
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
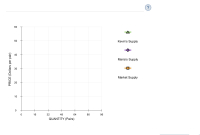
6. Individual and market supplySuppose that Kevin and Maria are the only suppliers of shoes in a particular market. The following table shows their annual supply schedules:
On the following graph, plot Kevin's supply of shoes using the green points (triangle symbol). Next, plot Maria's supply of shoes using the purple points (diamond symbol). Finally, plot the market supply of shoes using the orange points (square symbol).
Note: Line segments will automatically connect the points. Remember to plot from left to right.( the graph is attached as an image)
|
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (a) Suppose that tacos and pizza are substitutes, and that soda and pizza are complements. What effect will the increase in the price of pizza have on the market for tacos and market for sodas? Briefly explain your graphical analysis for each graph. (two separate graphs for sodas and tacos markets)arrow_forward6. Determinants of demand The following graph input tool shows the demand for sedans in New York City. For simplicity, assume that all sedans are identical and sell for the same price. Initially, the calculator shows market demand under the following circumstances: average household income is $50,000 per year, the price of a gallon of regular unleaded gas is $3 per gallon, and the price of a subway ride is $1.50. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the questions that follow. (Note: You will not be graded on any adjustment made to the graph used in the tool.) PRICE (Thousands of dollars per sedan) Demand 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 QUANTITY (Sedans per month) Graph Input Tool Price of a sedan (Thousands of dollars) Quantity of sedans (Sedans per month) Average Income (Thousands of dollars) Price of gasoline (Dollars per gallon) Price of a subway ride Suppose that the price of a sedan decreased from $25,000 to $20,000. This would cause a 25 450 50 $3.00 $1.50 Suppose that…arrow_forwardDuring the spring when demand for lobster is relatively low, Maine lobster fishermen are able to sell their lobster catches for about $4.50 per pound. During the summer when demand for lobster is much higher, Maine lobster fishermen are able to sell their lobster catches for only about $3.00 per pound. It may seem strange that the market price is higher when demand is low than when demand is high. Can you resolve this paradox with the help of a demand and supply graph? [You can attach your graph to your posting.] Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward
- Ch 23 Economicsarrow_forwardSuppose that Paolo and Sharon are the only suppliers of collectible action figures in a particular market. The following table shows their annual supply schedules: Price Paolo's Quantity Supplied Sharon's Quantity Supplied (Dollars per action figure) (Action figures) (Action figures) 10 A-Z 4 8. 18 6. 12 24 8. 14 28 10 16 30 On the following graph, plot Paolo's supply of collectible action figures using the green points (triange symbol). Next, plot Sharon's supply of collectible action figures using the purple points (diamond symbol). Finally, plot the market supply of collectible action figures using the orange points (square symbol). Note: Line segments will automatically connect the points. Remember to plot from left to right. 12 Paolo's Supply 10 Sharon's Supply MacBook Air F12 F11 F10 F9 FB F7 F6 吕0 F5 O00 F4 F3 * delete &arrow_forward2. Individual and market demand Suppose that Sean and Yvette are the only consumers of shoes in a particular market. The following table shows their annual demand schedules: Price (Dollars per pair) 10 20 30 40 50 PRICE (Dollars per pair) On the following graph, plot Sean's demand for shoes using the green points (triangle symbol). Next, plot Yvette's demand for shoes using the purple points (diamond symbol). Finally, plot the market demand for shoes using the blue points (circle symbol). (?) 60 50 30 20 10 0 0 16 Sean's Quantity Demanded Yvette's Quantity Demanded (Pairs) (Pairs) 32 64 20 48 12 32 4 24 0 16 32 48 64 QUANTITY (Pairs) 80 96 Sean's Demand Yvette's Demand O Market Demand Now, suppose that Yvette's twin brother, who likes shoes just as much a Yvette, moves to the area, adding another consumer in the market. As a result, there will be a ▼ the market demand curve because there will be a change in quantity demandedarrow_forward
- 9. Shirts in supply or demana 11 The following graph shows the market for croissants in San Diego, where there are over 1,000 bakeries at any given moment. Suppose an innovation in the baking process makes it possible to produce more croissants at a lower cost than ever before. Show the effect of this change on the market for croissants by shifting one or both of the curves on the following graph, holding all else constant. Note: Select and drag one or both of the curves to the desired position. Curves will snap into position, so if you try to move a curve and it snaps back to its original position, just drag it a little farther. PRICE (Dollars per croissant) QUANTITY (Croissants) Supply Demand Demand T Supply ?arrow_forward3. Individual and market demand Suppose that Hubert and Kate are the only consumers of pizza slices in a particular market. The following table shows their weekly demand schedules: Price (Dollars per slice) 1 2 3 4 5 Hubert's Quantity Demanded (Slices) 8 5 3 1 0 Kate's Quantity Demanded (Slices) 16 12 8 4 2 On the following graph, plot Hubert's demand for pizza slices using the green points (triangle symbol). Next, plot Kate's demand for pizza slices using the purple points (diamond symbol). Finally, plot the market demand for pizza slices using the blue points (circle symbol). Note: Line segments will automatically connect the points. Remember to plot from left to right.arrow_forward10. Market equilibrium The following table shows the monthly demand and supply in the market for shoes in San Francisco. Price Quantity Demanded Quantity Supplied (Dollars per pair of shoes) (Pairs of shoes) (Pairs of shoes) 20 1,650 300 40 1,200 750 60 600 1,050 80 300 1,350 100 150 1,500 On the following graph, plot the demand for shoes using the blue point (circle symbol). Next, plot the supply of shoes using the orange point (square symbol). Finally, use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the equilibrium price and quantity in the market for shoes. Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically. 120 100 Demand 80 Supply 60 Equilibrium 40 20 300 600 900 1200 1500 1800 QUANTITY (Pairs of shoes) PRICE (Dollars per pair of shoes)arrow_forward
- Tips ps Chapter 04 Homework The following table presents the monthly demand and supply in the market for oat milk in New York City. PRICE (Dolars per gallon of oat milk) 2 On the following graph, plot the demand for oat milk using the blue point (circle symbol). Next, plot the supply of oat milk using the orange point (square symbol). Finally, use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the equilibrium price and quantity in the market for oat milk. Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically. ? H 10 0 13 Price (Dollars per gallon of oat milk) 2 4 6 0 8 10 400 Quantity Demanded (Gallons of oat milk) 2,200 1,600 1,200 800 400 800 1200 1600 QUANTITY (Gations of oat mig 2000 Quantity Supplied (Gallons of oat milk) 400 1,000 1,800 2,000 2,400 12400 O Demand -P Supply + Equilibriumarrow_forwardPlease give a detailed solution with an explanation. Please make sure the graph is visible, clear, and detailed. Make sure to include the new equilibrium coordinate point as well.arrow_forwardThis problem involves solving demand and supply equations together to determine price and quantity. a. Consider a demand curve of the form QD=-2P+20, where QD is the quantity demanded of a good and P is the price of the good. Graph this demand curve. Also draw a graph of the supply curve Qs =2P-4, where Qs is the quantity supplied. Be sure to put P on the vertical axis and Q on the horizontal axis. Assume that all the Qs and Ps are nonnegative for parts a, b, and c. At what values of P and Q do these curves intersect-that is, where does QD = Qs ? b. Now, suppose at each price that individuals demand four more units of output-that the demand curve shifts to QD - 2P+24. Graph this new demand curve. At what values of P and Q does the new demand curve intersect the old supply curve-that is, where does QD = Qs ? c. Now finally, suppose the supply curve shifts to Q's=2P-8. Graph this new supply curve. At what values of P and Q does QD=Q's? Show all working calculations and label garph with…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education