
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
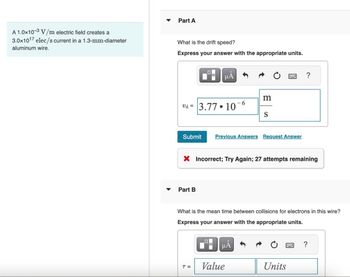
Transcribed Image Text:A 1.0x10-3 V/m electric field creates a
3.0x1017 elec/s current in a 1.3-mm-diameter
aluminum wire.
Part A
What is the drift speed?
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
O
ΜΑ
Vd=3.77 106
m
S
Submit Previous Answers Request Answer
× Incorrect; Try Again; 27 attempts remaining
Part B
What is the mean time between collisions for electrons in this wire?
Express your answer with the appropriate units.
ΜΑ
?
T =
Value
Units
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How many electrons strike the screen each second? 2.94x1014 electrons The electron beam inside a television picture tube is 0.300 mm in diameter and carries a current of 47.0 µA. This electron beam impinges on the inside of the picture tube screen. Submit Previous Answers v Correct Part B What is the current density in the electron beam? Eνα ΑΣφ A/m² Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 3 attempts remaining Review your calculations and make sure you round to 3 significant figures in the last step. Part C The electrons move with a velocity of 3.90 x107 m/s. What electric field strength is needed to accelerate electrons from rest to this velocity in a distance of 5.80 mm ? ? N/C Submit Request Answer Part D Each electron transfers its kinetic energy to the picture tube screen upon impact. What is the power delivered to the screen by the electron beam? να ΛΣφ. ? 0.2734 Submit Previous Answers Request Answer X Incorrect; Try Again; 5 attempts remainingarrow_forwardI need help with both parts, part A and Part Barrow_forwardA 50-A current is running through a cylindrical wire that has a cross-sectional area of 4.0 mm2. The drift velocity of the conduction electrons in the wire is 0.85 mm/s. What is the numebr density of the conduction electrons in the wire? a. 9.2 x 1028 electrons/m3 b. 1.4 x 1029 electrons/m3 c. 3.2 x 1030 electrons/m3 d. 4.6 x 1028 electrons/m3 e. 5.7 x 1029 electrons/m3arrow_forward
- An electrical conductor designed to carry large currents has a circular cross section 2.40 mm in diameter and is 14.8 m long. The resistance between its ends is 0.107 2 Part A What is the resistivity of the material? ? p= Submit Request Answer Part B If the electric field magnitude in the conductor is 1.29 V/m. what is the total current? ? I = Part C If the material has 8,5 x 1025 free electrons per cubic meter, find the average drift speed under the conditions of part B. VO AE m/s Submit Reguest Answtarrow_forwardCurrent and Resistance Problem 18: Consider two wires made of different materials. Wire A has a conductivity of 1.9 × 107 Ω-1m-1, and wire B has a conductivity of 8.5 × 107 Ω-1m-1. Part (a) Wire A has a circular cross-section with radius 2.74 mm. If there is an electric field of 0.059 V/m inside it, how much current, in amperes, is flowing through it? Part (b) Wire B has a square 2.74 mm × 2.74 mm cross-section. If wire B has the same electric field as Wire A did in part (a), what current, in amperes, would be passing through it?arrow_forwardA 0.870-mm-diameter silver wire carries a 30.0 mA current. 身 amView?assignment ProblemID=173522443&attemptNo=2 Part A What is the electric field in the wire? Express your answer with the appropriate units. E = Submit Part B F Ud= μA Value Request Answer What is the electron drift speed in the wire? Express your answer with the appropriate units. μA Value Units Submit Request Answer Units ? ?arrow_forward
- Solve it correctly please. I will rate accordingly.arrow_forwardA ΔV = 2.3 V battery loses E = 5.5 J of energy each day (t = 24 hrs) powering a cell phone. a) Input an expression for the average current, I, supplied to the phone.arrow_forwarde. An electric hot plate has a power output of 1.34 kW when connected to a 94.63 V source. What is the current (in Amperes) being drawn by the hot plate? Add your answerarrow_forward
- The mean time between collisions in iron is 4.8x10-15 s. ▼ Part A What electron current is driven through a 1.4-mm-diameter iron wire by a 0.070 V/m electric field? Express your answer as a number of electrons per second. 17 ΑΣΦ ie= = Submit Request Answer ? electron/sarrow_forwardAn aluminum wire 2.053 mm in diameter (12-gauge) carries a current of 1.5 amps. Overall Hint a. What is the number density of charge carriers (electrons) in the wire? Hint for (a) 1 The number density of electrons in the wire is m³ (Use "E" notation to enter your answer in scientific notation. For example, to enter 3.14 × 10¹2, enter "3.14E12".) b. What is the magnitude of the drift velocity of the electrons? Hint for (b) The drift velocity of the electrons is vd = c. What would be the drift velocity if the same gauge copper were used instead of aluminum? Hint for (c) For the same gauge copper wire, the drift velocity would be vd = m/s. m/s. There is a disconnect between how small drift velocities are and how quickly electrical signals travel through wires (nearly at the speed of light). For the moment, treat the two as completely unrelated to each other.arrow_forwardqs1arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON