
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
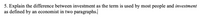
Transcribed Image Text:**Question 5: Explain the difference between investment as the term is used by most people and investment as defined by an economist in two paragraphs.**
*Note: No graphs or diagrams are present in the provided image.*
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Investment- Investment means to invest the money in productive and non productive activities to generate national income and to improve productive capacity in an economy. Investment leads towards capital formation .
Investment can be defined in terms of common people and economists.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4. Consider an economy that produces two different types of goods: apples and oranges. Assume that apple production rises 3% in 2013 (relative to 2012) and orange production rises 4% in 2013. Which of the following statements is TRUE? a) Nominal GDP growth is positive b) Real GDP growth is less than 3% c) Real GDP growth is between 3% and 4% d) Nominal GDP growth is zero.arrow_forward2. The circular-flow model The following diagram presents a circular-flow model of a simple economy. The outer set of arrows (shown in green) shows the flow of dollars, and the inner set of arrows (shown in red) shows the corresponding flow of inputs and outputs. Firms Markets for Goods and Services Markets for Factors of Production Based on this model, firms earn revenue when Event Households purchase Suppose Lucia earns $650 per week working as a corporate attorney for Rowan and Martin Associates. She uses $10 to order a mojito cocktail at Little Havana. Little Havana pays Kenji $350 per week to wait tables. Kenji uses $250 to purchase legal service from Rowan and Martin Associates. in product markets. Identify whether each of the following events in this scenario occurs in the factor market or the product market. Factor Market Product Market Kenji earns $350 per week working for Little Havana. Lucia spends $10 to order a mojito cocktail. Kenji spends $250 to purchase legal service…arrow_forward4. In a capitalist market economy, the decision to save is made by the same people who make the major investment decisionsarrow_forward
- 5. The circular flow model The following diagram presents a circular flow model of a simple economy. The outer set of arrovs (shown in green) shows the flow of dollars, and the inner set of arrows (shown in red) shows the corresponding flow of inputs and outputs. Markets for Goods and Services Firms Households Markets for Factors of Production Based on this model, households earn income when firms V purchase in the resource markets. resourcesarrow_forwardAn individual lives for 5 years - 4 years of work followed by 1 year of retirement. He earns $25,000 during each year of work but $0 during retirement. The interest rate is 5% Assume that the individual wants his consumption to be the same in each of the 5 years. a. What utility function would justify this choice of consumption pattern? b. Write out the intertemporal budget constraint in present value form.c. What level of consumption does he choose?d. What is the value of his assets at the beginning of retirement?arrow_forward2. Assume: Yd = $ 5000 billion %3D b = .95 a = $ 520 billion A)What is consumption (C) ? B)What are savings (S) ? C)What is APC ? D)What is APS ?arrow_forward
- Course: Microeconomics - Intertemporal Consumption Decisions Consider a person who consumes in the 2 periods (C1 and C2), but ONLY works and earns an income in the first period (C1). Assume that consumption in each period behaves as a normal good.a) What is the effect of a rise in income on welfare? And on consumption in both periods? GRAPHb) What is the effect of a rise in the interest rate (assume that r goes from 10% to 15%) that occurs before the consumption decisions on welfare? GRAPH and on consumption in both periods?) GRAPHarrow_forward6. Shifts in production possibilities Suppose Argentina produces two types of goods: agricultural and capital. The following diagram shows its current production possibilities curve (PPC) for barley, an agricultural good, and airplanes, a capital good. Drag the production possibilities curve (PPC) on the graph to show the effects of a time-saving innovation in the manufacturing of airplanes. Note: Select either end of the curve on the graph to make the endpoints appear. Then drag one or both endpoints to the desired position. Points will snap into position, so if you try to move a point and it snaps back to its original position, just drag it a little farther. AIRPLANES (Thousands) 180 150 120 8 O 60 30 0 0 70 PPC 140 210 280 BARLEY (Millions of bushels) 350 420 PPCarrow_forward3arrow_forward
- The following table contains data on the relationship between saving and income. a. Rearrange the income and saving data into an ascending order of income and graph them on the accompanying grid. Income per Year $ Saving per Year 15,000 $ 0 10,000 5,000 20,000 1,000 -500 500 0 1,500 Rearranged Rearranged Income per Year Saving per Yeararrow_forward3. Suppose you currently earn $80,000 a year. You are considering a job that will increase your lifetime earnings by $400,000 but that requires an MBA. The job will mean also attending business school full time for two years at an annual cost of $70,000. You already have a bachelor’s degree, for which you spent $150,000 in tuition and books. a. Which of the above information is relevant to your decision on whether to take the job? b. What is the opportunity cost of going to school to study MBA? c. Should you take the job? [Note: You will need to get the MBA]arrow_forward23 Introduction to Economics Please solve it very quickly ????arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education