
Concept explainers
8. Alta Ski Company's inventory records contained the following information regarding its latest ski model. The company uses a periodic inventory system.
| Beginning inventory, January 1, 2021 | 1,350 | units @ $100 each |
| Purchases: | ||
| January 15 | 2,800 | units @ $115 each |
| January 21 | 2,600 | units @ $120 each |
| Sales: | ||
| January 5 | 1,300 | units @ $140 each |
| January 22 | 1,700 | units @ $150 each |
| January 29 | 1,150 | units @ $155 each |
| Ending inventory, January 31, 2021 | 2,600 | units |
Required:
-
1a. Which method, FIFO or LIFO, will result in the highest cost of goods sold figure for January 2021?
-
1b. Which method will result in the highest ending inventory balance?
-
2. Compute cost of goods sold for January and the ending inventory using both the FIFO and LIFO methods.
-
3a. Assume that inventory costs were declining during January. The inventory purchased on January 15 had a unit cost of $90, and the inventory purchased on January 21 had a unit cost of $85. All other information is the same. Which method, FIFO or LIFO, will result in the highest cost of goods sold figure for January 2021?
-
3b. Which method will result in the highest ending inventory balance?
-
3c. Compute cost of goods sold for January and the ending inventory using both the FIFO and LIFO methods.
Assume that inventory costs were declining during January. Which method, FIFO or LIFO, will result in the highest cost of goods sold figure for January 2021 and highest ending inventory balance?
|
|
|
3c. Compute cost of goods sold for January and the ending inventory using both the FIFO and LIFO methods.
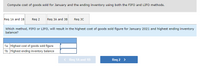
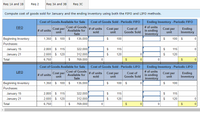
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

- Calculate the cost of goods sold dollar value for B67 Company for the month, considering the following transactions under three different cost allocation methods and using perpetual inventory updating. Provide calculations for weighted average (AVG).arrow_forwardBeginning inventory, purchases, and sales for Meta-B1 are as follows: Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, determine (a) the weighted average unit cost after the July 23 purchase, (b) the cost of the merchandise sold on July 26, and (c) the inventory on July 31.arrow_forwardUse the last-in, first-out (LIFO) cost allocation method, with perpetual inventory updating, to calculate (a) sales revenue, (b) cost of goods sold, and c) gross margin for A75 Company, considering the following transactions.arrow_forward
- Beginning inventory, purchases, and sales for 30xT are as follows: Assuming a perpetual inventory system and using the weighted average method, determine (a) the weighted average unit cost after the May 23 purchase, (b) the cost of the merchandise sold on May 26, and (c) the inventory on May 31.arrow_forwardCalculate a) cost of goods sold, b) ending inventory, and c) gross margin for A76 Company, considering the following transactions under three different cost allocation methods and using perpetual inventory updating. Provide calculations for last-in, first-out (LIFO).arrow_forwardCalculate a) cost of goods sold, b) ending inventory, and c) gross margin for A76 Company, considering the following transactions under three different cost allocation methods and using perpetual inventory updating. Provide calculations for weighted average (AVG).arrow_forward
- Calculate a) cost of goods sold, b) ending inventory, and c) gross margin for A76 Company, considering the following transactions under three different cost allocation methods and using perpetual inventory updating. Provide calculations for first-in, first-out (FIFO).arrow_forwardCalculate the cost of goods sold dollar value for A74 Company for the sale on March 11, considering the following transactions under three different cost allocation methods and using perpetual inventory updating. Provide calculations for (a) first-in, first-out (FIFO); (b) last-in, first-out (LIFO); and (c) weighted average (AVG).arrow_forwardUse the weighted-average (AVG) cost allocation method, with perpetual inventory updating, to calculate (a) sales revenue, (b) cost of goods sold, and c) gross margin for A75 Company, considering the following transactions.arrow_forward
- Trini Company had the following transactions for the month. Calculate the ending inventory dollar value for each of the following cost allocation methods, using periodic inventory updating. Provide your calculations. A. first-in, first-out (FIFO) B. last-in, first-out (LIFO) C. weighted average (AVG)arrow_forwardTrini Company had the following transactions for the month. Calculate the cost of goods sold dollar value for the period for each of the following cost allocation methods, using periodic inventory updating. Provide your calculations. A. first-in, first-out (FIFO) B. last-in, first-out (LIFO) C. weighted average (AVG)arrow_forwardAkira Company had the following transactions for the month. Calculate the ending inventory dollar value for the period for each of the following cost allocation methods, using periodic inventory updating. Provide your calculations. A. first-in, first-out (FIFO) B. last-in, first-out (LIFO) C. weighted average (AVG)arrow_forward
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning





