
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
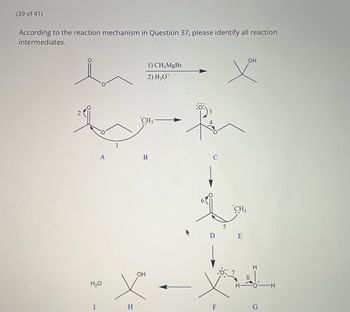
Transcribed Image Text:**Reaction Mechanism and Intermediates**
**Question Context:**
According to the reaction mechanism in Question 37, please identify all reaction intermediates.
**Reagents and Conditions:**
1) \( \text{CH}_3\text{MgBr} \)
2) \( \text{H}_3\text{O}^+ \)
**Target Product:**
The reaction leads to the formation of a tertiary alcohol (displayed as having an OH group attached to a tert-butyl group).
**Reaction Steps and Intermediates:**
1. **Intermediate A:**
- The mechanism begins with a ketone structure, where the carbonyl carbon is electrophilic.
2. **Intermediate B:**
- The \( \text{CH}_3\text{MgBr} \) performs a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon, breaking the \(C=O\) bond and forming an alkoxide ion.
3. **Intermediate C:**
- Rearrangement and stabilization of the alkoxide ion occur. The oxygen carries a negative charge represented with a lone pair, indicating its role as an anion.
4. **Intermediate D:**
- The alkoxide ion undergoes protonation facilitated by \( \text{H}_3\text{O}^+ \), leading to the formation of the alcohol intermediate.
5. **Intermediate E:**
- The carbonyl oxygen gains a proton (from \( \text{H}_3\text{O}^+ \)), resulting in an oxonium ion configuration.
6. **Intermediate F:**
- A rearrangement/transformation occurs, likely showing the pathway toward stabilization and final product formation.
7. **Intermediate G:**
- Further interaction with water (\( \text{H}_2\text{O} \)) leading to a stable hydration step that is characteristic in the final alcohol formation.
8. **Intermediate H:**
- Final deprotonation step to form the stable tertiary alcohol.
9. **Intermediate I:**
- The complete structure of the tertiary alcohol is shown. Any excess water interactions stabilize the reaction.
**Visualization:**
The diagrammatic sequence describes a multi-step reaction mechanism typical in Grignard reactions with ketones, resulting in alcohol products.
**Note:** The positions are numbered to depict electron/lone pair movements and structural changes throughout the reaction pathway.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Given reaction and mechanism
The given reaction is 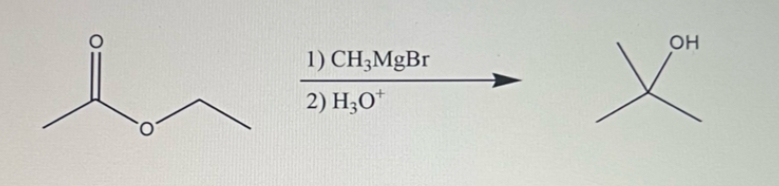
And, the given reaction mechanism also shown below
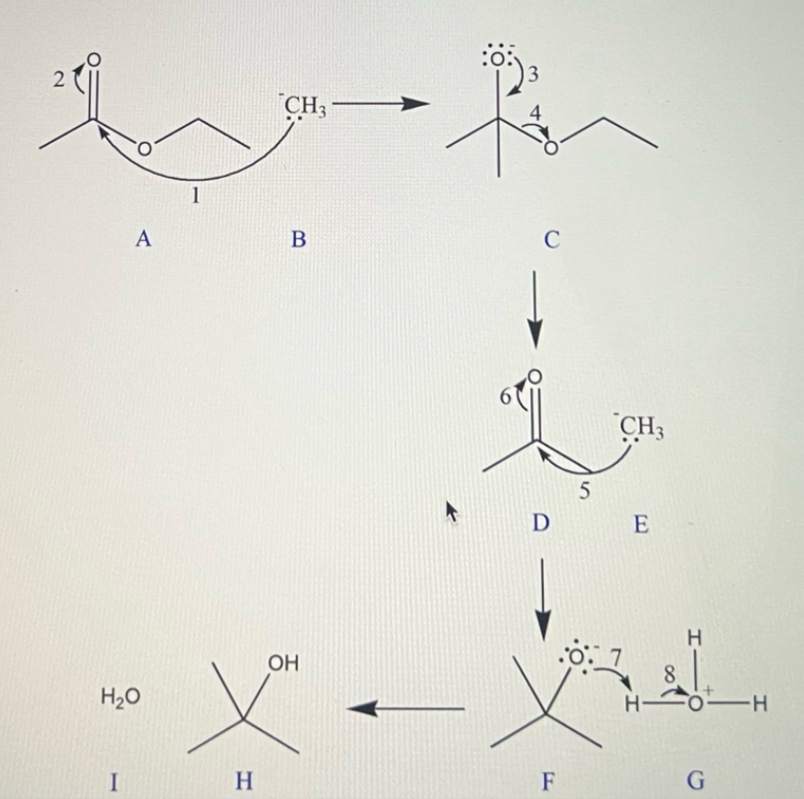
We have to determine all the reaction intermediates.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Analyze the following reaction mechanism. How many different reactants are involved in this mechanism (don't count the catalyst as a reactant)? in Acetone (CH3COCH 3) Select an answer and submit. For keyboard navigation, use the up/down arrow keys to select an answer. à None b 1 C 2 .Lt H₂O d 3 i :OH :OHarrow_forward1) Write the relative reaction rates for the following reaction: A + 2B Carrow_forwardMg(s) + 2HCl(ac) --> MgCl2 (ac) + H2 (g) What effect does changing the HCl concentration have on the rate of the reaction? Explain:arrow_forward
- Which of the following reactions is impossible to occur as a single step? Cl2(g) --> 2 CI(g) OCI + H20(1) --> HOCI(aq) + OH NO(g) + Cl2(g) NOCI2(g) --> O 2 NO(g) + O2(g) 2 NO2(g) -->arrow_forwardWhich species does the first transition state of the overall reaction most ressemble? What kind of transition state is this (late or early)?arrow_forwardCan i get the solarrow_forward
- Remaining Time: 1 hour, 16 minutes, 57 seconds. v Question Completion Status: A Moving to another question will save this response. Question 22 Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing reaction rate with HNOg04 2 1 O 3<1<2<4 O 3<4<1<2 O1<3<4<2 O1<2<3<4 A Moving to another question will save this responsearrow_forwardThe proposed 3-step mechanism for a reaction isStep 1) X(g) + Y(g) A(g) fast, reaches equilibrium (For Step 1, k1 = forward rate constant & k-1 = reverse rate constant.)Step 2) A(g) + Z(g) B(g) slow (k2 = rate constant) Step 3) B(g) P(g) fast (k3 = rate constant) a) What is the overall reaction? b) What is the rate law supported by this mechanism? Explain your answer. c) The following is experimental data found for this reaction: Initial [X] (M) Initial [Y] (M) Initial [Z] (M) Initial Rate (M/day) Exp 1 0.150 0.150 0.150 0.569 Exp 2 0.250 0.150 0.150 0.948 Exp 3 0.250 0.300 0.150 3.793 Exp 4 0.300 0.350 0.200 6.196 i) What is the experimentally determined rate law? ii) Determine the rate constant and include units. d) Does your experimentally determined rate law support the proposed mechanism? Explain your answer. e) ΔΔHo = -347 kJ/mol for the overall reaction. Draw a reasonable reaction profile for the proposed mechanism.…arrow_forwardFor the reaction CH 3 Br (aq) + OH - (aq) → CH 3 OH (aq) + Br- (aq) it is known that when the concentration of OH - doubles, the reaction rate doubles. When the concentration of CH 3 Br increases 1.2 times, the reaction rate increases 1.2 times. Write the rate equation for the reactionarrow_forward
- Find a reaction that is typically facilitated by a catalyst. Write a paragraph (2 at most) detailing what the reaction is, what it is used for, what the catalyst is, how the catalyst increases the reaction rate, and how fast the reaction is with the catalyst.arrow_forwardwhat is the mechanism of this reaction?arrow_forwardQuestions 8-10 refer to the following energy diagram for a reaction proceeds by a three-step mechanism. F D E В E IA G 8. Which transformation represents the rate-determining step for the reaction? a) A → C b) С >Е c) E → G d) A → E e) С -> G f) A → Garrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY