
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A concrete footing for cable anchorage is shown blow. The total weight of the concrete foundation
is 80 kips (assumed concentrated at its center of gravity). The cable force is acting horizontally
(F) equal to 100 k. What is the resultant moment about point A? Does the concrete foundation tip
over?
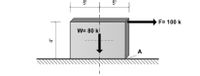
Transcribed Image Text:The diagram depicts a block resting on a surface, illustrating a statics problem. The block has a width of 10 feet and a height of 4 feet.
Key Elements:
1. **Block Dimensions**:
- Width: 10 feet (divided into 5 feet on each side of the central axis)
- Height: 4 feet
2. **Forces Acting on the Block**:
- Weight (W): Acts vertically downward through the center of the block with a magnitude of 80 kips.
- Horizontal Force (F): Applied on the right side of the block with a magnitude of 100 kips.
3. **Surface Interaction**:
- The block rests on a horizontal surface labeled as "A," which indicates the point or area where the block contacts the ground.
The diagram may be used to analyze the equilibrium conditions, calculate reactions at the base, or assess potential for tipping.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Structural member AB is to be supported by a strut CD. Determine the smallest length CD may have, and specify where D must be located for a strut of this length to be used. Take x= 120 mm. 60 mm D. y 20 mm E The smallest length CD may have is mm. The coordinates of point Dare ( and Imm.arrow_forwardModern commercial airliners are largely made of aluminum, a light and strong metal. But the fact that aluminum is cheap enough that airplanes can be made out of it is a bit of historical luck. Before the discovery of the Hall-Héroult process in 1886, aluminum was as rare and expensive as gold. What would happen if airplanes had to be made of steel? The fuselage of the Boeing 747, which can carry 400 passengers, is approximately a hollow aluminum cylinder without ends, 70.7 m long, 6.5 m wide, and 2.5 mm thick (see sketch at right). The fuselage of an airplane Suppose this fuselage was made of steel (density 7.87 g/cm³) instead of aluminum (density 2.70 g/cm³), and let's say the average passenger has a mass of 79 kg. We'll also assume the engines can't lift any greater mass than they already do. Calculate the number of passengers that the Boeing 747 could carry if its fuselage was made of steel. 0 Xarrow_forwardA high-carbon steel with a fully pearlitic microstructure was used to form a high-strength bolt (H.-C. Lee et al., J. Mater. Proc. Tech. 211, 1044 (2011)). It was found that the bolt head had an average interlamellar spacing of 257 nm whereas the average spacing in the body of the bolt was 134 nm. Assuming that dislocation pileup is the primary mechanism responsible for the strength of this alloy, what ratio of strength (or hardness) might be expected in the head and body of the bolt?arrow_forward
- Problem 5: A painter (of mass 71 kg) needs to reach out from a scaffolding to paint the side of a building, so he lays a plank across two bars of the scaffolding, and puts a heavy bucket of mass 27 kg directly over one of the bars (see figure). You can assume the plank is massless, and is long enough to reach to the other building. L d If the bars are separated by a distance 1.5 m, how far, d, from the bar on the the right can the painter walk before the plank starts to fall? d= m 9 HOME sin() cos() tan() J ( ) 7 8 cotan() asin() acos() E 1시 신 4 atan() acotan() sinh() 5 6 7 * 1 2 3arrow_forwardIn the figure below, suppose the length L of the uniform bar is 3.50 m and its weight is 240 N. Also, let the block's weight W = 350 N and angle 0 30°. The wire can withstand a maximum tension of 500 N. C - X→ com В (a) What is the maximum possible distance x before the wire breaks? (b) With the block placed at this maximum x, what is the horizontal component of the force on the bar from the hinge at A? N (right) (c) What is the vertical component of this force? N (up)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON