
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
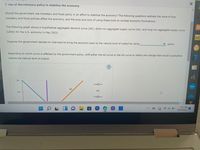
Transcribed Image Text:7. Use of discretionary policy to stabilize the economy
Should the government use monetary and fiscal policy in an effort to stabilize the economy? The following questions address the issue of how
monetary and fiscal policies affect the economy, and the pros and cons of using these tools to combat economic fluctuations.
The following graph shows a hypothetical aggregate demand curve (AD), short-run aggregate supply curve (AS), and long-run aggregate supply curve
(LRAS) for the U.S. economy in May 2023.
A-Z
Suppose the government decides to intervene to bring the economy back to the natural level of output by using
policy.
Depending on which curve is affected by the government policy, shift either the AS curve or the AD curve to reflect the change that would successfully
restore the natural level of output.
(?)
150
AS
1:23 PM
4/29/2022
130
AD
O
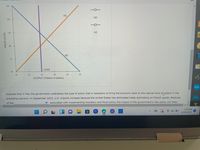
Transcribed Image Text:PRICE LEVEL
150
130
110
90
70
50
AS
22
AD
26
LRAS
20
24
26
30
OUTPUT (Trillions of dollars)
Suppose that in May the government undertakes the type of policy that is necessary to bring the economy back to the natural level of output in the
preceding scenario. In September 2023, U.S. imports increase because the United States has eliminated trade restrictions on French goods. Because
of the
associated with implementing monetary and fiscal policy, the impact of the government's new policy will likely
1:24 PM
4/29/2022
28
AD
AS
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 7. Use of discretionary policy to stabilize the economy Should the government use monetary and fiscal policy in an effort to stabilize the economy? The following questions address the issue of how monetary and fiscal policies affect the economy, as well as the pros and cons of using these tools to combat economic fluctuations. The following graph plots hypothetical aggregate demand (AD), short-run aggregate supply (AS), and long-run aggregate supply (LRAS) curves for the U.S. economy in January 2026. Suppose the government chooses to intervene in order to return the economy to the natural level of output by using Depending on which curve is affected by the government policy, shift either the AS curve or the AD curve to reflect the change that would successfully restore the natural level of output. PRICE LEVEL 150 130 110 90 AS AD D AS policy. ?arrow_forwardStart with a brief introduction that explains use of Government policy to control the economy. When is it appropriate to use monetary and fiscal policy to stimulate or stabilize the economy? Look at both. When is it inappropriate to use monetary and fiscal policy to stimulate or stabilize the economy? Look at both. What specific fiscal policy tools would you use to stimulate aggregate demand and how? What specific monetary policy tools would you use to stimulate aggregate demand and how? What is your conclusion, should policymakers use the monetary and or fiscal policy, or a combination of both, to stimulate aggregate demand? Explain your reasoning.arrow_forwardIn the graph of Figure I, the annual growth rate of the GDP of the United States economy is presented since the first quarter of 2004, while, in the graphs of Figure II, three different scenarios of the relationship are represented between demand and aggregate supply that reflect different situations of economic growth.2. Explain in detail what is happening in Graph A of Figure II (economic growth, expansion, inflation or reccesion) according to the long and short term aggregate supply curve and aggregate demand and general price level and, examining the data in the graph of Figure I Table 1.1.1., and identify in what period of time this situation (identified in the Graph A) is ocurring. Figure I = Real data of the United States economyFigure 2 = Representation of the aggregate demand and supply modelDA = AGGREGATE DEMANDGDP = GROSS DOMESTIC PRODUCTNGP = GENERAL PRICE LEVELOAL = LONG TERM AGGREGATE OFFEROAC = SHORT-TERM AGGREGATE OFFERarrow_forward
- Price level (GDP price index, 2012 140 130 120 110 105 100 90 90 19 Potential GDP ADO 21 20 AS 22 Real GDP (trillions of 2012 dollars) The figure above shows a nation's aggregate demand curve, aggregate supply curve, and potential GDP. In the figure above, the can change expenditure by gap is one trillion dollars. To close the gap, the government one trillion dollars. recessionary; exactly inflationary; more than recessionary; less than recessionary; more thanarrow_forward1. In the following table, determine how each event likely effects potential output (a.k.a., long-run aggregate supply). Direction of Potential Output Shift Event Left Right No Shift The government allows more immigration of working-age adults. For environmental and safety reasons, the government requires that the country’s nuclear power plants be permanently shut down. An investment tax credit increases the rate at which firms acquire machinery and equipment. 2. In the following table, determine how each event affects the position of the aggregate demand curve. Direction of AD Curve Shift Event Left Right No Shift A decrease in consumer confidence (suggests people believe a contraction/recession coming) A decrease in individual income tax rates An increase in the value/price of housing 3. What effect would an increase in aggregate demand…arrow_forwardTOPIC: Crowding Out.arrow_forward
- Question 76 During the 2020 campaign, Joe Biden proposed raising income taxes on those earning more than $400,000 per year and raising corporate taxes from about 21 percent to 28 percent. Consider the aggregate demand-aggregate supply diagram below, which represents the macroeconomy. Suppose the market is initially at an equilibrium at point A. What effect will a tax increase have on this graph? Question 76 options: 1.The long-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left. 2.The aggregate demand curve will shift to the right. 3.The aggregate demand curve will shift to the left. 4.The short-run aggregate supply curve will shift to the left. Question 77 During the 2020 campaign, Joe Biden proposed raising income taxes on those earning more than $400,000 per year and raising corporate taxes from about 21 percent to 28 percent. Consider the market for money illustrated in the figure below. Assume the market initially is in equilibrium at point A. What effect will the tax increase…arrow_forwardThe graph shows an economy's aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves and potential GDP. Does this economy have an inflationary gap or a recessionary gap? How does this economy return to full employment? This economy has _______ gap. It returns to full employment as _______. A. an inflationary; the money wage rate rises B. a recessionary; potential GDP increases C. a recessionary; the money wage rate falls D. an inflationary; aggregate demand decreasesarrow_forwardUsing the graph, illustrate the long-run impact of the increase in government spending by shifting both the aggregate demand (AD) curve and the short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve in the appropriate directions PRICE LEVEL 240 200 2 200 400 600 800 OUTPUT (Bions of dollars) AS 1000 1200 þ 2þ 2 In the long run, due to the increase in government spending, the price level natural level of output, and the unemployment rate ? the natural rate. the quantity of gotputarrow_forward
- 3/25/22, 8:59 PM Assignment Print View 8. Assume the economy is currently in equilibrium at its full-employment level of output, the money market is in equilibrium, and the MPC = 0.75. a. Suppose there is an increase in government spending that causes aggregate demand to increase by $16 billion. Show the increase in aggregate demand on the graph. Instructions: Use the tool provided "Aggregate Demand" to plot the new aggregate demand curve. Use the tool provided "New GDP" to plot the new equilibrium. AD and AS Model 200 Tools LRAS 180 AS 160 Aggregate Dei New GDP 140 120 100 80 60 AD 40 20 16 32 48 64 80 96 112 128 144 160 Real GDP (billions of dollars) Now suppose the Federal Reserve wants to keep inflation from hurting the economy and maintain output at the full-employment level. https://ezto.mheducation.com/hm.tpx?todo=c15SinglePrintView&singleQuestionNo=8.&postSubmissionView=13252718377637707&wid=13252718466136846&rol... 1/3 Price Levelarrow_forward2. The aggregate demand curve is best represented by which of the following equations? AD=C+I+G + NX AD=C+I+ G - NX AD=C+I+ G AD=C+I O AD=C+I- G - NXarrow_forwardQUESTION 5 05. The "crowding-out secondary effect expansionary macroeconomic policy a) For fiscal policy it is about government borrowing to finance the government budget deficit, associated with expansionary fiscal policy. This increased government borrowing tends to increase the market rate of interest, which dampens investment spending. b) For monetary policy it is about the expansion of the economy increasing the demand for money to service the increased volume of transactions. This tends to increase the market rate of interest, which dampens investment spending. c) Decreases the autonomous spending multiplier and thus the impact of expansionary policy. d) All of the above.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education