) to reach equilibrium? Explain. b. At equilibrium the concentrations of the ionized substances are:[C6H5NH2] = 0.0537 mol/L [C6H5NH3+] = 4.79 x 10-6 mol/L [OH-]= 4.79 x 10-6 mol/LIf this reaction is taking place in a 2.0L container, and 1.5 moles of phenylamine were added to thereaction, what will the new concentrations of the three ionic species be when…arrow_forward(b) Calculate the pH of 0.0005 mol dm-3 ethanois acid when its pKa = 4.75 CH;COOH() -> CH;COO (a H(a + Ka = pH =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305580350
Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. Foote
Publisher:Cengage Learning