
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781133939146
Author: Katz, Debora M.
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
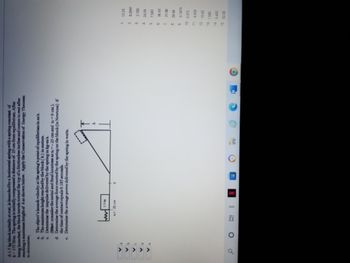
Transcribed Image Text:A 1.5 kg block initially at rest is launched by a horizontal spring with a spring constant of \( k = 175 \, \text{N/m} \). The spring is initially compressed a distance of 25 cm from equilibrium. After being launched, the block travels toward the top of a frictionless incline and comes to rest after reaching a maximum height \( h \) as shown below. Apply the Conservation of Energy Theorem to determine:
a. The object's launch velocity at the spring's point of equilibrium in m/s.
b. The maximum height reached by the block (\( h \)) in meters.
c. Determine the impulse delivered by the spring in kg-m/s.
(Hint: consider the initial and final locations as \( x_i = -25 \, \text{cm} \) and \( x_f = 0 \, \text{cm} \)).
d. Determine the average force exerted by the spring on the block (in Newtons) if the time of contact equals 0.185 seconds.
e. Determine the average power delivered by the spring in watts.
**Diagram Explanation:**
- The diagram features a spring attached to a block with a mass of 1.5 kg. The block is launched from a horizontal surface by the compressed spring.
- The spring's equilibrium position is marked, and the compression distance is noted as \( x_i = -25 \, \text{cm} \).
- The block moves up a frictionless incline and reaches the maximum height \( h \).
**List of Numerical Options:**
1. 12.23
2. 0.2547
3. 2.700
4. 24.59
5. 7.583
6. 36.43
7. 21.89
8. 29.58
9. 0.1870
10. 0.372
11. 4.050
12. 10.43
13. 1.580
14. 5.400
15. 32.58
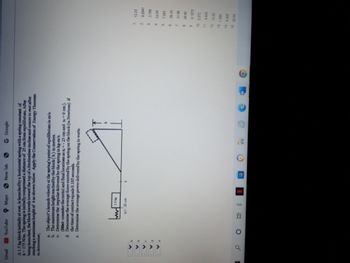
Transcribed Image Text:**Physics Problem: Spring Launch**
A 1.5 kg block initially at rest is launched by a horizontal spring with a spring constant of \( k = 175 \, \text{N/m} \). The spring is initially compressed a distance of 25 cm from equilibrium. After being launched, the block travels toward the top of a frictionless incline and comes to rest after reaching a maximum height \( h \) as shown. Apply the Conservation of Energy Theorem to determine:
a. The object's launch velocity at the spring's point of equilibrium in m/s.
b. The maximum height reached by the block (\( h \)) in meters.
c. Determine the impulse delivered by the spring in kg-m/s.
(Hint: consider the initial and final locations as \( x = -25 \, \text{cm} \) and \( x = 0 \, \text{cm} \) ).
d. Determine the average force exerted by the spring on the block (in Newtons) if the time of contact equals 0.185 seconds.
e. Determine the average power delivered by the spring in watts.
**Diagram Explanation:**
- The diagram shows a spring with a mass of 1.5 kg attached at the end. The spring is initially compressed by 25 cm.
- There is a frictionless incline, and the block ascends this incline to reach a maximum height \( h \).
**Multiple Choice Answers:**
1. 12.23
2. 0.2547
3. 2.700
4. 24.59
5. 7.588
6. 36.43
7. 21.80
8. 26.58
9. 0.1870
10. 0.372
11. 4.050
12. 10.43
13. 1.580
14. 5.490
15. 32.58
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A block on a frictionless, horizontal surface is attached to two springs as shown in Figure P8.28. The block is displaced, compressing one spring and stretching the other. a. Find an expression for the change in the blocksprings systems potential energy in terms of the parameters given in the figure. b. Is it possible to displace the block in such a way that the systems potential energy does not change? FIGURE P8.28arrow_forwardA horizontal spring attached to a wall has a force constant of k = 850 N/m. A block of mass m = 1.00 kg is attached to the spring and rests on a frictionless, horizontal surface as in Figure P8.35. (a) The block is pulled to a position xi = 6.00 cm from equilibrium and released. Find the elastic potential energy stored in the spring when the block is 6.00 cm from equilibrium and when the block passes through equilibrium. (b) Find the speed of the block as it passes through the equilibrium point. (c) What is the speed of the block when it is at a position xi/2 = 3.00 cm? (d) Why isnt the answer to part (c) half the answer to part (b)? Figure P8.35arrow_forwardA block is placed on top of a vertical spring, and the spring compresses. Figure P8.24 depicts a moment in time when the spring is compressed by an amount h. a. To calculate the change in the gravitational and elastic potential energies, what must be included in the system? b. Find an expression for the change in the systems potential energy in terms of the parameters shown in Figure P8.24. c. If m = 0.865 kg and k = 125 N/m, find the change in the systems potential energy when the blocks displacement is h = 0.0650 m, relative to its initial position. FIGURE P8.24arrow_forward
- A particle of mass m = 1.18 kg is attached between two identical springs on a frictionless, horizontal tabletop. Both springs have spring constant k and are initially unstressed, and the particle is at x = 0. (a) The particle is pulled a distance x along a direction perpendicular to the initial configuration of the springs as shown in Figure P7.50. Show that the force exerted by the springs on the particle is F=2kx(1Lx2+L2)i (b) Show that the potential energy of the system is U(x)=kx2+2kL(Lx2+L2) (c) Make a plot of U(x) versus x and identify all equilibrium points. Assume L = 1.20 m and k = 40.0 N/m. (d) If the panicle is pulled 0.500 m to the right and then released, what is its speed when it reaches x = 0? Figure P7.50arrow_forwardAs a simple pendulum swings back and forth, the forces acting on the suspended object are the force of gravity, the tension in the supporting cord, and air resistance, (a) Which of these forces, if any, does no work on the pendulum? (b) Which of these forces does negative work at all times during the pendulums motion? (c) Describe the work done by the force of gravity while the pendulum is swinging.arrow_forwardA block of mass m = 5.00 kg is released from point and slides on the frictionless track shown in Figure P8.3. Determine (a) the blocks speed at points and and (b) the net work done by the gravitational force on the block as it moves from point to point . Figure P8.3arrow_forward
- A particle moves in one dimension under the action of a conservative force. The potential energy of the system is given by the graph in Figure P8.55. Suppose the particle is given a total energy E, which is shown as a horizontal line on the graph. a. Sketch bar charts of the kinetic and potential energies at points x = 0, x = x1, and x = x2. b. At which location is the particle moving the fastest? c. What can be said about the speed of the particle at x = x3? FIGURE P8.55arrow_forwardA small 0.65-kg box is launched from rest by a horizontal spring as shown in Figure P9.50. The block slides on a track down a hill and comes to rest at a distance d from the base of the hill. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the box and the track is 0.35 along the entire track. The spring has a spring constant of 34.5 N/m, and is compressed 30.0 cm with the box attached. The block remains on the track at all times. a. What would you include in the system? Explain your choice. b. Calculate d. c. Compare your answer with your answer to Problem 50 if you did that problem.arrow_forwardRubber tends to be nonlinear as an elastic material. Suppose a particular rubber band exerts a restoring force given by Fx(x) = Ax Bx2, where the empirical constants are A = 14 N/m and B = 3.3 N/m2 so that Fx is in newtons when x is in meters. Calculate the change in elastic potential energy of the rubber band when an external force stretches it from x = 0 to x = 0.20 m.arrow_forward
- A certain uniform spring has spring constant k. Now the spring is cut in half. What is the relationship between k and the spring constant k of each resulting smaller spring? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardA light spring with spring constant 1 200 N/m is hung from an elevated support. From its lower end hangs a second light spring, which has spring constant 1 800 N/m. An object of mass 1.50 kg is hung at rest from the lower end of the second spring. (a) Find the total extension distance of the pair of springs. (b) Find the effective spring constant of the pair of springs as a system. We describe these springs as in series.arrow_forwardThe Flybar high-tech pogo stick is advertised as being capable of launching jumpers up to 6 ft. The ad says that the minimum weight of a jumper is 120 lb and the maximum weight is 250 lb. It also says that the pogo stick uses a patented system of elastometric rubber springs that provides up to 1200 lbs of thrust, something common helical spring sticks simply cannot achieve (rubber has 10 times the energy storing capability of steel). a. Use Figure P8.32 to estimate the maximum compression of the pogo sticks spring. Include the uncertainty in your estimate. b. What is the effective spring constant of the elastometric rubber springs? Comment on the claim that rubber has 10 times the energy-storing capability of steel. c. Check the ads claim that the maximum height a jumper can achieve is 6 ft.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning