
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:### Problem Statement
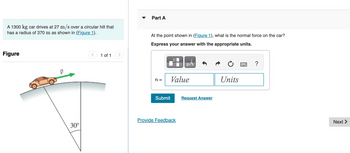
A 1300 kg car drives at 27 m/s over a circular hill that has a radius of 370 m as shown in Figure 1.
### Figure Explanation
**Figure 1:** The diagram illustrates a car driving over a circular hill. The hill is depicted in profile, showing its curved surface with the car moving along the top. An arrow labeled \( \vec{v} \) indicates the direction of the car's velocity tangent to the surface of the hill. Below the hill, a radial line extends from the center of the circle to the point on the surface directly beneath the car. This line is labeled with an angle of 30°.
### Question
**Part A:** At the point shown in Figure 1, what is the normal force on the car?
**Instructions:** Express your answer with the appropriate units.
- Input fields are provided for the value and units of the normal force, denoted by \( n = \).
- Options available: Submit, Request Answer, Provide Feedback.
This setup is part of a physics problem aimed at understanding forces involved in circular motion. The task involves calculating the normal force exerted on the car as it travels over the hill.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 25 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Juan pushes a lawn mower with a force of 75 N holding the handle in such a way that it makes an angle of 60.0 ° with the horizontal. Remember to make the diagram and identify the vectors. 1. What are the horizontal and vertical components of the force? 2. The handle is lowered so that it makes an angle of 30.0o with the horizontal. What are the horizontal and vertical components of the force?arrow_forwardMust provide correct answer.arrow_forwardplease circle answersarrow_forward
- The grid runs from -5 to 5 on both axes. Drawn on this grid are four vectors, labeled A⃗ A→ through D⃗ D→. This problem will ask you various questions about these vectors. All answers should be in decimal notation, unless otherwise specified. A. What is the xcomponent of A→? B.What is the y component of A⃗ ? C.What is the y component of B⃗ ? D.What is the x component of C⃗ ? E. In ordered pair notation, write down the components of vector B⃗ F. In ordered pair notation, write down the components of vector D G.What is true about B⃗ and D⃗ ? They have different components and are not the same vectors. They have the same components but are not the same vectors. They are the same vectors.arrow_forwardDisk - 0.20 m A coin C of mass 0.050 kg is placed on a horizontal disk at a distance of 0.20 m from the center, as shown above. The disk rotates at a constant rate in the clockwise direction as seen from above. The coin does not slip, and the time it takes for the coin to make a complete revolution is 1.2 s. a. The figure below shows the disk and coin as viewed from above. Draw and label vectors on the figure below to show the instantaneous acceleration and linear velocity vectors for the coin when it is at the position shown. b. Determine the speed of the coin. c. The rate of rotation of the disk is gradually increased. The coefficient of static friction between the coin and the disk is 0.50. Determine the speed of the coin when it just begins to slip. d. If the experiment in part (c) were repeated with a second, identical coin glued to the top of the first coin, how would this affect the answer to part (c) ? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardPart E Find x-component of F = (20.0 N, 36.9° counterclockwise from the positive y-axis). Express your answer with the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) Fx = Submit Part F Fy= μà Submit Value Find y-component of F = (20.0 N, 36.9° counterclockwise from the positive y-axis). Express your answer with the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) µÅ Units Value ? Units ?arrow_forward
- Stacked blocks and pulley Mass Ma lies on top of mass Mb, as shown. Assume Mb > Ma. The two blocks are pulled from rest by a massless rope passing over a pulley. The pulley is accelerated at rate A. Block Mb slides on the table without friction, but there is a constant friction force f between Ma and Mb due to their relative motion. Find the tension in the rope.arrow_forward1. The block in the figure to the right remains motionless against the wall because of an applied force and the force of static friction between the block and the wall. The coefficient of static friction is μs. Which equation correctly describes the magnitude of the frictional force between the wall and the block?a. Ff=(mgcosθ)μsb. Ff= (Fasinθ–mg) μsc. Ff= (Facosθ – mg) μsd. Ff= Facosθμse. Ff= (Facosθ + mg) μsarrow_forwardhe FBD of the block should have looked like this. 1. A contestant in a winter sporting event pushes a block of ice of mass m across a frozen lake as shown in the figure. The coefficient of static friction between the block and ice is μs, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is μk. θ is the angle the force makes with the x-axis. In this part, we are going to set-up Newton's second Law equations for the cases(1) when the ice block just starts moving, and(2) when it is accelerating to the right with an acceleration a. All answers are symbolic. ALL ANSWERS ARE CASE-SENSITIVE. Subpart 1: Newton's Second Law along the y-axis (i) Write Newton's Second Law along the y-axis by adding all forces in the y-direction taking into account their signs (forces pointing upwards are positive and downward are negative) in terms of the normal force N, weight mg, F and θ. In both scenarios, there is no acceleration along the y-direction, therefore, ay=0.…arrow_forward
- M Support Cable 37° M As shown in the diagram above, a rigid rod of mass M is hinged at its left end against a wall. A block of mass M hangs on the right edge of the rod. A support cable attached to the right end of the rod forms an angle of 37 degrees with horizontal. The tension in the string is 1,057 N. Calculate the mass M of the rod and the block. Express your answer in kilograms and round to the nearest tenth (1 decimal).arrow_forwardPls help ASAP. Pls show all work and calculations.arrow_forwardNiloarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON