
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A 300-g collar A is released from rest, slides down a frictionless rod, and strikes a 900-g collar B that is at rest and supported by a spring of constant 500 N/m. Knowing that the coefficient of restitution between the two collars is 0.9, determine (a) the maximum distance collar A moves up the rod after impact, (b) the maximum distance collar B moves down the rod after impact.
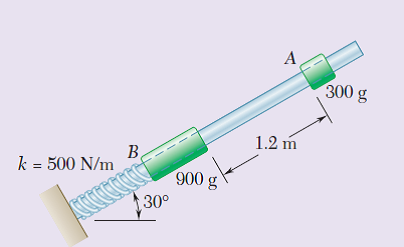
Transcribed Image Text:300 g
1.2 m
k = 500 N/m
అనువము
30°
900 g
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A curved incline is used to give a box a certain velocity as it slides down. The box has a mass of m1=4.92 kg. Friction is negligable. The box starts from rest at h= 5.00 m above the flat surface at the bottom of the incline. After moving down, it collides with a second box m2=10.5kg, also initially at rest. Teh collision is elastic. Find the maximum height to which m1 rises after the collisionarrow_forwardWITH FRICTION Find minimum and maximum mass of m1 to maintain the system in state of equilibrium; at rest. Given: m2= 3kg m3=10kg m4=23kgarrow_forwardKindly answer in 30 min will upvote.arrow_forward
- Two forces, F , = (-2,65î + 4.10ĵ) N and F, = (-4.50î + 7.10ĵ) N, act on a particle of mass 2.30 kg that is initially at rest at coordinates (+1.95 m, –4.20 m). (a) What are the components of the particle's velocity at t = 11.3 s? m/s (b) In what direction is the particle moving at t = 11.3 s? ° counterclockwise from the +x-axis (c) What displacement does the particle undergo during the first 11.3 s? AF = (d) What are the coordinates of the particle at t = 11.3 s? marrow_forwardThe force of that particle 2 exerts on 1 is given by: F→21(t)=Fxe^−(t/T)ı^+Fysin(2πt/T)ȷ^ Where the parameters have the values: Fx=−16.1 N, Fy=101 N, T=67 s.We will consider a time interval that begins at ti=0 s and ends at tf=321 s. the mass of particle 1 is 13.9 kg and its intial velocities are 54 m/s I^ + (-42 m/s)J^. What is the x and y displacement for particle 1?arrow_forwardA car of mass m slides across a patch of ice at a speed v with its brakeslocked. It the hits dry pavement and skids to a stop in a distance d. Thecoefficient of kinetic friction between the tires and the dry road is µ.2. If the car has a mass of 2m, it would have skidded a distance of(A) 0.5 d (B) d (C) 1.41 d (D) 2 d3. If the car has a speed of 2v, it would have skidded a distance of(A) d (B) 1.41 d (C) 2 d (D) 4 darrow_forward
- An acrobatic buccaneer swings from one rope to another in the rigging of a pirate ship. As she grasps the rope, her mass is m, 63.5 kg; knots on the rope make the rope's effective mass m, 1.50 kg. From the height %D she grabs the rope, she swings up a further distance of 1.50 m. Assuming that her collision with the rope is perfectly inelastic, answer the following questions: {Note: Treat as a ballistic pendulum problem!} mehanical a) Does the buccaneer's collision with the rope conserve her-kietie en- ergy? {Y/N?} b) Neglecting any energy losses due to friction, air drag, etc., determine the velocity of the buccaneer + rope system right after she grabs the rope in m/s. {Assume a closed system, thus Conservation of Energy} c) Is it possible to calculate the buccaneer's initial speed before she grabbed the rope from the information given? {Y/N?}arrow_forwardProblem 3: A particle with mass ma = 3.00 kg is located at ra = (2.50 i + 3.50 j) m, and a second particle of mass m2B = 5.00 kg is located at rB = (1.50 i - 3.00 j) m. Find the location of the center of mass of the system relative to the point (1,1).arrow_forwardGiven: The ball strikes the smooth wall with a velocity (v b) 1 = 20 m/ s. The coefficient of restitution between the ball and the wall is e = 0.75. Find height max and distance after impact. (Vb)2 0 30° (Vb)₁ = 20 m/s Ay Xarrow_forward
- Enter an expression for the initial acceleration of the rocket as it lifts vertically off of the ground with a mass m, assuming that it burns fuel at a rate R (kg/s) and shoots the resulting exhaust downward at speed vex. a = - Vex/m (m/R )| α a h В d j 0 50 K g k 9 HOME (1) 7 8 ^^^ 4 5 6 1 1 2 3 SANTarrow_forwardOn a frictionless plane, a body with mass m1 hits with velocity v a second body at rest (mass m2) and connects to it. Subsequently, the composite body hits via a spring (spring constant k) a third body at rest (mass m3). a) Determine the speed v of the mass m1 such that m3 remains at rest, if the plane solely at the location of m3 is rough (coefficient of static friction μ0). b) Determine the speed of m3 after collision if the plane at the location of m3 is also frictionless.arrow_forwardA basketball is dropped from a height of 2.5 m onto a gym floor. If the coefficient of restitution between ball and floor is.8, how high will the ball bounce?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON