
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
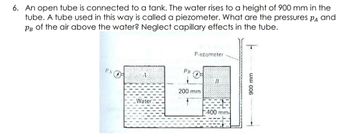
Transcribed Image Text:6. An open tube is connected to a tank. The water rises to a height of 900 mm in the
tube. A tube used in this way is called a piezometer. What are the pressures PA and
Рв of the air above the water? Neglect capillary effects in the tube.
PA
Water
PB
Piezometer
200 mm
B
400 mm-
T
900 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The open tank with piezometers attached on the side, contains two different liquids. Find the elevation of the liquid in piezometer A. А В El. 2.0m A(0.72) El. 0.3m h В(2.36)arrow_forwardAn orifice of 50 mm square, with c = 0.6 is located on one side of a closed cylindrical tank as shown. If the upper layer (4 m) of the tank is oil (s.g. = 0.8) and the remainder is water, then determine the discharge (Q) from the orifice [in m3/s]. [Note: the layer on top of oil is thin air with negligible pressure].arrow_forwardFlow rate of a fluid (p = 1000 kg/m³) in a small diameter tube is 800 mm³/s. The length and diameter of the tube are 2 m and 0.5 mm, respectively. The pressure drop in 2 m length of is equal to 2 MPa. The viscosity of the fluid is:arrow_forward
- If 29.89 in Hg is barometric pressure then convert below,arrow_forwardA manometer is attached to a water tank as shown in the figure. Find the height of the free water surface above the bottom of the tank Find the pressure at the interface of the water and the mercury. Find the absolute pressure at the bottom of the tank.arrow_forwardAn open jet of water at 20 ℃ exits a nozzle into sea-level air and strikes a stagnation tube, as shown in the sketch. If the pressure at the centerline of section (1) is 110kpa (abs), and losses are neglected, estimate: (a) the mass flow in kg/s, and (b) the height H of the fluid in the stagnation tube. (Atmospheric pressure =101.3 kpa)arrow_forward
- In fig. if H= 88 inches, the difference in pressure =---?(the fluid is water) Piezometer (static) tube- -Pitot tube 2 BAR CO -Fluid stagnates at point 2 (v₂ = 0) 357.6. lb/ft2 O 243 lb/ft2 O 457.6 lb/ft2. Oarrow_forwardDetermine the height h to which liquid should be poured into the cup so that it contacts half the surface area on the inside of the cup. Neglect the cup’s thickness for the calculation.arrow_forwardHeavy fuel oil flows at Q = 10 gallons per minute (gpm) in a horizontal steel pipe that connects two storage tanks. The diameter of the pipe is D = 1.5 inches. The length of the pipe is L = 100 feet. The depth of oil in the supply tank is 30 feet above the pipe entrance. The temperature of the oil is 60°F, the specific gravity of the oil is s.g.oin = 0.90, the specific weight of the oil is 56.13 lb/ft', and the kinematic viscosity of the oil is 0.00175 ft2/s. The pipe discharges into the bottom of the receiving tank. Neglect minor losses. a) Determine the pressure p at the pipe entrance in pounds per square foot (psf). b) Determine the velocity v in feet per second (fps). c) Determine the Reynolds number Re. d) Classify the flow based on the Reynolds number Re. e) Determine the Darcy-Weisbach friction factor f. f) Determine the friction head loss hfac in feet in the pipe between the two storage tanks. 8) Determine the depth of oil in feet above the exit from the pipe into the second…arrow_forward
- Suppose a Venturi tube (placed in the horizontal position of Pipe BC in Figure 1) from the right (Fig.2). The radius of the wide part of the tube is 5.0 cm; the radius of the thin part of the tube is 2.5 cm. The tube of shape U is filled with the mercury of the density 13600 kg/m . Determine what heightdifference will be stabilized between the surfaces of the mercury in U-tube. Ignore the losses.arrow_forwardA U-tube of uniform cross-section has both arms open to the atmosphere. The U-tube contains three immiscible liquids, with density PA, PB, and pc, as depicted in the diagram below, where po is the atmospheric pressure. We denote h to be the depth of the open surface of liquid A on the left arm, relative to the open surface of liquid Con the right arm. I is the depth of the interface between liquid B and C on the right arm and 2l is the depth of the interface between liquid A and liquid B on the right arm. Po PA (c) Po PC PB е е (a) Explain why the liquid densities need to satisfy the condition PA PB PC. (b) Write down an expression for the pressure at depth z below the surface of liquid A in the left-hand part of the tube. Show that l < h < 2l if PB + PC < PA•arrow_forwardWater flows steadily from a nozzle into a large tank as shown below. The water then flows from the tank as a jet of diameter d. (a) Using the piezometer tube shown, determine the flow rate through the nozzle. (b) Using the flow rate determine the value d if the water in the tank remains constant. Viscous effects are negligible.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning