
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
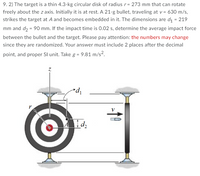
Transcribed Image Text:9. 2) The target is a thin 4.3-kg circular disk of radius r= 273 mm that can rotate
freely about the z axis. Initially it is at rest. A 21-g bullet, traveling at v = 630 m/s,
strikes the target at A and becomes embedded in it. The dimensions are di = 219
mm and d2 = 90 mm. If the impact time is 0.02 s, determine the average impact force
between the bullet and the target. Please pay attention: the numbers may change
since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal
point, and proper Sl unit. Take g = 9.81 m/s?.
'pe
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider a slender rod AB with a length l and a mass m. The ends are connected to blocks of negligible mass sliding along horizontal and vertical tracks. If the rod is released with no initial velocity from a horizontal position as shown in Fig.A, determine its angular velocity after it has rotated through an angle of θ (see Fig B) using the conservation of energy method. (Hint: Moment of inertia of rod about G = (1/12)ml2 The kinetic energy of a rigid body in plane motion isarrow_forward(Please solve by hand)arrow_forwardA smooth can C, having a mass of 5 kg, is lifted from a feed at A to a ramp at B by a rotating rod. The rod maintains a constant angular velocity of 0 = 0.5 rad/s, Neglect the effects of friction in the calculation and the size of the can so that r= (1.2 cos 0) m. The ramp from A to B is circular, having a radius of 600 mm (Figure 1) Figure 1 of 1 030.5 rad/s 600 mm 600 mmarrow_forward
- The rigid object shown below consists of three balls and three connecting rods, with M = 1.6 kg, L = 0.6 m and 0 = 30°. The balls may be treated as particles, and the connecting rods have negligible mass. Determine the rotational kinetic energy of the object if it has an angular speed of w = 1.2 rad/s about (a) an axis that passes through_point P and is perpendicular to the plane of the figure, coming out towards your eyes and (b) an axis that passes through point P and lies on the rod of length 2L in the plane of the figure. (Hint: the distance from a particle to the axis of rotation is the_length of the line connecting the particle to the axis that is perpendicular to the axis.) 2M L 2L M L 2Marrow_forwardSolve B,C,Darrow_forward1. Two children A and B, each having a mass 30kg, sit at the edge of the merry-go-round which is rotating with angular velocity @ = 2 rad/s. Excluding the children, the merry-go-round has a mass 180 kg and a radius of gyration k₂ = 0.8m. Determine the angular velocity of the merry-go-round if A jumps off horizontally in the -n direction (away from the merry-go-gound) with a speed of 3 m/s, measured with respect to the merry-go-round. After A jumps off, B then jumps off horizontally in the +t direction with a speed of 3 m/s, measured with respect to the merry-go-round - what is the merry-go-round's angular velocity now? Neglect friction and the size of each child. 1m 1m B w = 2 rad/sarrow_forward
- The 10-kg bar is released from rest in the horizontal position 1 and falls to positions 2. The unstretched lengthy of the spring is 0.6 m and the spring constant is k=20 N/m .what will be the bar 's angular velocity when it is in position 2.arrow_forwardThe velocity of the 7.6-kg cylinder is 0.49 m/s at a certain instant. What is its speed v after dropping an additional 1.87 m? The mass of the grooved drum is m = 10.1 kg, its centroidal radius of gyration is k = 260 mm, and the radius of its groove is r; = 225 mm. The frictional moment at O is a constant 15.3 N-m. Assume r, = 345 mm. m Answer: v = i m/sarrow_forwardParrow_forward
- A cylinder of mass m = 25 kg, initially at rest when t = 0, is acted upon by the force F as shown. Assuming that the disk rolls without slipping, determine the velocity of the cylinder's center G after 16 %3D %3D seconds. Write your answer in m/s but do not write the units. R = 0.4 m F = 120 N Taylor e am Answer:arrow_forwardThe uniform disk is initially at rest and has a mass of 24 kg. Its moment of inertia about its mass center is given by I =mr². A 100 N (constant) force F acts upon it as shown and it rolls without slip on the horizontal surface. Find: a) The velocity of its mass center G after it has moved 1.8 m. b) Include a detailed free body diagram(s)! f-100 Narrow_forwardThe velocity of the 8.2-kg cylinder is 0.46 m/s at a certain instant. What is its speed v after dropping 1.28 m? The mass of the grooved drum is m 12.8 kg, its centroidal radius of gyration is k 305 mm, and the radius of its groove is r 255 mm. The frictional moment at Ois a constant 9.0 N-m. an additional V Assume ro 400 mm. т i Answer: v m/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY