
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
For the venturi meter shown in figure 9, calculate the manometer deflection, h, if the velocity of flow of water in the 25mm diameter section is 10m/s
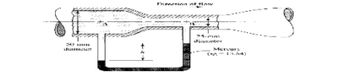
Transcribed Image Text:diamcomm
Dimetion of flow
25-mm
diameter
Mercury
(31:5.54)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- #2 Answer only the 2 question.arrow_forwardRequired information A 90° elbow in a horizontal pipe is used to direct water flow upward at a rate of 41 kg/s. Another identical elbow is attached to the existing elbow such that the water flow makes a U-turn as shown in the second figure. The diameter of the entire elbow is 10 cm. The elbow discharges water into the atmosphere, and thus the pressure at the exit is the local atmospheric pressure. The elevation difference between the centers of the exit and the inlet of the elbow is 50 cm. The weight of the elbow and the water in it is considered to be negligible. Take the momentum-flux correction factor to be 1.03 at both the inlet and the outlet. Take the density of water to be 1000 kg/m³. Water m kg/s L. X Water FR₂ 50 cm FRX 50 cm If another (identical) elbow is attached to the existing elbow so that the fluid makes a U-turn, determine the gage pressure at the center of the inlet of the elbow. The gage pressure at the center of the inlet of the elbow is kPa.arrow_forwardThe water speed coming out on the pipe from a cylindrical tank shelter as in the image beside is (in the picture) known g = 9.81 m / s² H is the initial high water (m), l is the length of the pipe (M), t is the time passing. Determine the high H needed to produce water speed v = 5 m/s at t = 2.5 seconds for pipe length L = 4 m, calculate 1. BISECTION 2. False position for initial guess XL = 0 and XU = 2 m Calculate up to £ = 1%arrow_forward
- A manometer is used to measure the pressure difference between points A and B in a pipe as shown. Water flows in the pipe, and the specific gravity of the manometer fluid is 3.0. The distances and manometer deflection are indicated on the figure. Find (a) the pressure differences and (b) the difference in Piezometric Pressure, (c) the difference in Piezometric head. Express both answers in kPa.arrow_forwardQ2) The flow-metering device shown consists of a stagnation probe at station 2 and a static pressure tap at station 1. The velocity at station 2 is 4 times that at station 1. Air with a density of 1.2 kg/m3 flows through the duct. A water manometer is connected between the stagnation probe and the pressure tap, and a deflection of Ah = 13.7 cm is measured. What is the velocity at Vertical station 2? Waterarrow_forwardThe venturi meter shown below carries water at 60°C. The inside dimensions are machined to the sizes shown in the figure. The specific gravity of the gage fluid in the manometer is 1.25. Calculate the velocity of flow at section A and the volume flow rate of water. 200-mm inside diameter Flow 0.46 m y is an unknown distance y 300- mm inside diameter 1.18 marrow_forward
- H.W.: A horizontal venturimeter with diameter 20cm and throat 10 cm is used to measure the flow of oil of r.d. 0.8. The discharge of oil through venturimeter is 60 L/s. Find the reading of the oil-mercury differential manometer (x=?), take Cd=0.98. Ans. X= 18.12 cm.arrow_forwardA manometer is attached to a water tank as shown in the figure. Find the height of the free water surface above the bottom of the tank. water 0.2m 0.15m 0.15m Hg(13.6)arrow_forwardWater flows at 0.07 cubic meter per second through a pipe. A horizontal venturi meter with throat diameter of 150-mm was used to measure the velocity inside the pipe. Based on manometer reading, the differential gauge is deflected 1.2 meter. If the specific gravity of the manometer fluid is 1.60, the velocity, in meter per second (m/s), of water inside the pipe is ____ ANSWER ASAParrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning