
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Can't Buy Time - Google Docs
Resume Builder · Resume.io
Action Center - Ocean Conservan X +
docs.google.com/document/d/1pQhEBaWXYWxTk327EPalSjdDio91Zaf8RIghg92dlXw/edit
Paused
Can't Buy Time * a O Saving.
Share
File Edit View Insert Format Tools Add-ons Help
Last edit was seconds ago
в IUA
E 1E
100%
Normal text
Verdana
16
Editing
31
1 |
2
3
6
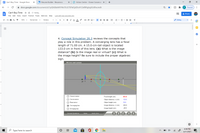
4. Concept Simulation 26.3 reviews the concepts that
play a role in this problem. A converging lens has a focal
length of 71.00 cm. A 15.0-cm-tall object is located
133.0 cm in front of this lens. (a) What is the image
distance? (b) Is the image real or virtual? (c) What is
the image height? Be sure to include the proper algebraic
sign.
Mirrors and Lenses
3.
2F X
2F
Concave mirror
Focal length (cm):
80.0
Convex mirror
Object distance, x (cm):
133.0
Plane mirror
Object height (cm):
33.0
Converging lens
Image distance, x' (cm):
200.8
Diverging lens
Image height (cm):
-49.8
Concept Questions
Notes
Audio Intro
>
6:38 PM
O Type here to search
后 の
4/21/2021
!!!
II
9
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- C=18arrow_forward1. Assume that a camera has a bi-convex lens. Should you move the lens toward or away from the sensor in order to zoom in (magnify)? 2. A camera has a bi-convex lens whose focal length is 50mm. The lens’s range of motion is 5.56mm starting from 50mm from the sensor and moving away. What are the minimum and maximum possible object positions for which the image is in focus? 3. For the camera in the previous question, when a 300mm tall object is at the minimum distance, will it fit on a Canon APS-C sensor? Hint: Look up the size of this camera sensor. 4. See Figure 10.7! A circular piece of glass (n=1.5) has been cut in half as shown and is being used as a lens for a set of five parallel rays. The angles at which the rays are incident on the circular side of the lens are shown, and the image is drawn to scale. First, calculate the 5 angles of refraction for each of the 5 angles of incidence, respectively. Second, use a protractor to draw the refracted rays such that they intersect the…arrow_forwardPlease Provide an explanation for the answer. Thank youarrow_forward
- An eyeglass prescription that specifies a power of -1.0 diopters is describing a lens that has a focal length of O a. + 1 meter O b.- 100 cm O C. - 1 meter O d. - 1 cm An object placed 25 cm to the left of a +20 cm focal length lens produces a real image 100 cm to the right of the lens. What is the magnification? O a. - 4 Ob. - 0.25 O C. + 2 O d. - 1arrow_forwardCreate a ray diagram for eyeglasses that contain a diverging lens. Assume you are looking at a 2 cm tall object that is 4 cm from the lens. The focal length is 3 cm. What type of vision are they used to correct? Give both names. How do they do this? Explain.arrow_forwardmpt in Progress Concept Simulation 26.3 reviews the concepts that play a role in this problem. A converging lens has a focal length of 74.00 cm. A 10.0- cm-tall object is located 170.0 cm in front of this lens. (a) What is the image distance? (b) Is the image real or virtual? (c) What is the image height? Be sure to include the proper algebraic sign. (a) Number i Units V (b) The image is (c) Number i Units Hint real virtualarrow_forward
- B. CONVERGING LENSES: After performing this activity, the students should be able to: Sketch the location of the image in the concave mirror, measure the distance and the height of the image, and describe the object and the image in every case. MATERIALS: Rufer PROCEDURES 2 Construct the image of the following, given the focal length, distance of the object (do) (f) and height of the object (ho) in centimeters. Describe the location of both the object and the image being constructed. Determine the exact distance and the height of the image. identify the case number of each. Complete the table below. NOTE: Arrows that represent the secondary axes should be in red color, arrow that represent the object and the image is in blue color as well as the line that shows the bending of light ray, the rest of the construction is in black color. That is why you will be needing 3 colored ballpen for this activity. Use another sheet of bond paper for your construction. Use accurate maeasure. three…arrow_forwardThe good expert Hand written solution is not allowed.arrow_forwardAnne's retina is 1.8 cm from the lens. The nearest object she can see clearly without corrective lenses is 2.0 m away. 1. Sketch a ray diagram to show (qualitatively) what happens when she tries to look at something closer than 2.0 m without corrective lenses. 2. What should the focal length of her contact lenses be so that she can see clearly objects as close as 20.0 cm from her eye?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON