
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
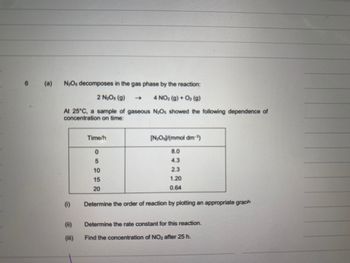
Transcribed Image Text:6
(a)
N₂Os decomposes in the gas phase by the reaction:
2 N₂O₁ (g)
4 NO₂ (g) + O₂(g)
At 25°C, a sample of gaseous N:Os showed the following dependence of
concentration on time:
Time/h
0
5
10
15
20
[N:O)/(mmol dm³)
8.0
4.3
2.3
1.20
0.64
Determine the order of reaction by plotting an appropriate graph
Determine the rate constant for this reaction.
Find the concentration of NO₂ after 25 h.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 26.20 The data provided in Figure 26.7 are based on the diffusion of O₂ into SiO₂ formed from the oxidation of (100) crystalline silicon at 1000°C. Estimate the diffusion coefficient of O₂ in SiO₂ formed from the oxidation of (111) crystalline silicon at 1000 °C, using the data in the table below, provided by Hess (1990).* Time 1.0 2.0 4.0 7.0 16.0 Measured SiO₂ Film Thickness (um) 0.049 0.078 0.124 0.180 0.298 0.070 0.105 0.154 0.212 0.339 The maximum solubility of O₂ in the SiO₂ is 9.6-10-8 mole 0₂/cm³ solid at 1000°C and 1.0 atm O₂ gas partial pressure. *D.W. Hess, Chem. Eng. Education, 24, 34 (1990).arrow_forwardtype solution in wordarrow_forward(2) Calculate the heat of reaction at 298K for the following reactions a) 3NO2(g) + H₂O(0) b) C3Hs (g) +02 (8) c) CaCO3(s) 2HNO3(+NO(g) ►CO2(g) + H₂O(n CaO(s)+COz(g)arrow_forward
- One half-cell in a voltaic cell is constructed from a copper wire electrode in a 4.0 x 10-8 M solution of Cu(NO3)2. The other half-cell consists of a zinc electrode in a 0.75 M solution of Zn(NO3)2. Calculate the cell potential. You may need to use the following data: Zn²+ (aq) + 2 e¯ + Zn(s) E° = -0.763 V Cu²+ (aq) + 2 e → Cu(s) E° = +0.337 V Potential =arrow_forward8.2 L of chlorine gas at 298 K and 3.0 atm is added to a rigid 4.0 L reaction vessel containing 3.2 moles of He gas and 2.4 moles of fluorine gas? Chlorine and Fluorine gas react according to the following reaction at 298 K. Cl2 (g) + 3 F2 (g) à 2 ClF3 (g) What is the partial pressure of ClF3 after the reaction is complete? If the reaction proceeded with a percent yield of 40%, what would be the partial pressure of ClF3?arrow_forwardUsing the phase diagram here, at what temperature will a solution of 36 mole % A begin to boil? Temperature-Composition Phase Diagram for Compositions of Compounds A and B 500 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 100 50 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 Composition (mole fraction B) Temperature (°C)arrow_forward
- The balanced equation below is for the reaction of magnesium with hydrochloric acid: • Mg(s) + 2HCI(aq) – MgCl,(aq) + H;(g) This reaction can be used to produce hydrogen gas, which is flammable (can catch on fire). If you have 2 moles of pure magnesium (Mg), and 2 moles of hydrochloric acid (HCI), according to the equation which is the limiting reactant? Show your work and/orarrow_forward29.2 Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) is a common contaminant in natural gas. The dissolution of H₂S gas in water is a linear function of partial pressure, as is described by Henry's law of the form PA = H x. Values of H vs. temperature are provided below: T (°C) H (atm) mole H₂S/ mole MEA 20 483 PA (mm Hg) 30 449 Given the relatively low solubility of H₂S in water, an amine- based chelating agent is added to the water to improve the solubility of H₂S. Equilibrium distribution data for H₂S in a 15.9 wt% solution of monoethanolamine (MEA) in water at 40°C is provided below: 40 520 50 577 0.000 0.125 0.208 0.362 0.643 0.729 0.814 0.00 0.96 3.00 9.10 43.1 59.7 106 Describe the effect of temperature on the solubility of H₂S gas in water. b. Prepare equilibrium distribution plots, in mole-fraction coordinates (y₁ -— XÃ), for the solubility of H₂S in water vs. H₂S in 15.9 wt% MEA solution at 40°C and 1.0 atm total system pressure. Comment on the relative solubility of H₂S in water vs. MEA solution.arrow_forwardP2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The