
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
3B. A summary of resilient modulus test conducted on a subgrade soil, according to the AASHTO T307-99 protocol, is summarized below. Determine the resilient modulus for Sequence No. 8, knowing the average recoverable strain of last five cycles of this sequence is 0.0005.
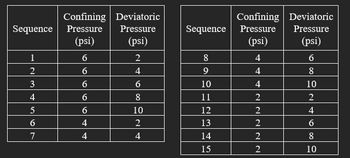
Transcribed Image Text:Sequence Pressure
(psi)
1
2
SFW N
3
4
Confining Deviatoric
5
6
7
6
6
6
6
6
4
4
Pressure
(psi)
2
4
6
8
10
2
4
Sequence
8
9
10
11
WNTO
12
13
14
15
Confining Deviatoric
Pressure
Pressure
(psi)
(psi)
4
4
4
N|N|N|N|N
2
2
2
2
2
6
8
10
2
4
16
50⁰
8
10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For an unconsolidated undrained test on a soil having USCS classification of CL and sample diameter of 2.5 inches, the axial load on the sample at failure (10% strain) was 180 pounds. What is the undrained shear strength, Su, of the sample in pounds per square foot? Sketch and label the Mohr's Circle and Mohr-Coulomb failure envelope.arrow_forwardA series of consolidated-drained (CD) triaxial tests were performed on the soil with same initial density. Each test was continued until failure. Following data was recorded. Test Number 1 03' (kPa) 200 300 400 0₁' (kPa) 570 875 1162 Plot the relevant Mohr stress circles and determine effective/drained shear strength parameters.arrow_forwardA permeability test is carried out on a sample of and cross section is 1500mm^ 2 a soil whose k = 3 * 10^(-1) m / s. Briefly identify this while indicating its degree of permeability What diameter of measuring pipe do we use knowing that the load goes from 275 mm to 200 mm in 5 min? Compare the permeability of this soil identified in question a) with that of a sandy silt. Justify your answer Compare the frost hardness of the soil identified in question a) with that of gradual sand. Between these two soils, which will be the most suitable as road fill without risk of frost swelling? Justify your answerarrow_forward
- Below are results from three unconsolidated undrained triaxial tests performed on a fully saturated clay specimen: Test No. 1 2 Minor principal stress (psi) Major principal stress at failure (psi) 10 25 33 22 37 45 Moisture content = 21 % Determine: a) Void ratio (e) of the soil. You may use eS = wG_ (assume Gs = 2.70) %3D b) Deviatory stress at failure for each test trial c) Shear strength parameters (cu and ø). Hint: Sketch the Mohr's circles for the three trials. 3.arrow_forwardFigure 1 office illustrates the soil profile at a site for a proposed building. It is expected that the vertical stress at the middle of the clay layer will increase by 32 kPa. Calculate the final consolidation settlement. Ground water level is at the top of the clay layer. An oedometer test on a sample of the clay revealed that 90% consolidation on a 20-mm thick sample occurred in 40 minutes. The sample was drained on the upper and lower boundaries. Estimate the consolidation settlement in one year. Gs(clay) = 2.70 and Gs(sand) = 2.60. 5 m w = 23% Sand S = 90% w = 40% 10 m C= 0.3 OCR = 1 Clay Impervious rock Figure 1 0.9 U. avg 0.00 0.000 0.8 0.0 0.1 0.0 0.008 0.031 0.071 0.05 0.252 0.10 0.357 0.197 0.500 0.7 02 0.3 0.20 0.30 0.40 0.504 0.6 04 0.126 0.613 0.698 0.764 0.816 0.856 0.887 0.848 0.900 0.912 0.931 0.980 0.5 0.197 0.5 0.6 0.287 0.50 0.7 0.403 0.60 0.4 0.567 0.70 0.848 0.95 1.163 0,9 0.80 0.3 1.0 0.90 02 1.00 1.50 2.00 0.1 0.994 02 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 Time factor, T…arrow_forwardThe results of two consolidated drained triaxial tests are as follows: Test a, (kN/m²) Ar,(kN/m²) 66 91 134.77 169.1 Determine c and o. Also determine the magnitudes of the normal and shcar stress on the planes of failure for the two specimens used in the tests.arrow_forward
- 5. A laboratory consolidation test was performed on a cohesive soil specimen with drainage on top and at the bottom. The original height of the specimen was 2.54 cm. Based on the log time versus deformation data, the time to achieve 50% average degree of consolidation was 11 min. Calculate the coefficient of consolidation (in cm²/min) for the soil sample.arrow_forwardQ': A- Classification tests have been performed on a soil sample and the grading curve that shown in (Fig. 1) and Atterberg limits obtained. Classify the soil using the USCS? L.L=32 and P.L=26 100 80 60 40 20 Fig. 1 0.1 1 Particle size (mm) 0.0001 0.001 0.01 10 100 % Finerarrow_forwardplease help me... If a soil sample tested in a direct shear box of 60 mm by 60 mm and the maximum readings for normal loads of 0.3, 0.5 and 1.0kN were 202, 265 and 511 kN, determine the strength parameters corresponding to effective stress. Please find: 1) UU test; Unconsolidated Untrained (Q-test or quick test) 2) CD test; Consolidated Drained ( S-test or slow test) 3) CU test; Consolidated Untrained (R-test) 4) UC test; Unconfined Compression (σ_3=0) Thank you..arrow_forward
- 9.4 A clay specimen was tested in a laboratory consolidation device, which was 12.7 mm (1/2 in.) thick and the top and the bottom boundaries were drained. A 50% consolidation time on the specimen was obtained as 28.4 minutes. Determine the following: (a) Time for 50% consolidation in the field with this soil with a 2.5 m thickness where only the top layer is drained (b) Time for 90% consolidation in the field with this soil with a 2.5 m thickness where only the top layer is drained (c) For the same field condition above, at the end of 1 year after the placement of load, how much primary consolidation settlement occurs relative to its final amount of the settlement? (d) The same question as in (c), but at the end of 5 yearsarrow_forwardI need the correct answerarrow_forward2- The following are the results of four drained direct shear tests on undisturbed normally consolidated clay samples having a diameter of 2.0 inches and height of 1.0 inch. a) Draw a graph on excel for shear stress at failure against the normal stress and determine the drained angle of friction from the graph. b) If a drained triaxial test is conducted on the same soil with a chamber confining pressure of 4,344 lb/ft², what would be the deviator stress at failure? c) For part b, what is the inclination of the failure plane with the major principal plane? Shear Force at Test No. Normal Force (lbf) Failure (lbf) 1 56.2 31.2 84.3 47.0 101.1 56.2 121.4 67.4 23+ 2 4arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning