
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
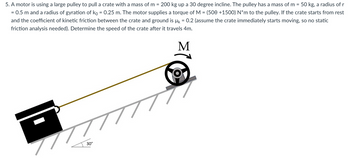
Transcribed Image Text:5. A motor is using a large pulley to pull a crate with a mass of m= 200 kg up a 30 degree incline. The pulley has a mass of m = 50 kg, a radius of r
= 0.5 m and a radius of gyration of ko = 0.25 m. The motor supplies a torque of M = (500 +1500) N*m to the pulley. If the crate starts from rest
and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and ground is µ = 0.2 (assume the crate immediately starts moving, so no static
friction analysis needed). Determine the speed of the crate after it travels 4m.
M
777
30°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 13 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 6 The uniform solid cylinder shown in the figure is released from rest on the 0 = 60 degree incline and slips as it rolls down the incline. The cylinder has mass m = 10 kg and radius r = 0.45 m. The coefficient of friction between the cylinder and the incline is µ = 0.15. Take the acceleration due to gravity to be g = 9.81 m/s². link to image 0 (c) Calculate the following: (a) the normal reaction N between the cylinder and the incline; g (b) the linear acceleration a of the centre of mass of the cylinder; the angular acceleration a of the cylinder; X A Moving to another question will save this response. (d) the minimum coefficient of friction required to prevent the cylinder slipping down the incline. 截图和草 截图已保存 选择此处标arrow_forwardThe tension in a pulley belt is 300 N when stationary. The smaller pulley has a diameter of 300 mm and a speed of 1420 rev/min. The coefficient of friction between the belt and the pulley is 0·4 and the angle of lap is 160°. (a) Calculate the tension in each side of the belt at operating speed. (b) Determine the power transmitted when the belt is on the point of slipping. If the pulley system uses a flat belt of CSA 500 mm² and density 1300 kg/m3, determine: (c) The power transmitted, when the mass of the belt is taken into consideration.arrow_forward2. Bar AB starts from rest at 0 = 0 with the constant angular acceleration of 6 rad/sec?. The block of mass m begins sliding on the bar When e = 45 degrees, 0.20 m a. Compute time for the bar to reach 45 degrees from the horizontal b. Compute the normal reaction between the bar and block. c. Determine the coefficient of static friction between the block and the bar.arrow_forward
- The uniform cylindrical drum D weighs 42.0 lb. The coefficient of static friction at all surfaces is 0.600, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.500 at all surfaces. The cylinder is pushed by force P applied to a pad as shown, and it is intended for the cylinder to translate horizontally without rotation. a) Calculate the minimum force P required.b) Calculate the acceleration of the drum.arrow_forwardA pile-driver hammer has a mass of 300 kg and is to be raised 16 m in 4 sec. The total friction on the guides is constant at 400 N. What constant pull must be exerted on the cable?arrow_forwardconsider the mass and pulley system in the attached file. mass m1 = 29 kg and mass m2 = 12kg. the angle of the inclined plane is given and the coefficient of kinetic friction between mass m2 and the inclined plane is uk = 0.12. assume the pulleys are massless and frictionless when mass m2 moves a distance 4.94 m up the ramp, how far downward does mass m1 move? d= ?arrow_forward
- Situation 5: Suppose the coefficient of kinetic friction between me and the plane as shown in figure is µ = 0.2 and that m = 20 kg and m² = 20 kg 53. What is the acceleration of Block A 0.605 -0.605 0.303 -0.303 60° 54. What is the tension on the chord? 80.31 N 72.12 N 78.17 N 66.71 N 1.1 m/s 52. What is mass of block B in order to move 1m up in an inclined when the block initially at rest 18.83 kg 20.41 kg 15.61 kg 25.12 kg 30° 55. What is the time required for block B to reach the top assuming it is initially 2.5 m away. 4.06 S 1.07 s 2.87 s 3.24 sarrow_forwardA tire has a weight of 55 lb and a radius of gyration of kg=0.6 ft. If the coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the tire and plane are µs=0.2 and Hk=0.15, a) Draw the FBD and KD of the tirearrow_forwardA block of wood of mass 20 kg is supported as shown in the diagram. If the string suspending the 10 kg mass and connected to the 20 kg mass is light and inextensible and the coefficient of friction, u between the mass and the plane is 0.3 neglecting friction in the pulley (i) Compute the acceleration of the block. (ii) Determine the tension in the rope. 20 kg 10 kg 30°arrow_forward
- The torsional spring has a stiffness of 20 N-m/rad and is undeflected when the 3-kg uniform slender bar is in an upright position. If the bar is released from rest in the horizontal position shown, find its angular velocity as it passes the vertical position. Neglect friction effects. 4 Type here to search ThinkVision K - Pan Tab Cape Look Esc Q A Z G FT W S # ONDA 3 F2 E D A $ 4 R F 5 F4 T G XCVB 8 a Y H N P6 F6 U J M F7 K ( F8 F10 F11 +Backspace Enter T F12 Shift Print Screen SysRq Insert 0.5 m Scroll Lock Delete Home Break End Page Up Page Down Naam Lock K 37°F Cloudy Home Lenovo B 20arrow_forwardA box with mass m = 2.75 kg rests on the top of a table. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the table is μs = 0.71 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is μk = 0.34. Write an expression for Fm the minimum force required to produce movement of the box on the top of the table. Solve numerically for the magnitude of the force Fm in Newtons. Write an expression for a, the box's acceleration, after it begins moving. (Assume the minimum force, Fm, continues to be applied.) Solve numerically for the acceleration, a in m/s2.arrow_forwardIf the coefficient of static friction between 150kg crate and the ground is US=0.3, calculate the minimun coefficient of static between the man shoes and the ground so that man can move the createarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY