
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
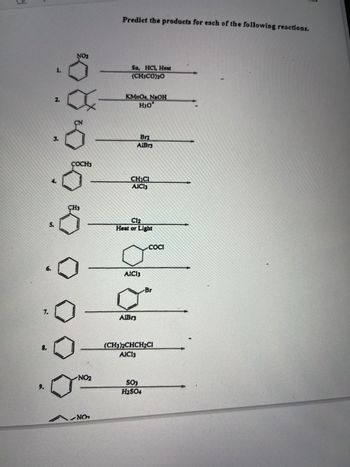
Transcribed Image Text:7.
9.
5.
6.
book
ÇOCH3
CH3
6
NO₂
NO
Predict the products for each of the following reactions.
Sn, HCl, Heat
(CHJCO)O
KMnO4, NaOH
H30*
Brz
AlBr3
CH3CI
AIC13
göteb
C12
Heat or Light
AIC13
AlBr
COCI
SO₂
H2SO4
Br
(CH3)2CHCH2CI
AICI3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- + |/ IM II g38 N K. H. P. R 7. 5. 4. %24 Q Search or enter website name MacBook Pro %3D Tinal this metal, initially at 20.0 °C? The specific heat of a certain type of metal is 0.128 J/(g-°C). What is the final temperature if 305 J of heat is added to 63.6 g ofarrow_forwardearned Activity 3.4.3. Solve me! 1. Calculate the heat of hydrogenation of ethane, C2H4 given the following thermochemical equations: 2 C(graphite) +3 H2 (g)-> C2H6 (g) 2 C (graphite) +2 H2 (g)-> C2H4 (g) AH3D-84.5 kJ/mol AH = 52.3 kJ/molarrow_forward2.5 p stion 4 What would the effect on the specific heat of your metal if one drop (0.05mL) of water at 100 degrees Celsius remained on your metal? O the effect would be negligible O the effect would cause the specific heat to be much higher O none of these choices are correctarrow_forward
- (6.3: Avogadro's Law, Similar to Question 38 on page 256) A cylinder with a moveable piston contains 0.200 mol of gas and has a volume of 125 mL. What is its volume (in mL) if an additional 0.200 mol of gas is added to the cylinder. Assume constant pressure and temperature. O 500 mL O 62.5 mL O 250 ml. 125 mlarrow_forwardJania.20 Chapter 3 3.100 When 1.0 9 of gasoline burns, it releases gasoline 0.749/ML SI (3.4.3.6) A) HOw many megajoules arc released srs 1.0 gai ot gasoline burns? Whenarrow_forwardFind the AH for the reaction below, given the following reactions and subsequent AH values: Reaction 3: 2cO2(g) + H2O(g) C2H2(g) + 5/202(g) C2H2(g) + 2H2(g) C2H6(g) AH = -194.5 kJ H2(g) + 1/2O2 (g) 2CO2(g) H20(g) → ΔΗ -55.2 kJ C2H6(g) + 7/202(g) 3H20(g) AH = -454 kJarrow_forward
- 53. The combustion of glucose, CH1,O, forms carbon dioxide gas and water vapour. When a 1.00 g sample of glucose was burned, it raised the temperature 100.0 mL of water by 37.0 °C. (5.2, 5.3, 5.5) AA (a) Write a balanced chemical equation for this reaction. (b) Use AH to calculate the enthalpy change of this of reaction. (c) Use bond energies in Table 1 on page 307 to calculate the enthalpy change of this reaction. The structural formula of glucose is shown in Figure 1.arrow_forward(6.37. Diatomic Elements The stable forms of hydrogen and oxygen at room temperature and pressure are gas phase, diatomic molecules H₂ and O₂. What is the sign of AH for the following processes? book Wiatomic es.a a. A solid with metallic properties is formed when hydrogen gas is compressed under extremely high pressures: £ show do 6.20 wirk?. ed in no H₂(g) → H₂(s) b. High-energy light shines on oxygen gas in the reaches of the atmosphere, converting oxygen gas to upper oxygen atoms: FAST 10 E,S O₂(g) → 2 0(g)arrow_forward.. The temperature of a 15.0 g sample of a metal (specific heat 0.040 J/g.°C) is raised by 18.2°C. How much heat (in J) has been absorbed by the metal? (15.09)(0.040g )arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY