
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780618974122
Author: Andrei Straumanis
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
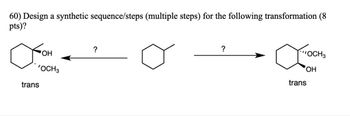
Transcribed Image Text:60) Design a synthetic sequence/steps (multiple steps) for the following transformation (8
pts)?
о
?
'OCH3
trans
?
OCH3
OH
trans
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 4arrow_forwardComplete the following reactions by identifying the majority product(s) or the reaction conditions that are missing. No mechanism is neededarrow_forwardConsider the nucleophilic substitution reaction shown here. Based on the stereochemistry, does it proceed by an Sy1 or Sy2 mechanism? Explain. OH KOCH3 Enantiomer CH;OH `OCH3arrow_forward
- Draw a step-wise mechanism for the following substitution reaction. Be sure to add lone pairs and charges where relevant. I CH CH, CH, OHarrow_forwardKk.174. Please fill out this reaction mechanism with the missing reagents and intermediate products with a complete arrow-pushing mechanism.arrow_forwardDraw an arrow pushing mechanism and explain why less than two substitutions are observed in the productarrow_forward
- Mechanism. Draw complete arrow-pushing mechanisms for the following reactions.arrow_forwardEach of the following may participate in an elimination reaction, under the proper conditions. (a) Circle the alpha (a) carbon. (b) Circle the beta (B) carbon(s). (c) Draw the alkene product(s) that may form, with the new double bond between the a and ß positions. (d) If more than one alkene product is possible, circle the most stable (Zaitsev) product. A В J C K E F G 33-0arrow_forwardDraw the substitution and elimination products.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning
