
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
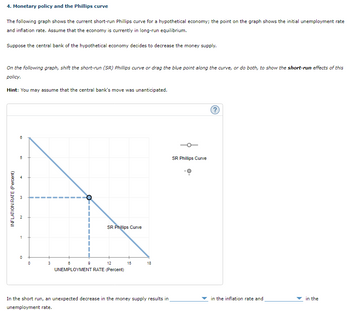
Transcribed Image Text:4. Monetary policy and the Phillips curve
The following graph shows the current short-run Phillips curve for a hypothetical economy; the point on the graph shows the initial unemployment rate
and inflation rate. Assume that the economy is currently in long-run equilibrium.
Suppose the central bank of the hypothetical economy decides to decrease the money supply.
On the following graph, shift the short-run (SR) Phillips curve or drag the blue point along the curve, or do both, to show the short-run effects of this
policy.
Hint: You may assume that the central bank's move was unanticipated.
INFLATION RATE (Percent)
8
5
3
N
1
0
0
3
9
SR Phillips Curve
8
12
UNEMPLOYMENT RATE (Percent)
15
18
In the short run, an unexpected decrease in the money supply results in
unemployment rate.
SR Phillips Curve
in the inflation rate and
in the
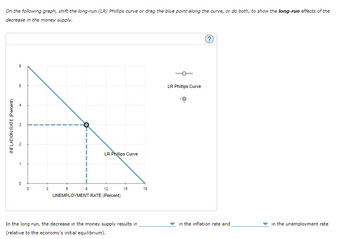
Transcribed Image Text:On the following graph, shift the long-run (LR) Phillips curve or drag the blue point along the curve, or do both, to show the long-run effects of the
decrease in the money supply.
INFLATION RATE (Percent)
CO
6
5
1
0
0
3
LR Phillips Curve
9
8
12
UNEMPLOYMENT RATE (Percent)
15
In the long run, the decrease in the money supply results in
(relative to the economy's initial equilibrium).
18
LR Phillips Curve
?
in the inflation rate and
in the unemployment rate
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 23 The Fed's Policies under Volcker In the years 1979 to 1982, under the leadership of Paul Volcker, the Fed adopted a tight money policy to reduce the nation's inflation rate. Based on the aggregate supply - aggregate demand model, what would happen to the price level in the long run as a result of the Fed's tight money policy under Volcker's leadership? Choose one answer below: O The price level would end up higher in the long run. The price level would end up lower in the long run. O The price level would end up at its initial level in the long run.arrow_forward16. Keynes (1936) argued that, from a policy perspective, everything that can be achieved by a nominal wage cut can be more effectively achieved through an appropriate monetary policy. (a) Does this statement hold in the deficient-demand Keynesian model for a negative shock to (i) aggregate demand and (ii) aggregate labor productivity? (b) Does this statement hold in the new Keynesian model for a negative shock to (i) aggregate demand and (ii) aggregate labor productivity?arrow_forwardPlz help nowarrow_forward
- The data on aggregate expenditure and unemployment was little changed since June. But the Fed expected the unemployment rate to fall and inflation to remain below 2 percent in the near term and then stabilize around the Fed's goal of 2 percent over the medium term.Source: FOMC Minutes, July 25-26, 2017ls the Fed predicting that the U.S. economy will move along a short-run Phillips curve or that the short - run Phillips curve will shift through 2017 and 2018? Explain.arrow_forward1. Monetary policy and the Phillips curve The following graph shows the current short-run Phillips curve for a hypothetical economy; the point on the graph shows the initial unemployment rate and inflation rate. Assume that the economy is currently in long-run equilibrium. Suppose the central bank of the hypothetical economy decides to decrease the money supply.arrow_forward1. What are the main reasons that the U.S. inflation surged last year? 2. What is the monetary policy the Fed (central bank of the U.S.) uses to control inflation? 3. How did the monetary policy cause the bankruptcy of Silicon Valley Bank?arrow_forward
- 4. Monetary policy and the Phillips curve The following graph shows the current short-run Phillips curve for a hypothetical economy; the point on the graph shows the initial unemployment rate and inflation rate. Assume that the economy is currently in long-run equilibrium. Suppose the central bank of the hypothetical economy decides to increase the money supply. On the following graph, shift the curve or drag the blue point along the curve, or do both, to show the short-run effects of this policy. Hint: You may assume that the central bank's move was unanticipated. INFLATION RATE (Percent) 6 5 N 1 0 0 SR Phillips Curve + 4 2 3 UNEMPLOYMENT RATE (Percent) 1 5 SR Phillips Curve In the short run, an unexpected increase in the money supply results in the unemployment rate. (?) in the inflation rate and inarrow_forwardWhat do monetarists predict will happen in the short run and in the long run as a result of each of the following? (In each case assume the economy is currently in long-run equilibrium). (a) Velocity rises. (b) Velocity falls. (c) The money supply rises. (d) The money supply falls.arrow_forwardQuestion 9 Using the Fed model linking the IS-MP framework with the Phillips curve, draw a graph that illustrates the following scenario: Expected inflation is 1.5%. The economy is initially in macroeconomic equilibrium with a real interest rate of 3%, an output gap of -1%, and an actual inflation rate of 1%. Upload Choose a Filearrow_forward
- 6arrow_forwardSuppose that velocity of money is constant, the expected inflation rate is always equal to the actual inflation rate, and the expected real interest rate is 3%. Answer the following questions. Justify your answers. a)Let the growth rate of the money supply rise to 10% without affecting the growth rate of real GDP or velocity. What happens to the inflation rate? If this new inflation rate becomes the expected inflation rate what happens to the nominal interest rate? b)Has the increase in the growth rate of money supply been generated by an open market operation conducted by the central bank? If so, how did the central bank generate this increase in the money supply? Only a qualitative answer is required.arrow_forward5arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education