
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781305970939
Author: Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
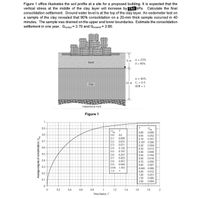
Transcribed Image Text:Figure 1 office illustrates the soil profile at a site for a proposed building. It is expected that the
vertical stress at the middle of the clay layer will increase by 32 kPa. Calculate the final
consolidation settlement. Ground water level is at the top of the clay layer. An oedometer test on
a sample of the clay revealed that 90% consolidation on a 20-mm thick sample occurred in 40
minutes. The sample was drained on the upper and lower boundaries. Estimate the consolidation
settlement in one year. Gs(clay) = 2.70 and Gs(sand) = 2.60.
5 m
w = 23%
Sand
S = 90%
w = 40%
10 m C= 0.3
OCR = 1
Clay
Impervious rock
Figure 1
0.9
U.
avg
0.00
0.000
0.8
0.0
0.1
0.0
0.008
0.031
0.071
0.05
0.252
0.10
0.357
0.197 0.500
0.7
02
0.3
0.20
0.30
0.40
0.504
0.6
04
0.126
0.613
0.698
0.764
0.816
0.856
0.887
0.848 0.900
0.912
0.931
0.980
0.5
0.197
0.5
0.6
0.287
0.50
0.7
0.403
0.60
0.4
0.567
0.70
0.848
0.95 1.163
0,9
0.80
0.3
1.0
0.90
02
1.00
1.50
2.00
0.1
0.994
02
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
1.4
1.6
1.8
Time factor, T
Averagedegree of consolidation, U
으 67898
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305081550
Author:Braja M. Das
Publisher:Cengage Learning