
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
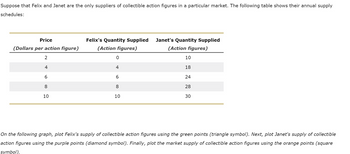
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose that Felix and Janet are the only suppliers of collectible action figures in a particular market. The following table shows their annual supply
schedules:
Price
(Dollars per action figure)
2
4
6
8
10
Felix's Quantity Supplied Janet's Quantity Supplied
(Action figures)
(Action figures)
0
4
6
8
10
10
18
24
28
30
On the following graph, plot Felix's supply of collectible action figures using the green points (triangle symbol). Next, plot Janet's supply of collectible
action figures using the purple points (diamond symbol). Finally, plot the market supply of collectible action figures using the orange points (square
symbol).
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. As an agriculture analyst for the Union of American Fruit Producers (UAFP), you are in charge of monitoring the US peach market. The market can be described by the following "calibrated" demand and supply functions: Qd = 1600-8P +8Pn Qs = 34P-102 (1) (2) where P is the price of a crate of peaches, Pn is the price for a crate of nectarines, and Qd and Q, are the quantity demanded and the quantity supplied of peaches (measured in thousands of crates). (a) Find the inverse demand and inverse supply equations. Hypothetically, how many crates of peaches should UAFP expect consumers to buy if peaches are given away free of charge in a marketing campaign? If the price of a crate of peaches was to increase, at what price would buyers no longer be willing to buy any peaches? (Hint: your previous answers will be expressions that depend on the value of P) If the price of peaches was to decrease, at what price would the quantity of peaches supplied fall to zero? (b) Assuming that P₁ = $55,…arrow_forwardQuantity Demanded Price Quantity Supplied 9 $ 11 13 10 10 12 11 9 11 12 8 10 13 7 9 14 6 15 5 8 7 Refer to the above table. If demand decreased by 4 units at each price and supply decreased by 2 units at each price, what would the new equilibrium price and quantity be? Multiple Choice $10 and 10 units $8 and 8 units $9 and 9 units $7 and 9 unitsarrow_forwardAssume the following demand and supply equations: Qd=900-20P, and Qs=150+10P. a) Calculate the slopes of the two curves b) Calculate the equilibrium price and quantity c) If the price was $30, how much would the quantity demanded be? d) If the price was $30, how much would the quantity supplied be? e) At a price of $30, is there a shortage or a surplus? How can you tell?arrow_forward
- 1. The estimated demand for Canadian Processed Pork is given by Qp = 171 – 20p+ 20pB + 3pc +2Y where Qp is the quantity of pork demanded (millions of kg), p is the dollar price per kg, pB is the price of beef per kg, pc is the price of chicken per kg, and Y is average consumer income in thousands of dollars. The supply for this market is given by Qs = 178 + 40p – 60pB (a) According to the equations, what is the effect of an increase of Pc on the market for pork? Specifically, which curve will shift, in what direction does the curve shift, and how will the equilibrium price and quantity change (increase/decrease). On a corresponding graph of the supply and demand, draw the shifting curve and change in equilibrium. Note that no specific numbers are required here. Just the direction of change. (b) Use the equations to solve for the equilibrium price of pork and quan- tity of pork as functions of the exogenous variables pB, Pc, and Y. These will be linear functions. (c) Suppose pB = 1.5,…arrow_forwardRefer to the demand and supply schedule shown in the table below.Please provide explanation to each question. Price ($) Quantity demanded (slices) Quantity supplied (slices) 0.00 350 0 0.50 300 100 1.00 250 150 1.50 200 200 2.00 150 250 2.50 100 300 3.00 50 350 3.50 0 400 If pizza parlours charge $3.50 per slice, there will be an excess: demand of 400 units. supply of 400 units. demand of 200 units. supply of 200 units. If pizza parlours charge $1.00 per slice, there will be an excess: supply of 100 units. demand of 150 units. demand of 100 units. supply of 150 units. The equilibrium price is $ per slice, and the equilibrium quantity is slices of pizza. References Worksheet Learning Objective: 03-06 Explain how supply and demand interact to drive markets to equilibrium. In each of the following examples, name the factor…arrow_forwardDetermine the equilibrium price and quantity for the following laws of demand and supply in the manufacture of computer parts Demand: 3p + 5x = 200Bid: 7p - 3x = 56arrow_forward
- The following table indicates the demand schedules for four types of consumers A, B, C, and D and the number of consumers in each group (top row). The quantity demanded by each type of comuner (GxGO and O shown for market prices ranging from $10 down to $4 What is the combined quantity demanded at a market price of $77 Number of Consumers A = 200 B=300 Q C=300 D=200 Market Price QA Q Q $10 D 0 1 1 D 1 2 3 1 3 3 3 4 7 $ 9 6 11 OC 4700 OD 3.000 OA 25.000 4.750 9 S 2 3 4 5 MI 5 8 11 16 20arrow_forwardSubject: Economics 1.) The demand equation for the Drake GPS Navigator is x + 4p − 1070 = 0, where x is the quantity demanded per week and p is the wholesale unit price in dollars. The supply equation x − 19p + 1000 = 0, where x is the quantity, the supplier will make available in the market each week when the wholesale price is p dollars each. Find the equilibrium quantity and the equilibrium price for the GPS Navigators. (a) equilibrium quantity= units(b) equilibrium price $=arrow_forwardSuppose that Jacques and Kyoko are the only consumers of scented candles in a particular market. The following table shows their annual demand schedules: Price (Dollars per candle) 2 4 6 8 10 Jacques's Quantity Demanded Kyoko's Quantity Demanded (Candies) (Candles) 12 28 6 20 4 12 2 6 0 2arrow_forward
- A baker will supply 17 jumbo cinnamon rolls to a cafe at a price of $3.91 each. If she is offered $3.15, then she will supply 4 fewer rolls to the cafe. The cafe's demand for jumbo cinnamon rolls is given by p = D(x) = -0.48x + 8.05. What is the equilibrium point? ___ rolls at a price of $ ___ eacharrow_forwardSuppose the Canadian demand for and the Japanese supply of cars to Canada is shown in the table below (quantities in thousands). Quantity Supplied (before tariff) Quantity supplied (after tariff) Price ($) 13,000 14,000 15,000 16,000 17,000 18,000 19,000 20,000 Quantity Demanded 170 150 130 110 90 70 50 30 50 70 90 110 130 150 170 190 a) The present equilibrium price is $ and quantity is b) Suppose that the Canadian government imposes a $2,000 per car tariff on imported Japanese cars. Show the new supply in the last column above. thousand. thousand. c) The new equilibrium price is $ and quantity is d) The total revenue received by the government will be $ e) Assume, instead, that the government imposes an import quota of 90,000 cars. The new equilibrium price is $ quantity is thousand. f) Does the government now receive any revenue? No million. andarrow_forwardSuppose you are given the following supply and demand equations for your company's product, executive fountain pens: Qd = 12,000 - 2P + 3Py - 5Pn - 2Pk + 4M + 3A Qs = 8,000 + 4,000P - 7Pm - 3Pw where: Qd = quantity demanded of fountain pens Qs = quantity supplied of fountain pens P = price per unit of fountain pens Py = price per unit of pencils Pn = price per unit of notebooks Pk = price per bottle of ink M = consumer income A = number of units of advertising purchased by the company Pm = cost of purchasing materials (inputs) for fountain pens Pw = cost of hiring a worker (wage rate) a) given the signs of the coefficients in the demand equation, how does the demand for fountain pens react to each variable (i.e., substitutes, complements, normal good, inferior good)? b) given the signs of the coefficients in the supply equation, how does the supply for fountain pens react to each variable? c) suppose you are given the following data: Py = $10 Pn = $15 Pk = $8 M = $20,000 A =…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education