
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
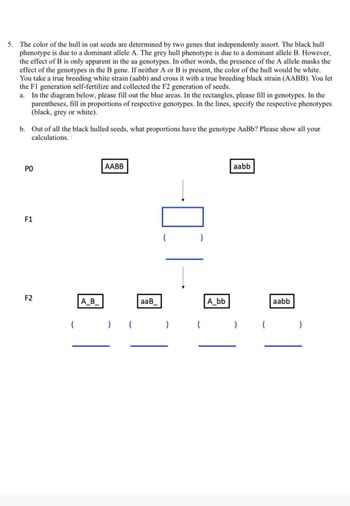
Transcribed Image Text:5. The color of the hull in oat seeds are determined by two genes that independently assort. The black hull
phenotype is due to a dominant allele A. The grey hull phenotype is due to a dominant allele B. However,
the effect of B is only apparent in the aa genotypes. In other words, the presence of the A allele masks the
effect of the genotypes in the B gene. If neither A or B is present, the color of the hull would be white.
You take a true breeding white strain (aabb) and cross it with a true breeding black strain (AABB). You let
the F1 generation self-fertilize and collected the F2 generation of seeds.
a. In the diagram below, please fill out the blue areas. In the rectangles, please fill in genotypes. In the
parentheses, fill in proportions of respective genotypes. In the lines, specify the respective phenotypes
(black, grey or white)..
b. Out of all the black hulled seeds, what proportions have the genotype AaBb? Please show all
calculations..
your
PO
F1
F2
(
A_B_
AABB
(
aaB
(
)
(
A_bb
aabb
)
aabb
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 1 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The color of chickens is determined by interacting loci: AA or Aa give white, aaBB or aaBb give colored, and aabb produce white. Describe the epistatic interactions occurring between these two genes: A. aa is epistatic to B_, bb and bb are epistatic to A_,aa B. A_ is epistatic to B_,bb and bb is epistatic to A_,aa C. None of the abovearrow_forward5. Flower color in snapdragons is inherited in an incompletely dominant manner. Assume that RR = red flowers, Rr = pink flowers, and rr = white flowers. What would be the genotype and phenotype ratios of the offspring of two plants with pink flowers?arrow_forward1. In fruit flies, the phenotype for eye color is determined by a certain locus. E indicates the dominant allele and eindicates the recessive allele. The cross between a male wild-type fruit fly and a female white-eyed fruit flyproduced the following offspring.Wild-typeMaleWild-typeFemaleWhite-eyedMaleWhite-eyedFemaleBrown-eyedFemaleF1 0 45 55 0 1The wild-type and white-eyed individuals from the F1 generation were then crossed to produce the followingoffspring.F2 23 31 22 24 0(a) Determine the genotypes of the original parents (P generation) and explain your reasoning. You may usePunnett squares to enhance your description, but the results from the Punnett squares must be discussed inyour answer.(b) Use a Chi-squared test on the F2 generation data to analyze your prediction of the parental genotypes. Showall your work and explain the importance of your final answer.(c) The brown-eyed female in the F1 generation resulted from a mutational change. Explain what a mutation is,and discuss…arrow_forward
- 1. A new species of animal called the rekamriliob has been found in the wild. The lab you work in has been tasked with studying its genetics. So far, there have been 2 main phenotypes found in the wild. Through selective breeding, your lab has determined that the gene for purple color (P) is dominant to the gene for golden color (p). Another lab has determined that the thick limb trait is dominant to the thin limb variety. If you breed a purebred purple thick limbed rekamreliob male with a golden thin limbed female, you get 100% thick limed offspring that are purple in color. If you take two of these organisms and breed them together, please predict the following. Assume that rekameliobs lay an average of 32 eggs. The gametes produced if the genes are unlinked b. genes The expected numbers of the possible phenotype in the offspring with unlinked The gametes produced if the genes are linked (list all possibilities, and show which ones are the result of crossing over) d. List the…arrow_forward3. In poultry, a gene C produces creeper (very short legs) in the heterozygous condition and is lethal in the homozygous condition. The c allele of the gene produces normal legs in the homozygous condition. Barring is due to a dominant sex-linked gene, B, and nonbarred to its recessive allele, b. In chickens, males are ZZ (similar to XX) and females are ZW (similar to XY). A creeper male homozygous for barring is mated with a creeper female who is nonbarred. What kinds of offspring can be expected from this cross and in what proportions will each kind occur?arrow_forward1. You are given a female F1 of unknown genotype. You cross the female fly to a homozygous male that has forked bristles and malformed eyes. The offspring of the cross is shown below: (Define symbols for your traits) Phenotype Forked bristles, normal eyes 752 Number Genotype Forked bristles, malformed 56 eyes Malformed eyes, normal bristles Normal eyes, normal bristles 820 64 a. What are the genotypes of the offspring? b. Based on the progeny, what were the genotypes of the F1 parents? What is the distance between for and mal?arrow_forward
- 8. In guinea pigs, the allele for black fur (B) is dominant over the allele for white fur (b). Similarly, the allele for straight hair (H) is dominant over the allele for having rough hair (h). Pure breeding rough haired guinea pigs with black fur were crossed with pure breeding straight haired guinea pigs with white fur. a. State the genotype and the phenotype of the F1 individuals produced as a result of this cross.b. Two F1 offspring were mated together. Calculate the expected ratio of phenotypes in the F2 generation.c. Show the completed Punnett square below.arrow_forward6. There are two enzymes LDH1 and LDH2. The gene that encodes this enzyme is X-linked. You extract the enzyme from different cells in several people and carry out electrophoresis. Give the genotypes for each person Draw the banding pattern that you would expect in the gel. Male with Male with Female Female Heterozygous LDH1 gene homozygous female LDH2 homozygous for LDH2 for LDH1arrow_forward17. Three recessive traits in aardwolf (a real animal) are stripe-less (s), dwarf (d), and fluffy mane (f). A stripe-less and fluffy female aardwolf mates with a dwarf male aardwolf to produce an F1 that is all WT (has stripes, normal size, and non-fluffy mane). When an F1 is test crossed to a fully recessive aardwolf, the following F2 are produced: Stripe-less, fluffy, normal sized 89 Striped, non-fluffy, dwarf 92 Stripe-less, non-fluffy, dwarf 1 Striped, fluffy, normal sized 2 11 13 19 20arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education