
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
solve show solutions, modern incompressible flow
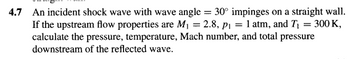
Transcribed Image Text:4.7 An incident shock wave with wave angle = 30° impinges on a straight wall.
If the upstream flow properties are M₁ = 2.8, p₁ = 1 atm, and T₁ = 300 K,
calculate the pressure, temperature, Mach number, and total pressure
downstream of the reflected wave.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Q3. A supersonic flow of air has a pressure of 1 x 105 N/m2 and M a temperature of 350 K. After expanding through a 35° turm, the Mach number is 3.5. Determine: Angles 8,,02 and 03. 0= ? Final flow properties p2 and T2. Figure Q3arrow_forwardQ2: Air (y = 1.4) enters a converging-diverging diffuser with a Mach number of 2.8, static pressure pi of 100 kPa, and a static temperature of 20°C. For the flow situation shown in Figure, find the exit velocity, exit static pressure, and exit stagnation pressure. Ans: Ve = 55.093 m/s; Pe = 2236.678 kPa; Poe = 2252.44 kPa i M₁ = 2.8 A₁ = 0.10 m² A₂ = 0.50 m² A₁ = 0.25 m²arrow_forward1.ABarrow_forward
- What is the minimum nozzle-diameter ratio De/D0 for which we can safely neglect compressibility effects if V0 = 10 m/s?arrow_forwardA normal shock occurs in a stream of oxygen. The oxygen flows at Ma=1.8 and the upstream pressure and temperature are 40 psia and 85 degrees Fahrenheit. a) Calculate the following on the downstream side of the shock: static pressure, stagnation pressure, static temperature, stagnation temperature, static density, and velocity. b)If the Mach number is doubled to 3.6, what will be the resulting values of the parameters listed in part (a)?arrow_forwardThe flow just upstream of a normal shock wave is given by p1 = 1 atm,T1 = 288 K, and M1 = 2.6. Calculate the following properties justdownstream of the shock: p2, T2, ρ2, M2, p0,2, T0,2, and the change inentropy across the shock.arrow_forward
- An air tank with a nozzle, has a pressure of twice the standard sea level pressure and density of 2.45 kg/m³. Outside the converging-diverging nozzle, the pressure corresponds to an altitude of 3km and designed to have a mach number of 1.0 and 1.8 at the throat and exit, respectively. The area at the throat is 0.15 square meters. Calculate: a) the temperature and speed of sound in the tank. b) pressure and density at the throat c) mass flow rate at the exit.arrow_forwardare 3000 ft/s and 500°R, respectively Calculate the Mach number M and the characteristic Mach number M* at this point 3.4. Consider a normal shock wave in air The upstream conditions are given by M = 3; P1 M2, u2, Po,, and T %3! = 1 atm, and p, = 1 23 kg/m Calculate the downstream values of P2, 02 35 Consider a Pitot static tube mounted on the pose of an experımental airplane Aarrow_forwardAir with Mach number of 2.5, To 300 K and P. = 2 bar passes through the steps shown in figure. Determine: (1) The fan angle of the expansion wave (2) M, Ts and P4. M₁ = 2.5 T₂ = 300 Po 2 bar M₁ May M 20° 10arrow_forward
- 3.4. Consider a normal shock wave in air The upstream conditions are given by M1 = 3; 1 23 kg/m' Calculate the downstream values of p2, T,, 1 atm, and p1 M2, u2, Po,, and T, P1 P24 02 Disarrow_forwardAir flows isentropically through a duct as shown in the figure below. For the conditions shown, find the Mach number at both stations 1 and 2 and the flowrate. The diameter is not necessarily constant. Ma₁ (1) D₁ = 0.15 m V₁ = 40 m/s P1 = 4 atm abs. Ma₁ = Ma₂ = i m₁ = M. kg/s Ma₂ (2 T₂ = 225 K P2 = 2 atm abs.arrow_forwardAt a point in the flow over an F-15 high-performance fighter airplane, the density,temperature and Mach number are 1 kg/m3, 240 Kelvin, and Mach 1.6.(a) At this point, calculate T0, ρ0, p0, a0, T ∗, a∗, p∗ and the flow velocity.(b) Calculate M ∗1 and, using the Prandtl relation, calculate M ∗2 and u2 after a normalshock.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY