
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:Practice Problems
Date:
gpb.org/physics-motion
Work each of the following problems. SHOW ALL WORK.
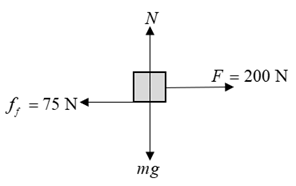
5. A 25 kg block is pulled with an applied force of 200 N across a horizontal surface. The block experiences a
frictional force of 75 N.
a. Draw a free-body diagram for the block, including all forces acting on the block.
b. Determine the net force acting on the block.
c. Calculate the acceleration of the block.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
a)
Draw the free-body diagram of the block.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3. Starting from rest, a 150 kg body experiences a force of 100 newtons acting on it in a direction parallel to the positive x-axis and a force of 150 newtons acting at 55° with respect to the positive x-axis.a. What is the net force acting on the body? Include direction.b. What is the acceleration of the body?c. What velocity does it reach after 5 seconds?arrow_forwardA heavy ball is thrown straight upward. After the ball leaves the thrower's hand, what forces act on the ball? a. A constant downward force from gravity, along with a steadily decreasing upward force from the thrower. b. A steadily decreasing upward force from the thrower on the way up, then a nearly constant force from gravity on the way down. c. A downward force of gravity that decreases substantially as the ball gains height, then increases substantially as the ball falls back downward. d. A steadily decreasing upward force from the thrower on the way up, then a steadily increasing force from gravity on the way down. e. A nearly constant downward force of gravity.arrow_forward5. DETAILS Three boxes, A, B, and C, are placed on a frictionless surface as shown in the diagram below. с Additional Materials Reading OSCOLPHYS2016 4.5.WA.048. B If you push on box A with a force of 8.25 N, find the contact force (in N) between each pair of boxes. Here m 5.15 kg, ma 3.40 kg, and me 1.50 kg. contact force between A and B contact force between B and C MY NOTES PRACTICE ANOTHER Narrow_forward
- A 67 kg circus gymnast is suspended in the air by two ribbons which are tied to the ceiling above him. The two ribbons make an angle of 48 degrees withrespect to the ceiling. Assume gymnast is at rest. a. What is the magnitude of the tension force in each of the ropes?b. What is the reaction force associated with the gymnast’s weight?c. If the gymnast suddenly lets go of one of the ropes, what will be the horizontal component of his acceleration just after letting go?arrow_forwardStarting from rest, a 150 kg body experiences a force of 100 newtons acting on it in a direction parallel to the positive x-axis and a force of 150 newtons acting at 55° with respect to the positive x-axis. a. What is the net force acting on the body? Include direction. b. What is the acceleration of the body? c. What velocity does it reach after 5 seconds?arrow_forward3. Starting from rest, a 125 kg body experiences a force of 150 newtons acting on it in a direction parallel to the positive x-axis and a force of 125 newtons acting at 45° with respect to the positive x-axis. a. What is the net force acting on the body? Include direction. b. What is the acceleration of the body? c. What velocity does it reach after 2.5 seconds?arrow_forward
- A box is being pulled across a level floor by a rope attached to the box The rope is pulling partly upward at an angle of 30 degrees to the horizontal. In this circumstance A. The normal force between the box and the floor is greater than the weight of the box. B. The normal force between the box and the floor is less than the force of gravity on the box. C. The normal force between the box and the floor is the same as the force of gravity on the box. D. Which of the above is correct depends on whether or not the box is accelerating. E. Which of the above is correct depends on whether or not there is friction between the box and the floor. F. None of the above answers is correct.arrow_forward1.arrow_forwardExplain Newton's second Law and solve related problems Given a block which is at rest on a perfectly flat smooth table. You push with your hand horizontally on the block with some force. If the mass of the block = 2.00 kg and the acceleration of the block = 5.00 m/s2 then what is the force on the block from your hand in SI units? a. 2.50 N b. 0.100 N c. 0.400 N d. 10.0 N e. zeroarrow_forward
- You push a lawnmower (mass=15kg) across the lawn at constant speed. To do so, you must excert 200 N of force. The handle makes a 35° angle with the horizontal. A. Draw the force diagram B. What is the x-component of the force you apply? C. How does it compare to the frictional force which opposes your effort? Explain. D. If the frictional force is reduced to 100 N, determine the acceleration of the lawnmower.arrow_forward2. A 10. Kg box pulled with a 40. N force at an angle of 20. degrees above the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.20. Note it is moving along the table top. a) Draw a FBD showing all forces and the components of the pulling force. b) Determine the normal force. c) Determine force of friction acting on the box. d) Determine the acceleration of the box. e) Assume the box started from rest and was pulled for 2.0 seconds. Then the pulling force was removed. (i) Find the speed of the box after the 2.0 seconds. (ii) Determine how long it took for the box to come to rest after the pulling force was removed. 10kg -> 40N <200arrow_forward5. A 3 kg book is held against a wall with a force F at an angle of 30° as shown below. The coefficient of friction of the wall with the book is 0.3. A. Draw a free body diagram for the book. B. Determine the minimum force F needed for the book not to slide down the wall.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON