Question
WITH FRICTION
Find minimum and maximum mass of m1 to maintain the system in state of equilibrium; at rest.
Given:
m2= 3kg
m3=10kg
m4=23kg
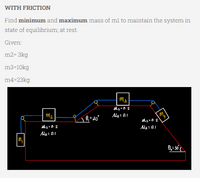
Transcribed Image Text:WITH FRICTION
Find minimum and maximum mass of m1 to maintain the system in
state of equilibrium; at rest.
Given:
m2-3kg
m3-10kg
m4-23kg
M3
Ms.0.2
M₂ = 0.1
my
M₁
M₂
Ms=0.2
M₁ = 0.1
L 0₁=20°
Ms=0.2
M₂ = 0.1
Ð₂ = 30°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 10 kg - mass 500 N/m - k 0.2 m = x 30° = θ (theta) 0.2 = μk REQUIRED d = ?arrow_forwardA crate of mass m1 slides down a well-lubricated hill of height h, with negligible friction. At the bottom, where it is moving horizontally, it collides with another crate, of mass m2, that initially was sitting at rest and that is attached to a wall by a spring of spring constant k that initially is at its equilibrium length. Assume that the spring itself has negligible mass. a)Given that the distance d that the crates compress the spring is d=0.35 m, calculate the speed v2 of the crates immediately after the collision, in units of meters per second. Use the following values:k=950 N/mm1=2.4 kgm2=2.6 kgμ=0.49g=9.8 m/s2 b)What was the speed of the crate of mass m1 just before the collision with the second block, in meters per second? c) What is the height h of the hill, in meters?arrow_forwardA crate of mass m1 slides down a well-lubricated hill of height h, with negligible friction. At the bottom, where it is moving horizontally, it collides with another crate, of mass m2, that initially was sitting at rest and that is attached to a wall by a spring of spring constant k that initially is at its equilibrium length. Assume that the spring itself has negligible mass. a)Given that the distance d that the crates compress the spring is d=0.35 m, calculate the speed v2 of the crates immediately after the collision, in units of meters per second. Use the following values:k=950 N/mm1=2.4 kgm2=2.6 kgμ=0.49g=9.8 m/s2 b) What was the speed of the crate of mass m1 just before the collision with the second block, in meters per second? c)What is the height h of the hill, in meters?arrow_forward
- 1. As part of your role at a heavy-goods vehicle manufacturer, you have been asked to determine the drag caused by the boundary layer developing along a section of the trailer roof, which can be treated as having constant pressure, as the truck travels at 10 m/s. The velocity profile in this region is given by: - A (+ 1) + 1 us where us is the velocity at the edge of the boundary layer. A and B are constants.arrow_forwardA 1.2 kg glider moving at 3.0 m/s [right] undergoes an elastic head-on collision with a glider of equal mass moving at 3.0 m/s [left]. The collision is cushioned by a spring whose spring constant, k, is 6.0 x 104 N/m. Determine the compression in the spring when the second glider is moving left at 1.6 m/s.arrow_forwardA 70 kg stunt- woman falls off a bridge and travels 29.0 before colliding with a pile of mattresses. The mattresses are compressed 1.00 m before she is brought to rest. Calculate the magnitude of the average force exerted by the mattresses on the stunt-woman.arrow_forward
- 9arrow_forwardAt the instant r = 2 m, the 8-kg disk is given a speed of v = 8 m/s, perpendicular to the elastic cord. Determine the speed of the disk at the instant r=1.1 m. The disk slides on the smooth horizontal plane. Neglect its size. The cord has an unstretched length of 0.5 m. k= 200 N/m Barrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios