
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
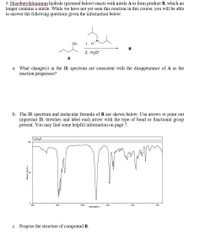
Transcribed Image Text:5. Diisobutylaluminum hydride (pictured below) reacts with nitrile A to form product B, which no
longer contains a nitrile. While we have not yet seen this reaction in this course, you will be able
to answer the following questions given the information below.
-A.
CN
1. H
B
2. H30*
A
What change(s) in the IR spectrum are consistent with the disappearance of A as the
reaction progresses?
a.
b. The IR spectrum and molecular formula of B are shown below. Use arrows to point out
important IR stretches and label each arrow with the type of bond or functional group
present. You may find some helpful information on page 7.
CH120
L00
4000
3000
200
1000
HAVENUNBERI l
c. Propose the structure of compound B.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please give a reasonable mechanism for the following reaction using a multiple component reactions. Please draw it out and write out the steps. PLEASE SHOW WITH ARROWS. 5 PhNH + n-Bu 10 mol% TI (NM)2(doma) + ABU-NC tol 100 °C, 48 h, 77% Bu n-Buarrow_forward9arrow_forwardDevelop the following reaction mechanisms:arrow_forward
- Please help….in simple terms Because I’m very confused.arrow_forward8. Consider each reaction below carefully. Identify the acid and base on the reactant side of the reaction. Draw the expected product of a proton transfer between the acid and base. Estimate the pka of the acid and conjugate acid. Determine whether the reaction is product or reactant favored. a. b. C. d. OH @O HICI HO NaH 39arrow_forwardQuestion 8 Please predict the products for each of the following reactions: ABCD A 1. Na 2. PrBr Na 10 1. TsCI, Py 2. NaBr, DMSO SOCI₂, Py H-NG Cro₂Cl Py (pyridine) OH PCC Na2Cr2O7 H2SO4 HCI ZnCl2 1. MsCI, Et N (base) 2. KI, DMF B с D Brarrow_forward
- Which synthesis plan is best to make the following target molecule? CN target molecule option 3 + NaCN Br option 1 + NaCN OH + HCN option 4 Br option 2 + HCN ÕHarrow_forwardDraw the product of the reaction shown below. Ignore inorganic byproducts. O₂N 1 1 1 1 NaOCH3 Drawing TV 1 www 1 1 NO2 CI 1 I 1 Iarrow_forwardQuestion 7 Please predict the products for each of the following reactions: ABCD 1. Na 2. PrBr Na 10 1. TsCI, Py 2. NaBr, DMSO A SOCI₂, Py TsCl Py (pyridine) H-N→ CrO3Cl B PCC OH Na2Cr2O7 H₂SO4 HCI ZnCl2 2. KI, DMF 1. MsCI, Et₂N (base) с D ox oarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY