
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
- Sales
- Variable
manufacturing cost - Fixed manufacturing cost
- Less ending inventory
- Fixed selling expenses
- Variable Selling Expenses
- Variable manufacturing cost
- Less ending inventory
- Variable selling expenses
- Fixed manufacturing cost
From the information given in the sheet determine 1-10.
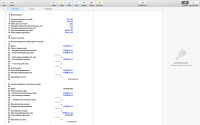
Transcribed Image Text:6 Data Section:
7
8 Actual production in units
9 Sales in units
10 Sales price per unit
11 Variable manufacturing costs per unit
12 Variable selling costs per unit
13 Fixed manufacturing costs
14 Fixed selling expenses
100,000
80,000
$30
$14
$2
$630,000
$100,000
A
15 -
16 Answer Section:
17 Income statement: Absorption costing
18
19 Sales
FORMULA1
20 Cost of goods sold:
21 Variable manufacturing costs
22 Fixed manufacturing costs
FORMULA2
FORMULA3
23
24 Total goods available for sale
25 Less ending inventory
FORMULA4
26
27
Cost of goods sold
28
29 Gross profit
30 Fixed selling expenses
31 Variable selling expenses
FORMULA5
FORMULA6
32
33 Operating income
34
=== ==== ===
35 Income statement: Variable costing
36
37 Sales
$2,400,000
38 Cost of goods sold:
39 Variable manufacturing costs
40 Less ending inventory
FORMULA7
FORMULA8
41
42
Variable cost of goods sold
43
44 Manufacturing margin
45 Variable selling expenses
FORMULA9
46
47 Contribution margin
48 Fixed manufacturing costs
49 Fixed selling expenses
FORMULA10
$100,000
50
51 Operating income
52
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Match each phrase that follows with the term it describes.arrow_forwardWhen using the high-low method to estimate costs, the formula “Change in Cost divided by Change in Units” (or “Change in Total Cost divided by Change in Activity Level”) is used to estimate the: Fixed cost per unit Mixed cost per unit Profit per unit Indirect cost per unit Variable cost per unit Differential cost per unit Opportunity cost per unitarrow_forwardUnder variable costing, all fixed manufacturing costs are treated as a a. product cost included in the cost of goods manufactured. b. product cost included in the cost of ending inventory. c. period expense deducted from manufacturing margin. d. period expense deducted from contribution margin.arrow_forward
- Chapter 3- CVP Cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis requires an understanding of cost behavior: variable and fixed costs. Cost behavior differs from the GAAP-based financial reporting focus: product and period costs. The two ways to categorize costs results in TWo different income statements: Absorption costing income statement: S-C-GM-SA-NI (Key assumption: Split costs into product and period costs) Variable costing income statement: S-VE-CM-FE-NI (Key assumption: Split costs into variable and fixed) 1. 2. Absorption Costing Income Statement Variable Costing Income Statement Sales $500,000 Sales $500,000 Less: Variable expenses Less: Cost of goods sold: Variable (DM+DL+VOH) Fixed (FOH) Gross margin 100,000 Product costs 100,000 60,000 S&A costs 110,000 340,000 Contribution margin 290,000 Less: Fixed expenses Less: Selling & administrative Variable 110,000 Product costs 60,000 Fixed 140,000 S&A costs 140,000 Taxable income $90,000 Taxable income $90,000 LINK THE LINEAR COST FUNCTION TO…arrow_forward7arrow_forwardDogarrow_forward
- Sunland Products manufactures and sells a variety of camping products. Recently the company opened a new factory to manufacture a deluxe portable cooking unit. Cost and sales data for the first month of operation are shown below: Beginning inventory Units produced Units sold Manufacturing costs Fixed overhead Variable overhead Direct labour Direct material Selling and administrative costs Fixed Variable 0 units 11,200 10,100 $100,800 $3 $12 $28 $207,100 per unit. per unit per unit $3 per unit sold The portable cooking unit sells for $110. Management is interested in the opening month's results and has asked for an income statement.arrow_forwardThe inventory cost computed under absorption costing is ____ the inventory cost computed using variable costing. Group of answer choices half of thrice as much equal to greater thanarrow_forwardUnder variable costing, which of the following are costs that can be inventoried Select one: O O a. variable manufacturing overhead b. fixed selling and administrative expense c. variable selling and administrative expense d. fixed manufacturing overheadarrow_forward
- An analyst is constructing a simple model to determine the gross and net profit of a product, given its profit per unit, quantity sold, and the total costs assigned to the product. The calculation for gross profit is Profit per Unit times Quantity. The calculation for Net Profit is Gross Profit minus Total Costs. A B 1. 2 Profit per Unit 8 3 Quantity |10,100 4 Gross Profit 5 6 Total Costs 6,100 7 8 Net Profit With the values for Profit per Unit, Quantity, and Total Costs shown above, what should the model return for the following calculated cells? Cell Value Gross Profit Net Profitarrow_forwardThe cost of the ending inventory under absorption costing is higher than the cost of ending inventory under varibale costing by 1. an amount equal to the fixed overhead cost per unit. 2. an amount computed by multiplying the units in the ending inventory by the fixed costs per unit. 3. an amount equal to the difference in the income amounts under both costing methods. 4. the amount equal to the fixed overhead cost charged to expense during the period.arrow_forward7. Which of the following is the best definition of a variable cost? A. A variable cost is one which is directly traceable to an activity of the business for which the cost will be used. B. A variable cost is one which is associated with goods or services purchased, or produced, for sale to customers. C. A variable cost is one which changes with changes in the level of activity, over a defined period of time. D. A variable cost is one which is spread over a number of activities of the business for which costs are to be determined.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education