
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
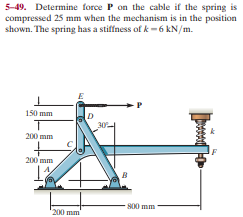
Transcribed Image Text:5-49. Determine force P on the cable if the spring is
compressed 25 mm when the mechanism is in the position
shown. The spring has a stiffness of k -6 kN/m.
150 mm
200 mm
200 mm
800 mm
200 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 5-78. The hatch door has a weight of 80 lb and center of gravity at G. If the force F applied to the handle at C has coordinate direction angles of a = 60°, ß = 45°, and y = 60°, determine the magnitude of F needed to hold the door slightly open as shown. If the hinge at A becomes loose from its attachment and is ineffective, what are the x, y, z components of reaction at hinge B? 2 4 ft 3 ft. 2 ft 3 ft C B X F Probs. 5-77/78arrow_forward*5-16. Determine the tension in the cable and the horizontal and vertical components of reaction of the pin A. The pulley at D is frictionless and the cylinder weighs 80 lb. A 5 ft- D B 2 5 ft 3 ft Prob. 5-16 Carrow_forward3-33. If the spring on rope OB has been stretched 2 in. and fixed in place as shown, determine the tension developed in each of the other three ropes in order to hold the 225-lb weight in equilibrium. Rope OD lies in the x-y plane. Z 2 fu A X (-2ft, -3ft, 3ft) 3 ft 4 ft B k = 20 lb/in. 2-4 ft- 30° D 4 ft T 4 ftarrow_forward
- R5-5. Determine the x, y, z components of reaction at the fixed wall A. The 150-N force is parallel to the z axis and the 200-N force is parallel to the y axis. x Z 2 m 150 N 1 m 2 m 2.5 m -200 Narrow_forwardThe homogeneous box has mass m. The magnitude of force Pis slowly increased until motion occurs. Motion could occur as slipping or tipping and you must decide which occurs first. Find the value of P which first causes motion. P А 30° d = 0.40 B 2.2 d Answer: P = i mgarrow_forwardThe uniform steel beam of mass m = 19.6 kg and length I= 780 mm is suspended by the two cables at A and B. If the cable at B suddenly breaks, determine the tension Tin the cable at A immediately after the break occurs. Treat the beam as a slender rod. Assume e = 56°. Answer: T = Narrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY