
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
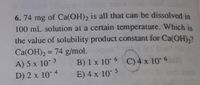
Transcribed Image Text:6. 74 mg of Ca(OH)2 is all that can be dissolved in
100 mL solution at a certain temperature. Which is
the value of solubility product constant for Ca(OH),?
Ca(OH)2 = 74 g/mol.
A) 5 x 10 3
D) 2 x 10 4
B) 1 x 10 6 C) 4 x 10 6
E) 4 x 10 5
il
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 22 of 30 Submit A 185.0 mL sample of 1.200 M Pb(NO3)2 is mixed with 123.50 mL of 1.500 M NaCI, and the PbCl, precipitate is filtered from the solution. Then 200.0 mL of 3.000 M NaBr is added to the remaining solution, and the PbBr, precipitate is also collected and dried. What is the mass (in grams) of the PbBr, precipitate, assuming the yield in each precipitation step is 100%? 1 4 6. C 7 +/- x 10 0 Tap here or pull up for additional resources LO 00arrow_forwardExample: Let us determine the concentrations of Ag+, CN, and Ag(CN)₂ when 10.0 mL of 2.00 M KCN is mixed with 10.0 mL of 0.0200 M of AgNO3. Kf for Ag(CN)₂¯ = 1.0 × 10²¹. := Q16.86 What is the initial concentration of Ag+ ion (in M) after mixing but before reaction or equilibrium is established? Type your numeric answer and submit Answered - Incorrect 3 attempts left Q16.87 What is the initial concentration of CN (in M) after mixing but before reaction or equilibrium is established? Cannot be empty Resubmitarrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwriting solutions...arrow_forward
- The Ksp for an ionic solid, AB2, is 4.602*10-8. The molar mass of this ionic solid is 85.51 g/mol. Calculate the solubility of this ionic solid in grams per Liter.arrow_forwardCalculate the solubility of silver phosphate, Ag3PO4 in units of grams per liter. Ksp (Ag3PO4) = 1.3x10-20. solubility g/Larrow_forwardDetermine the solubility product constant (Ksp) for PbCl 2 . The solubility of PbCl 2 is 0.016 mol/D at 25 degrees Celsius. What does the solubility (0.016 mol/L) represent?arrow_forward
- A solution is prepared by adding 150.0 mL of a 0.0100 M Mg(NO3)2 solution to 250.0 mL of a 0.100 M NaF solution. Will anything precipitate from this solution and, if so, what is the precipitate? a. No, nothing will precipitate. b. Yes, MgF 2 c. There is not enough information to answer this question. d. Yes, Mg(NO 3 ) 2 e. Yes, NaNO 3arrow_forwardThe Solubility Product Constant for silver phosphate is 1.3 x 10-20. The maximum amount of silver phosphate that will dissolve in a 0.280 M potassium phosphate solution is M.arrow_forward13. The Kp of SrCO3 is 1.6 x 10. What is the solubility of SrCO3 (in mol/L) in pure water? sp 14. The KOH(aq) concentration is 1.2 x 10³ M. What concentration of Fe³ must be added to just start forming a precipitate Fe(OH),(s)? 3 15. The solubility of LaF¸ in water is 1.8 x 10°³ g/L. What is the value of K? sp 16. The K of PbBг, is 4.6 x 106. What is the solubility of PbBr₂ (in g/L) in pure water? sparrow_forward
- A solution contains 5.72×10-3 M potassium sulfate and 6.78×10-3 M ammonium fluoride.Solid lead nitrate is added slowly to this mixture.What is the concentration of sulfate ion when fluoride ion begins to precipitate?[sulfate] = _______Marrow_forwardThe solubility of lead(II) chloride, PbCl2 (MM: 278.1 g/mol), in water at 60 °C is 1.94 g/L. Ksp for lead(II) chloride = 1.37×10^-6 a) Using your value of Ksp, what is the molar solubility of lead(II) chloride in a 0.102 M solution of NaCl?arrow_forward4.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY