
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
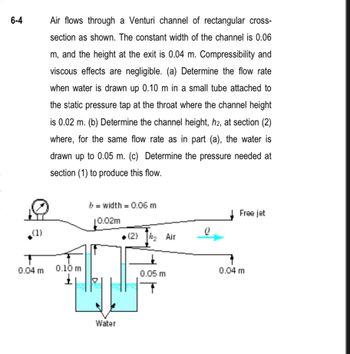
Transcribed Image Text:6-4
(1)
Air flows through a Venturi channel of rectangular cross-
section as shown. The constant width of the channel is 0.06
m, and the height at the exit is 0.04 m. Compressibility and
viscous effects are negligible. (a) Determine the flow rate
when water is drawn up 0.10 m in a small tube attached to
the static pressure tap at the throat where the channel height
is 0.02 m. (b) Determine the channel height, h2, at section (2)
where, for the same flow rate as in part (a), the water is
drawn up to 0.05 m. (c) Determine the pressure needed at
section (1) to produce this flow.
0.04 m 0.10 m
b = width = 0.06 m
10.02m
Water
(2) ₂ Air
0.05 m
Q
Free jet
0.04 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- answer first item onlyarrow_forwardWater is being pumped the through one inch diameter piping arrangement to a higher elevation (5 meters up). Assume incompressible fluid conditions and some heat losses to the surroundings. At the inlet water pressure is 1 bar, temperature 15C, and volumetric flow rate is 0.02 m3/s. At the exit pressure is 2.2 bar, temperature is 10C and velocity of the stream is 40 m/s. Determine: a.Density of the inlet stream using NIST tables. b.Mass flow rate [kg/s] c.Determine h2 from known p2 and T2 using NIST tables d.Find heat rate removed from Q=m(h1-h2) Use Energy Balance Equation with enthalpy difference and in the units of kW to find pumping power in kW. NOTE: The heat is removed from the system, so it should be negative in your equation! show all steps pleasearrow_forwardPROBLEM 5: In Lake Geneva (Switzerland), there is a water jet (called the Jet d’Eau) that is discharged 130 m straight upward (measured from the surface of the lake). The exit of the discharge pipe is 20 cm in diameter.arrow_forward
- Problem 5. A horizontal rough pipe with surface roughness of 1.5 × 104 m is used to transport pressurized air at a flow rate of 7 × 102 m³/s. The design guidance requires that the pressure drop must be no more than 4.2 kPa per 50 m length of the pipe. Determine the minimum diameter of the pipearrow_forwardWater is being pumped the through one inch diameter piping arrangement to a higher elevation (5 meters up). Assume incompressible fluid conditions and some heat losses to the surroundings. At the inlet water pressure is 1 bar, temperature 15C, and volumetric flow rate is 0.02 m3/s. At the exit pressure is 2.2 bar, temperature is 10C and velocity of the stream is 40 m/s. Determine: a.Density of the inlet stream using NIST tables. b.Mass flow rate [kg/s] c.Determine h2 from known p2 and T2 using NIST tables d.Find heat rate removed from Q=m(h1-h2) Use Energy Balance Equation with enthalpy difference and in the units of kW to find pumping power in kW. NOTE: The heat is removed from the system, so it should be negative in your equation! show all steps pleasearrow_forwardTank 1 Tank 2 g Question 1 Consider the flow of water (p= 10³ kg/m³, u = 10³ Pa-s) from tank 1 to tank 2. A centrifugal pump is installed in this piping system with length L = 300 m and diameter D = 40 cm cast-iron pipe. The water surface of tank 1 is 15 m higher than the water surface of tank 2. You may neglect minor losses but not major losses. The gravity cannot be neglected. Assume steady-state and no friction in the tanks. (a) Simplify the equation of the system curve Ap vs Q. Do not place numerical data. (b) Plot the system curve Ap vs Q (0 ≤Q≤2 m³/s). (c) Find the volumetric flow rate when the pump is not operating. (d) Find the power supplied to the water and to the pump if n = 0.9 and 1 m³/s. (e) Consider a pump: Ap = 106 105 Q², where Ap in Pa and Q in m³/s. Find the operating point. What is the minimum and maximum volumetric flow rate that this pump can deliver?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY