
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305501607
Author: Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
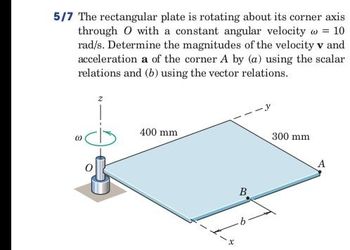
Transcribed Image Text:5/7 The rectangular plate is rotating about its corner axis
through O with a constant angular velocity = 10
rad/s. Determine the magnitudes of the velocity v and
acceleration a of the corner A by (a) using the scalar
relations and (b) using the vector relations.
400 mm
300 mm
x
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A rifle at A is fired at a target at B. If the speed of the bullet is 1400 ft/s, determine the rectangular form of the velocity vector v.arrow_forwardA light fixture of negligible mass, has three applied forces acting on it as shown. |F,| = 4 kN 1.2 m 1.2 m 1.2 m 2.8 m |F,| = 6 kN y 45° |F| = 5 kN Using the coordinate system shown, determine the components of vector F = Fxi + F,J+F,k (Answer in Kilo Newtons) Fy Choose. F: Choose.. F. Choose.. Choose... 10.11 -6 -4 3.54arrow_forward1. The slotted link is pinned at 0, and as a result of the constant angular velocity é = 6 rad's it drives the peg P for a short distance along the spiral guide r = (0.6 0) m where e is in radians. When e = 80 deg, Find: a. Find e, é, ë,r,r, ř. (in radians) b. The radial components, transverse components, and magnitudes of the velocity [4maeie). - The radial components, transverse components, and magnitudes of the acceleration of P at the instant. asks). %3D 0.8 m r=0.6 0 ô =6 rad/sarrow_forward
- An automobile P is traveling along a circular track of radius R=958.4 m. At position "A" on the track, the automobile has a speed of UA = 10.3 m/s. At this position, the driver of the automobile applies the brakes causing the speed of the automobile to change with distance s traveled along the track according to the following equation: U(S) = VA COS(0.001s) m/s (cos is in radians), where s is given in meters. Determine the magnitude of the acceleration for the driver when the automobile reaches position "B" on the track where "B" is a quarter of the distance around the track from position "A". R B O circular trackarrow_forwardFor the circular thin plate with a square hole as shown in the image below, its radius R = 0.32 m and the side of the square /= 0.22 m, and the material has a mass per unit area of 14 kg/m2. If at the instant shown, it is subjected to a force P= 44 N, and has a counterclockwise angular velocity of W = 3.8 rad/s, determine the angular acceleration (in rad/s?) of this plate. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s?. R Parrow_forward4. 2) The hydraulic cylinder D extends, moves the rigid rod ABC, and causes the collar A to move with velocity and acceleration both to the left. If the dimensions 4 1.0 ft, and 2 = 1.7 ft, VA = 4.9 ft/s, aa = 2.6 ft/s2, and the angle 0 = 27°, determine the speed of point B. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper unit. В 12 D a Your Answer: Answer units 1,arrow_forward
- For the circular thin plate with a square hole as shown in the image below, its radius R = 0.42 m and the side of the square /= 0.15 m, and the material has a mass per unit area of 15 kg/m2. If at the instant shown, it is subjected to a force P= 47 N, and has a counterclockwise angular velocity of w = 2.1 rad/s, determine the angular acceleration (in rad/s?) of this plate. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s². R 4 3 Your Answer: Answerarrow_forwardFor the circular thin plate with a square hole as shown in the image below, its radius R = 0.49 m and the side of the square /= 0.22 m, and the material has a mass per unit area of 14 kg/m². If at the instant shown, it is subjected to a force P= 43 N, and has a counterclockwise angular velocity of W = 2.3 rad/s, determine the angular acceleration (in rad/s²) of this plate. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s². R @ Your Answer: Answer 5 3 Parrow_forwardThe length of link OB is 325 mm and it is rotating about fixed axis O at a speed of 116 rev/min. Find the liner velocity of point B in m/sec. VB = m/s %3Darrow_forward
- If the rod AB rotates counterclockwise with angular velocity, ω AB =8rad / s Calculate the velocities of the blocks C and D at the moment shown in the figure below.arrow_forward4. 3) The hydraulic cylinder D extends, moves the rigid rod ABC, and causes the collar A to move with velocity and acceleration both to the left. If the dimensions 4 = 1.0 ft, and 2 = 1.6 ft, VA = 3.6 ft/s, aa = 2.2 ft/s2, and the angle 0 = 27°, determine the speed of point C. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point, and proper unit. %3D В 12 D Your Answer: Answer units 1,arrow_forward1. What is the vertical acceleration and normal velocity when the spring is stretched an extra 0.70.7 mm (note as d in the drawing)? 2. What is velocity and acceleration when the stretch, d, is 0.10.1 mm?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L