
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
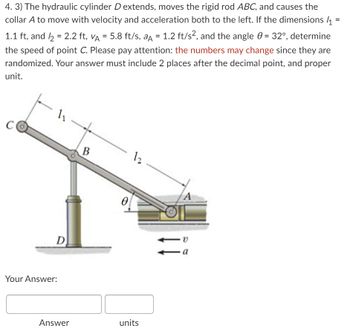
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem 4.3:**
A hydraulic cylinder \( D \) extends, moving the rigid rod \( ABC \), and causes the collar \( A \) to move with velocity and acceleration both to the left. Given:
- \( l_1 = 1.1 \, \text{ft} \)
- \( l_2 = 2.2 \, \text{ft} \)
- \( v_A = 5.8 \, \text{ft/s} \)
- \( a_A = 1.2 \, \text{ft/s}^2 \)
- The angle \( \theta = 32^\circ \)
Determine the speed of point \( C \).
**Important:** Numbers may change, as they are randomized. Provide your answer with two decimal places and include the appropriate unit.
---
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram shows a hydraulic cylinder \( D \) supporting a rod structure \( ABC \).
- Point \( A \) moves horizontally to the left with marked velocity \( v \) and acceleration \( a \).
- The rod extends from point \( A \) to point \( B \), and then to point \( C \).
- The lengths \( l_1 \) and \( l_2 \) represent segments \( BC \) and \( AB \) respectively.
- The angle \( \theta \) is between rod \( AB \) and the horizontal line.
- The speed of point \( C \) is to be calculated based on this setup.
**Your Answer:**
| Answer | Units |
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. A box slides down a ramp with position vector given by r= 0.5t i + 3f² j + 8t k (m), where t is in s. At t = 3 s, what is the box's velocity and acceleration? What is the box's speed?arrow_forwardIn this question, assume the "additional displacement" is in the positive u direction. A mass weighing 16 lbs stretches a spring 8 inches. The mass is in a medium that exerts a viscous resistance of 1 lbs when the mass has a velocity of 2 ft/sec. Suppose the object is displaced an additional 5 inches and released. Find an equation for the object's displacement, u(t), in feet after t seconds. u(t) =arrow_forward1. F3 The lateral-direction equations of motion of an aircraft in steady, straight and level flight are v=-0.243v-136.25r+9.80-0.7595 +4.825 p+0.0557r=-0.195v-1.695p+0.913r+16.535 +6.995 0.0152p+ 0.106v+0.039p-0.624r +0.3195-6.43% O=P (a) 4 € Consider the state-space representation of the equations of motion given by. Xlat Alat Alat + Blatulat ' and where and with F4 % Ylat 5 = Clat Xlat + Dlat lat Xlat = (V, p, r, $)T Ylat = (Y1, Y2, 3), Y₁ =B=V/VR, Determine the matrices Alat Blat, Clat, and Dlat- 10 F5 ^ Y2 = r, 6 1) F6 H y3 = (ay) eg 7 PrtScn F7 = V +136.25r. W * 8 Home F8 ( 9 End F9 ) PgUp 0arrow_forward
- HW help: Just part c please.arrow_forwardSolve the following application problem: The model s(t) = -16?2 + 5? + 3 describes the height(in feet) of a diver at time ? is measured in seconds. Find the velocity of the diver when the diver hits the water.arrow_forwardA four-bar mechanism is used to transmit power to slider E. Link AC rotates counterclockwise at 100 rpm. A and B are fixed points. The following linkages are measured in cm: AC=35, AB=70, CD=45, BD=45, DE=40. Find the instantaneous velocity of slider E in cm/s 1.Draw the mechanism in appropriate scale on your paper2. Find the instantaneous linear velocity of C3. Find a point on your paper to draw the velocity polygon and scale the magnitude of the computed linearvelocity4. Use the relative velocity equation for finding the linearvelocity of D; ? = ? + ?? ? ?/?5. Remember that although the magnitudes are unknown, their directions can be identified6. Obtain the magnitudes of the unknown velocities from the velocity polygon7. For Link DE, repeat the process by using ? = ? + ??the line as much as needed8. Remember that E is a SLIDER therefore it can only goin the direction where its movement is not constrained? . Add the vector ? to the head of ? and extend?/? ?/??arrow_forward
- Steam enters an adiabatic turbine steadily at 6 MPa and 450 °C and leaves at 500 kPa and 250 °C. If the power output of the turbine is 3.9 MW determine the isentrFopic efficiency of the turbine and the mass flow rate of the steam flowing through the turbine. TI Pi T2 P2 %23arrow_forwardWe can make assumptions for the unknown value to to be able to find these: Length of swing arm is 19 in, length of sling is 10.5 in Find: A)position vectors for location B and C B) angular velocity for swing arm and sling C) angular acceleration of the swing arm and slingarrow_forwardI need help with this physics problemarrow_forward
- A particle is held and then let go at the edge of a circular shaped hill of radius R = shown below. The angular motion of the particle is governed by the following ODE: + 0.4 02 - 2 cos 0 + 0.8 sin 0 = 0 where is the angle in rad measured from the top (CCW: +), ė 5m, as = wis the velocity in rad/s, ==a is the angular acceleration in rad/s². Use MATLAB to numerically integrate the second order ODE and predict the motion of the particle. (a) Plot and w vs. time (b) How long does it take for the particle to fall off the ring at the bottom? (c) What is the particle speed at the bottom. Hint v = Rw. in de all questions the particles inside the tube. /2/07/25 Particle R 0 0 R eled witharrow_forwardExample (3): A body moves on a straight line according to the equation: S = 4 t + 2 t2- 2 t + 5, where (s) is displacement, (t) is the time interva , Find out displacement, velocity , and acceleration when t= 3 sec . Solution: 2 12 - 2 t+ 5arrow_forwardA point P has position vector Top = at²î + bt°j + ct®k. Assume: a = 1.8 m/s?, b dV,l = 1.6 m/s3, c = 1.4 m/s. Find dt (in m/s2) at t = 0.6 s.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY