
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
An open tube is attached to a tank, as shown in figure. If the water rises to a height of 800 m in the tube, what are the pressures P. and of the air above the water? Neglect capillary ellects in the tube.
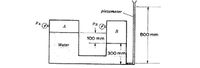
Transcribed Image Text:piezometer
PA
PB O
A
800 mm
100 mm
Water
300 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In figure 5, determine the pressure head difference in feet of water between m and n, when z is: (a) 3.77 in.; (b) 10.77; (c) 15.77 in Determine the value of z if the pressure at n is 1.477 lb per sq. in. greater than at m. If the pressure at m is 20.77 lb per sq. in, what is the corresponding pressure at n when z = 8.77 in.arrow_forwardDetermine the hydrostatic force in liquid 1, 2 and 3arrow_forward5. Compute the magnitude of the resultant force on the indicated area and the location of the centre of pressure as shown in Figure 5. Show the resultant force on its location. 0.80 m 0.5 m Semicircular hatch 1.50-m diameter Turpentine sg =0,88 70 Figure 5: A Tankarrow_forward
- The jet of a horizontal nozzle strikes a vertical plate with a force equal to 7000N. If the discharge flowing at the nozzle is 0.12 m3/s. Compute the diameter of the jetarrow_forwardIn the Figure below, a pool of liquid sodium is sitting in open atmosphere (and somehow not exploding from the moisture in the air) and an absolute pressure measurement device. The measurement device reads an absolute pressure of P2 at the depth of L in the pool. dP a) Calculate the pressure gradient (-) b) Using Excel plot the pressure distribution from the P2 and P1. Figure 1: A 2-D pool of Sodium on Earth that magically is keeping all of it's liquid inside even though it has no front and back sides.arrow_forwardA right circular cylindrical tank container, 2m in diameter and 4m high is 1/2 full of water. When rotated about its vertical axis at the rate of 60 rpm:A.) How many meters will the water surface drop at the center of the vessel? B.) What is the pressure, in kPa, at the base of the container along the perimeter? C.) What is the volume, in m^3, of the paraboloid formed by the rotation of the vessel? (Show complete solution)arrow_forward
- As shown in the figure compute the amount and location of the vertical and horizontal components of the hydrostatic pressure on XY SECTOR GATE L=12M 6.5M I 60° 10M Pv P Y W.S PHarrow_forwardProblem 8: EGL and HGL (IV) Consider a storage reservoir with a water surface elevation of 270 m. It is connected to a closed conduit (i.e., a pipe) that carries water down to a turbine at elevation 60 m. The friction head loss in the conduit is 20 m. Part A At point D, what are the pressure head P/y, the elevation head z, and the HGL? Part B Copy the diagram below. If the conduit is a closed pipe flowing full, is the velocity head V²/(2g) constant D→E? Answer yes or no, then sketch the EGL above the pipe D-E. Use a solid line. D E z = 270 m T Part C Based on your answer to Part B, sketch the HGL from D-E. Use a dashed line. z = 270 m Part D Now assume the conduit is an open channel. Copy the diagram below. Is the velocity head V²/(2g) constant D→E? Answer yes or no, then sketch the EGL above the pipe D→E. Use a solid line. E D z = 60 m T z = 60 m Part E Based on your answer to Part D, sketch the HGL from D-E. Use a dashed line.arrow_forwardS3. In a large reservoir, the water level is kept constant, and the water is discharged through a vertical pipe. Whole neglecting the energy losses, the flow rate flowing through the pipe and the relative pressure at points B, C, D Calculate the values. 10 cm A 5 cm Во Co ↓ D ** E 2 m 5m 5m 1 marrow_forward
- The two springs are identical, with unstretched length 0.4 m. When the 50-Kg mass is suspended at B, the length of each spring increases to 0.6 m. What is the spring constant K?arrow_forwardA 2.10 m diameter closed cylinder, 2.75 m high is completely filled with oil having sp. gr. Of 0.8 under a pressure of 5 kg/cm^2 at the top. Compute the pressure force exerted by oil on the side of the tank in kg.arrow_forwardWhat flows through a 0.305m vertical pipe downwards at a rate of 1.70 x 10^(-4) m^3/s exiting into the atmosphere. the pipes diameter remains constant at 0.013m. The velocity at the exit of the pipe was measured to be 1.28 m/s. Determine the pressure at the top of the pipe.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning